Introduction
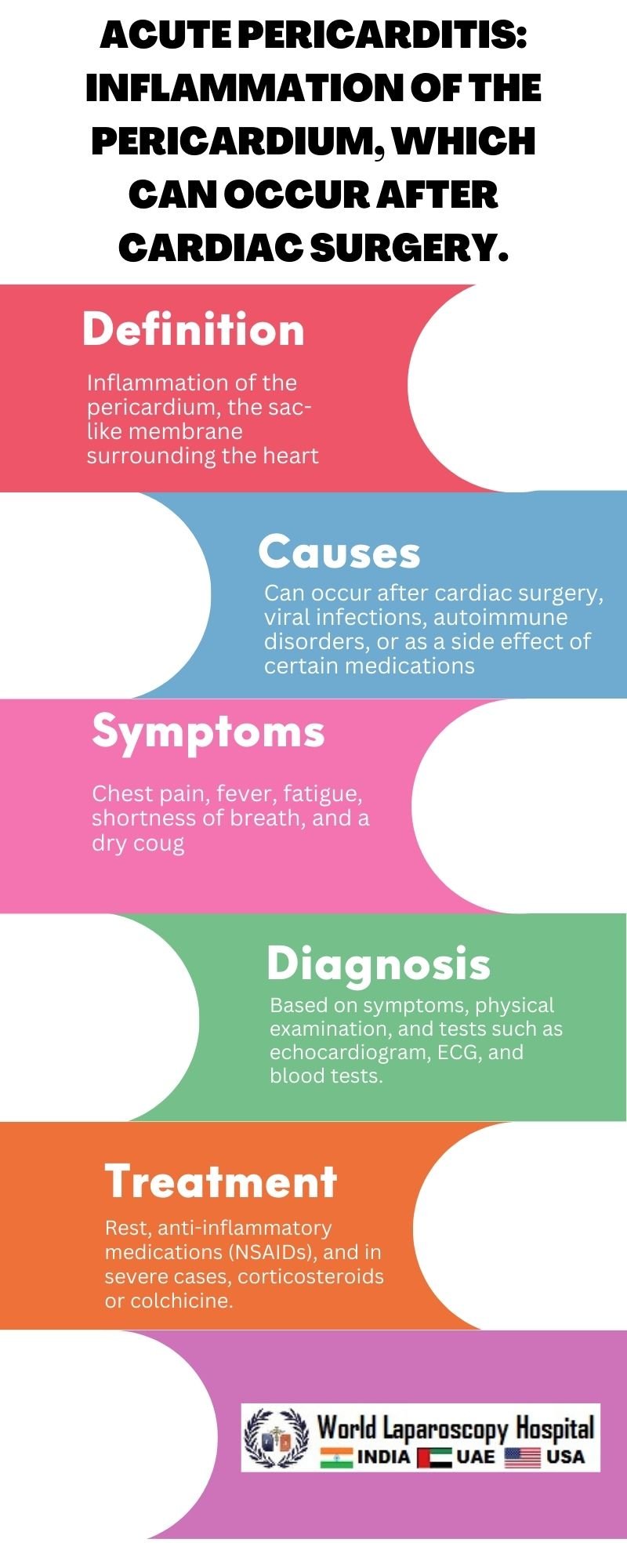
The pericardium is a double-layered sac that surrounds the heart and helps to protect it. Acute pericarditis occurs when the pericardium becomes inflamed, causing chest pain and other symptoms. This inflammation can be caused by various factors, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and injuries. In some cases, acute pericarditis can occur after cardiac surgery, such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or valve replacement surgery.
Causes of Acute Pericarditis Following Cardiac Surgery
The exact cause of acute pericarditis following cardiac surgery is not always clear. However, several factors may contribute to its development. These include:
Surgical Trauma:
The manipulation of the heart and pericardium during surgery can lead to inflammation and irritation of the pericardium.
Infection: Surgical sites can become infected, leading to pericardial inflammation.
Autoimmune Response:
In some cases, the body's immune system may mistakenly attack the pericardium, leading to inflammation.
Other Factors:
Other factors, such as medications used during surgery or underlying medical conditions, may also play a role.
Symptoms of Acute Pericarditis Following Cardiac Surgery
The symptoms of acute pericarditis following cardiac surgery can vary from person to person. Common symptoms include:
Chest Pain:
Sharp, stabbing chest pain is a hallmark symptom of acute pericarditis. The pain may worsen when lying down or breathing deeply and may improve when sitting up or leaning forward.
Fever:
A low-grade fever is common in people with acute pericarditis.
Difficulty Breathing:
Some people may experience shortness of breath, especially when lying down or with exertion.
Fatigue:
Fatigue and weakness may occur due to the underlying inflammation.
Other Symptoms:
Other symptoms may include a dry cough, palpitations, and swelling of the legs or abdomen.
Diagnosis of Acute Pericarditis Following Cardiac Surgery
Diagnosing acute pericarditis following cardiac surgery often involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. These may include:
Medical History and Physical Examination:
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history and perform a physical examination to look for signs of pericarditis.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG can help identify characteristic changes associated with acute pericarditis, such as ST-segment elevations or PR-segment depressions.
Echocardiogram:
An echocardiogram uses sound waves to create images of the heart and pericardium, allowing doctors to assess for signs of inflammation or fluid buildup.
Blood Tests:
Blood tests can help identify markers of inflammation, such as elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) or erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
Treatment of Acute Pericarditis Following Cardiac Surgery
Treatment for acute pericarditis following cardiac surgery aims to relieve symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent complications. Treatment options may include:
Medications:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or indomethacin, are often used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Colchicine:
Colchicine is another medication that may be used to reduce inflammation and prevent recurrence of pericarditis.
Corticosteroids:
In some cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, especially if other treatments are not effective.
Pericardiocentesis: In severe cases of acute pericarditis with fluid buildup (pericardial effusion), a procedure called pericardiocentesis may be performed to drain the fluid.
Complications of Acute Pericarditis Following Cardiac Surgery
While most cases of acute pericarditis following cardiac surgery resolve with treatment, complications can occur. These may include:
Pericardial Effusion:
A buildup of fluid in the pericardial sac, which can lead to cardiac tamponade, a life-threatening condition.
Constrictive Pericarditis:
In some cases, chronic inflammation of the pericardium can lead to the development of constrictive pericarditis, a condition where the pericardium becomes thickened and rigid, affecting heart function.
Recurrence:
Acute pericarditis can recur in some cases, requiring ongoing monitoring and treatment.
Conclusion
Acute pericarditis following cardiac surgery is a challenging condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. While most cases resolve with medication, severe cases may require additional interventions. If you have undergone cardiac surgery and experience symptoms of acute pericarditis, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to receive appropriate care and prevent complications.