Page 53 - WJOLS
P. 53
WJOLS
Laparoscopic Segmental Colectomy as Management of a Delayed Post Colonoscopic Polypectomy Bleeding
The patient was supine with legs bent with a vesical villous adenoma with highgrade dysplasia. A monitoring
probe. We introduce the first 10 mm trocart supraumbilical schedule was introduced.
by ‘opencoelioscopy’ and two others of 5 mm in right iliac The cosmetic result was good (Fig. 6).
fossa and left hypochondrium. The operative table was then
tilted in a maximum Trendelenburg position with maximum DISCuSSION
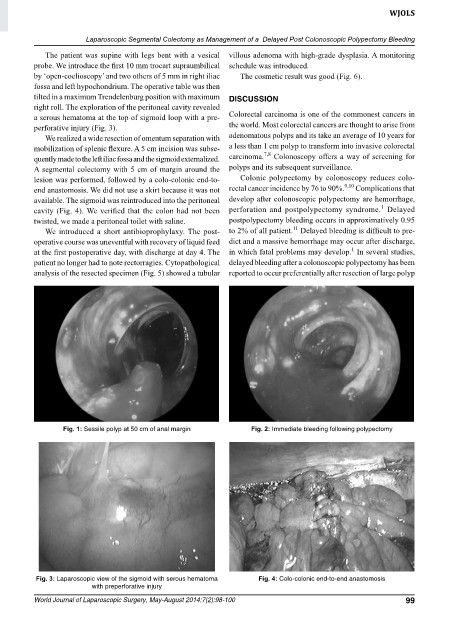
right roll. The exploration of the peritoneal cavity revealed
a serous hematoma at the top of sigmoid loop with a pre colorectal carcinoma is one of the commonest cancers in
perforative injury (Fig. 3). the world. Most colorectal cancers are thought to arise from
We realized a wide resection of omentum separation with adenomatous polyps and its take an average of 10 years for
mobi lization of splenic flexure. A 5 cm incision was subse a less than 1 cm polyp to transform into invasive colorectal
7,8
quently made to the left iliac fossa and the sigmoid externalized. carcinoma. colonoscopy offers a way of screening for
A segmental colectomy with 5 cm of margin around the polyps and its subsequent surveillance.
lesion was performed, followed by a colocolonic endto colonic polypectomy by colonoscopy reduces colo
end anastomosis. We did not use a skirt because it was not rectal cancer incidence by 76 to 90%. 9,10 complications that
available. The sigmoid was reintroduced into the peritoneal develop after colonoscopic polypectomy are hemorrhage,
1
cavity (Fig. 4). We verified that the colon had not been perforation and postpolypectomy syndrome. Delayed
twisted, we made a peritoneal toilet with saline. postpolypectomy bleeding occurs in approximatively 0.95
11
We introduced a short antibioprophylaxy. The post to 2% of all patient. Delayed bleeding is difficult to pre
operative course was uneventful with recovery of liquid feed dict and a massive hemorrhage may occur after discharge,
1
at the first postoperative day, with discharge at day 4. The in which fatal problems may develop. In several studies,
patient no longer had to note rectorragies. cytopathological delayed bleeding after a colonoscopic polypectomy has been
analysis of the resected specimen (Fig. 5) showed a tubular reported to occur preferentially after resection of large polyp
Fig. 1: sessile polyp at 50 cm of anal margin Fig. 2: Immediate bleeding following polypectomy
Fig. 3: Laparoscopic view of the sigmoid with serous hematoma Fig. 4: Colo-colonic end-to-end anastomosis
with preperforative injury
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, May-August 2014;7(2):98-100 99