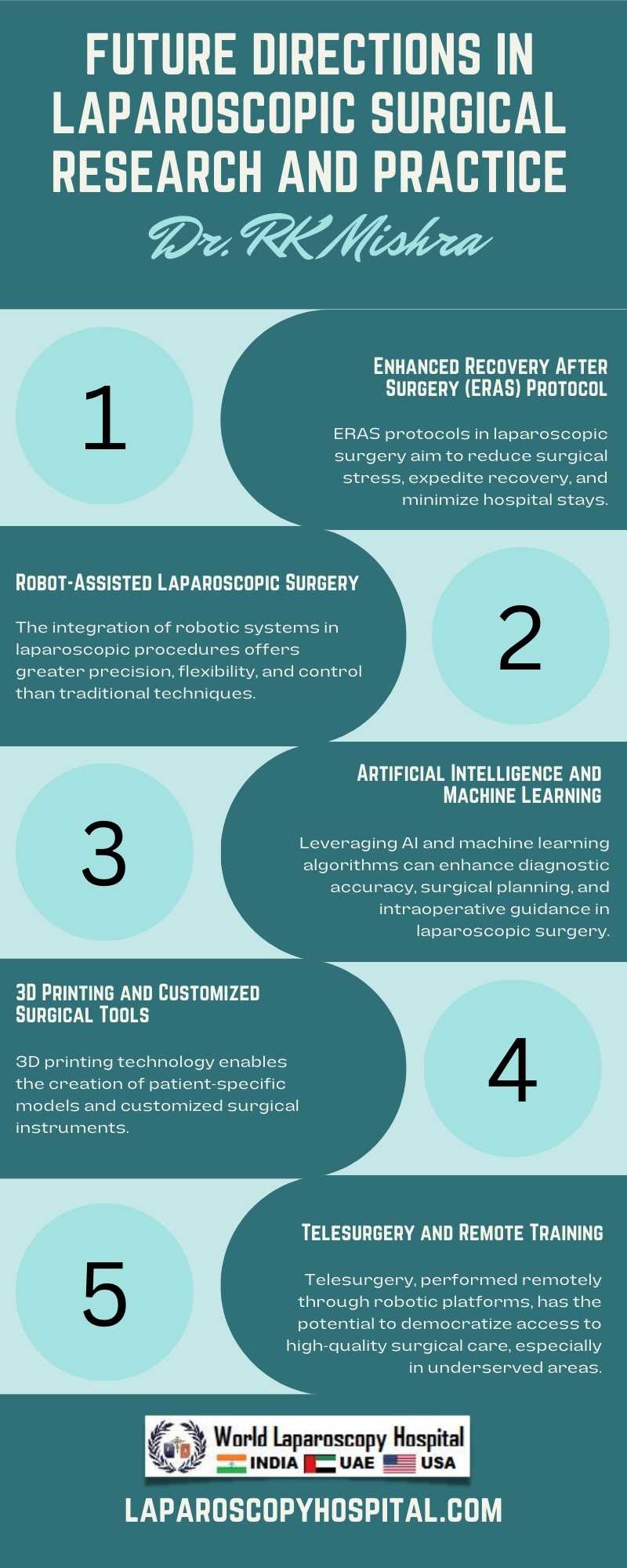
Technological Advancements: One of the primary drivers of future developments in laparoscopic surgery will be continued technological innovation. Robotics, already a significant part of modern laparoscopic procedures, is expected to become even more sophisticated. Advancements in robotic systems will likely offer improved dexterity, precision, and control, allowing surgeons to perform complex maneuvers that are currently challenging or impossible. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with robotic systems could lead to predictive analytics, enhancing decision-making during surgeries.
Imaging and Visualization Techniques: Enhanced imaging and visualization are critical for the success of laparoscopic procedures. Future research is likely to focus on developing more advanced imaging technologies that provide clearer, real-time, three-dimensional views of the surgical field. Innovations such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) could be integrated into laparoscopic systems, offering surgeons immersive and detailed views of the anatomy, potentially improving the precision of surgeries and reducing risks.
Instrumentation and Equipment: The development of new instruments and equipment is crucial for expanding the capabilities of laparoscopic surgery. This includes creating more flexible, multifunctional tools that can adapt to different surgical tasks, reducing the need for multiple instruments and incisions. Additionally, advancements in materials science could lead to the creation of smarter, more durable instruments that are better suited to the unique challenges of minimally invasive surgery.
Training and Education: As laparoscopic techniques become more advanced, the need for comprehensive training and education becomes more critical. Future directions may include the development of more sophisticated simulation-based training platforms that use VR and AR to provide realistic, hands-on experience without patient risk. These platforms can be constantly updated to reflect the latest techniques and technologies, ensuring that surgeons are always prepared for the evolving landscape of laparoscopic surgery.
Patient-Specific Procedures: Personalized medicine is becoming increasingly important in all areas of healthcare, including surgery. In the future, laparoscopic procedures may be tailored more precisely to individual patients, taking into account their specific anatomy, pathology, and genetic profile. This could involve preoperative planning with advanced imaging and modeling techniques to create a customized surgical plan that minimizes risk and optimizes outcomes.
Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering: The integration of regenerative medicine and tissue engineering with laparoscopic surgery could open new avenues for treating conditions that currently require more invasive interventions. For example, the delivery of stem cells or bioengineered tissues through laparoscopic techniques could be used to repair or regenerate damaged organs and tissues, offering new hope for patients with chronic diseases or injuries.
Telemedicine and Remote Surgery: The future of laparoscopic surgery may also see an expansion of telemedicine and remote surgical capabilities. With advancements in communication technology and robotic systems, surgeons could perform laparoscopic procedures from remote locations, breaking down geographical barriers to care and making specialized surgical expertise more accessible to underserved populations.
Conclusion:
The future of laparoscopic surgical research and practice is bright, with numerous avenues for innovation and improvement. By focusing on technological advancements, enhanced imaging and visualization, improved instruments and equipment, comprehensive training, patient-specific procedures, integration with regenerative medicine, and the expansion of telemedicine, the field can continue to evolve, offering better patient outcomes, reduced recovery times, and access to minimally invasive options for an ever-expanding range of conditions.