Page 42 - WJOLS
P. 42
Ashon Sa’adi et al
estimation of disease burden should be considered by policy out during the course of other surgical treatment for endo-
makers when planning gynecological services. 6,7 metriosis. The most common of these nerve transection
procedures are laparoscopic uterine nerve ablation (LUNA) and
AIM/OBJECTIVES presacral neurectomy (PSN).
The aim of this review is to analyse role and useful technique of
laparoscopic presacral neurolysis (PSN) and laparoscopic Laparoscopic Uterine Nerve Ablation (LUNA)
uterine nerve ablation (LUNA) to report followed cases on Procedure
symptom resolution. What LUNA and PSN still useful for pain The goal is the interruption of uterine nerve fibers traveling
treatment performance and it has dangerous side effects?
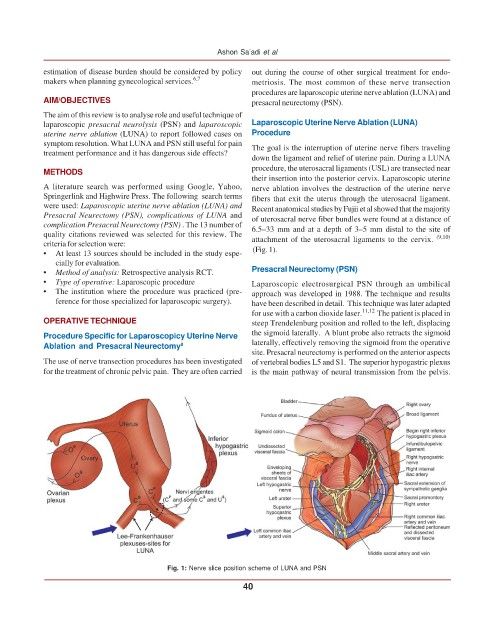
down the ligament and relief of uterine pain. During a LUNA
procedure, the uterosacral ligaments (USL) are transected near
METHODS
their insertion into the posterior cervix. Laparoscopic uterine
A literature search was performed using Google, Yahoo, nerve ablation involves the destruction of the uterine nerve
Springerlink and Highwire Press. The following search terms fibers that exit the uterus through the uterosacral ligament.
were used: Laparoscopic uterine nerve ablation (LUNA) and Recent anatomical studies by Fujii et al showed that the majority
Presacral Neurectomy (PSN), complications of LUNA and of uterosacral nerve fiber bundles were found at a distance of
complication Presacral Neurectomy (PSN) . The 13 number of 6.5–33 mm and at a depth of 3–5 mm distal to the site of
quality citations reviewed was selected for this review. The attachment of the uterosacral ligaments to the cervix. (9,10)
criteria for selection were:
• At least 13 sources should be included in the study espe- (Fig. 1).
cially for evaluation.
• Method of analysis: Retrospective analysis RCT. Presacral Neurectomy (PSN)
• Type of operative: Laparoscopic procedure Laparoscopic electrosurgical PSN through an umbilical
• The institution where the procedure was practiced (pre- approach was developed in 1988. The technique and results
ference for those specialized for laparoscopic surgery). have been described in detail. This technique was later adapted
for use with a carbon dioxide laser. 11,12 The patient is placed in
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE steep Trendelenburg position and rolled to the left, displacing
Procedure Specific for Laparoscopicy Uterine Nerve the sigmoid laterally. A blunt probe also retracts the sigmoid
Ablation and Presacral Neurectomy 8 laterally, effectively removing the sigmoid from the operative
site. Presacral neurectomy is performed on the anterior aspects
The use of nerve transection procedures has been investigated of vertebral bodies L5 and S1. The superior hypogastric plexus
for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain. They are often carried is the main pathway of neural transmission from the pelvis.
Fig. 1: Nerve slice position scheme of LUNA and PSN
40