Page 6 - Journal of WALS
P. 6
WJOLS
10.5005/jp-journals-10007-1120
REVIEW ARTICLE Laparoscopic Splenectomy using a Single Incision Access
Laparoscopic Splenectomy using a Single
Incision Access
Paul A Kisanga
Department of Surgery, Arusha Lutheran Medical Center, Arusha, Tanzania
ABSTRACT
Conventional laparoscopic splenectomy is now considered standard in splenectomy. The superior cosmetic result of single incision
laparoscopic surgery (SILS) has seen an increasing interest in all areas of surgery, including splenectomy. Literature search was done,
and 26 cases reported in literature were reviewed. Age of the patient, position, access technique, duration of surgery, intraoperative
complications, postoperative hospital stay, cosmetic and patient/parents satisfaction were noted. Age range was from 7 months to
73 years with satisfactory outcome.
Conclusion: Single incision splenectomy can be performed safely in patients of all ages. Immediate indicators show superior cosmetic
outcome compared to conventional laparoscopic splenectomy, however, bigger series with long-term follow-up are required.
Keywords: Laparoscopy, Single incision, Splenectomy.
INTRODUCTION late 80s and early 1990s, have led to laparoscopic splenectomy
as a standard operation for small and medium size spleen and
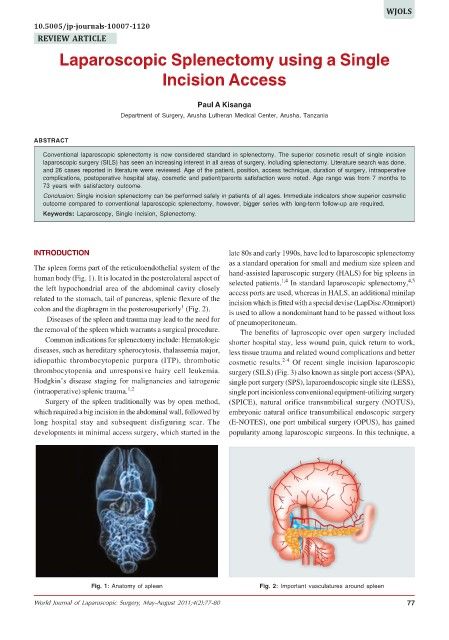
The spleen forms part of the reticuloendothelial system of the hand-assisted laparoscopic surgery (HALS) for big spleens in
human body (Fig. 1). It is located in the posterolateral aspect of selected patients. In standard laparoscopic splenectomy, 4,5
1,4
the left hypochondrial area of the abdominal cavity closely access ports are used, whereas in HALS, an additional minilap
related to the stomach, tail of pancreas, splenic flexure of the incision which is fitted with a special devise (LapDisc /Omniport)
1
colon and the diaphragm in the posterosuperiorly (Fig. 2). is used to allow a nondominant hand to be passed without loss
Diseases of the spleen and trauma may lead to the need for of pneumoperitoneum.
the removal of the spleen which warrants a surgical procedure. The benefits of laproscopic over open surgery included
Common indications for splenectomy include: Hematologic shorter hospital stay, less wound pain, quick return to work,
diseases, such as hereditary spherocytosis, thalassemia major, less tissue trauma and related wound complications and better
idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), thrombotic cosmetic results. Of recent single incision laparoscopic
2-4
thrombocytopenia and unresponsive hairy cell leukemia. surgery (SILS) (Fig. 3) also known as single port access (SPA),
Hodgkin’s disease staging for malignancies and iatrogenic single port surgery (SPS), laparoendoscopic single site (LESS),
(intraoperative) splenic trauma. 1,2 single port incisionless conventional equipment-utilizing surgery
Surgery of the spleen traditionally was by open method, (SPICE), natural orifice transumbilical surgery (NOTUS),
which required a big incision in the abdominal wall, followed by embryonic natural orifice transumbilical endoscopic surgery
long hospital stay and subsequent disfiguring scar. The (E-NOTES), one port umbilical surgery (OPUS), has gained
developments in minimal access surgery, which started in the popularity among laparoscopic surgeons. In this technique, a
Fig. 1: Anatomy of spleen Fig. 2: Important vasculatures around spleen
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, May-August 2011;4(2):77-80 77