Page 21 - Journal of WALS
P. 21
WJOLS
A Comparative Study of the use of Different Energy Sources in Laparoscopic Management of Endometriosis-Associated Infertility
peritoneal washing is given and hemostasis achieved. The ovary it and then control hemostasis using bipolar electrocoagulation.
is left unsutured since sutures can cause adhesion formation. Monopolar electrocoagulation must be avoided because of the
However, when necessary, suture is placed within ovarian risks of accidents and complete coagulation of the ovarian
stroma and the knot is tied inside the ovary to minimize adhesion vascularization.
formation. Alternatively, biological glue can be applied and Laser Vaporization of Endometrioma
edges of the incision brought together.
Draining the endometrioma or partially removing its wall is The endometrioma is opened, aspirated and washed. It is then
inadequate because the cyst lining remains functional leading largely incised to evert the internal layer which is destroyed by
2
to reoccurrence of the symptoms. Two randomized controlled vaporization with a CO laser, introduced through the
trials reported that laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy for laparoscope. The results are apparently equivalent with different
endometriomata results in a better pregnancy rate than drainage types of lasers, but Argon or KTP lasers induce less bleeding
alone. 30,31 and are easier to use since they can travel through flexible
Another advantage of excision over ablation is that the fibers. This is easily done with small cysts (< 3 cm), but in cases
cyst can be examined histologically and a diagnosis of ovarian of larger cysts it is impossible to be sure that all the internal
cancer excluded. layer has been destroyed.
Hemorrhage: Any bleeding from the intraovarian vasculature Rectovaginal Septum and Uterosacral
is minimal and is self-controlled within a few minutes. Ligaments Endometriosis
Hemorrhage from the hilus may occur during the dissection of Deep endometriosis exists when the lesions penetrate 5 mm or
32
the inferior pole of the cyst. This can be difficult to locate. The more. In addition to pain, most of these patients suffer from
immediate solution is to evert the entire ovary in order to localize associated infertility. Operative laparoscopy for these lesions
Fig. 3. Flimsy adhesions can be directly cut by sharp dissection Fig. 5: Puncture of endometriotic cyst using monopolar with tritome
with scissors for drainage and aspiration of the cyst contents
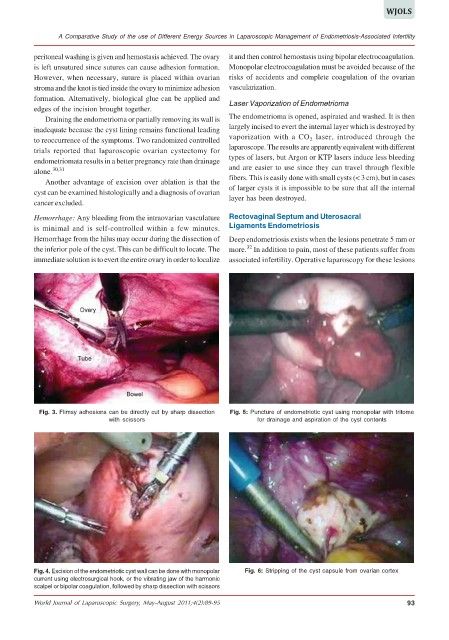
Fig. 4. Excision of the endometriotic cyst wall can be done with monopolar Fig. 6: Stripping of the cyst capsule from ovarian cortex
current using electrosurgical hook, or the vibrating jaw of the harmonic
scalpel or bipolar coagulation, followed by sharp dissection with scissors
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, May-August 2011;4(2):89-95 93