Introduction
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, has revolutionized the field of medicine, offering precise, minimally invasive procedures with enhanced dexterity and visualization. While the benefits of robotic surgery are clear, its implementation in hospitals comes with a set of challenges. These challenges range from cost considerations to training and integration into existing workflows. Overcoming these barriers is crucial for hospitals to fully leverage the potential of robotic surgery and improve patient outcomes.
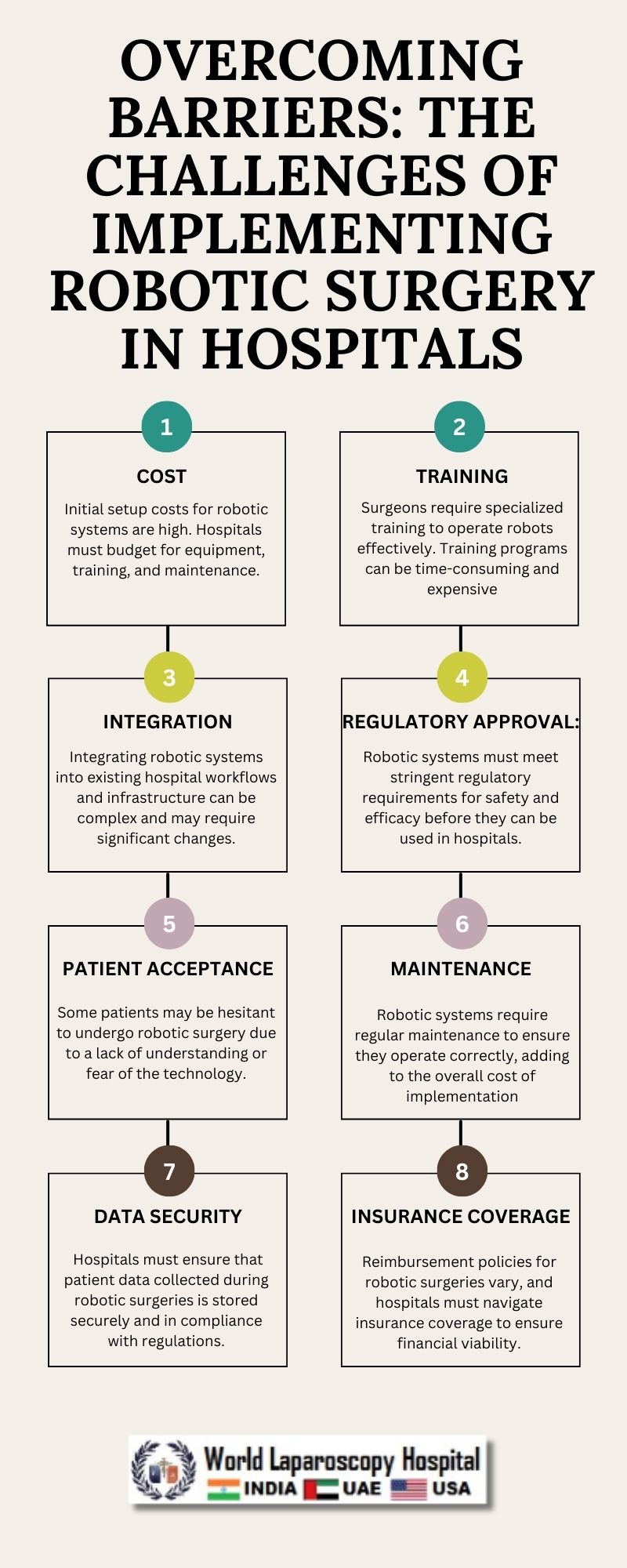
Cost Considerations
One of the primary challenges hospitals face in implementing robotic surgery is the high cost associated with acquiring and maintaining robotic systems. The initial investment for a robotic surgery system can range from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the brand and model. Additionally, there are ongoing costs for maintenance, instrument replacement, and training.
For many hospitals, especially smaller or resource-constrained facilities, the cost of robotic surgery systems can be prohibitive. This limits access to robotic surgery for patients and puts pressure on hospitals to justify the return on investment. To overcome this barrier, hospitals can explore various financing options, such as leasing or partnering with equipment manufacturers. Additionally, hospitals can conduct cost-benefit analyses to demonstrate the long-term savings and improved outcomes associated with robotic surgery.
Training and Credentialing
Another challenge in implementing robotic surgery is the need for specialized training and credentialing for surgeons and staff. Robotic surgery requires a different skill set than traditional surgery, and surgeons must undergo extensive training to become proficient in using robotic systems. This training includes both simulation-based training and proctoring by experienced robotic surgeons.
Credentialing for robotic surgery is also a complex process, requiring hospitals to establish criteria for privileging surgeons to perform robotic procedures. This process involves assessing surgeons' skills, experience, and outcomes, as well as ensuring that they adhere to best practices and safety guidelines. To address these challenges, hospitals can invest in comprehensive training programs and establish clear credentialing pathways for robotic surgery.
Integration into Existing Workflows
Integrating robotic surgery into existing workflows presents another challenge for hospitals. Robotic surgery requires coordination among various departments, including surgery, nursing, anesthesia, and administration. Hospitals must ensure that staff are trained and familiar with the robotic system, and that workflows are optimized to maximize efficiency and patient safety.
Additionally, robotic surgery may require changes to operating room setup and scheduling practices to accommodate the unique requirements of robotic procedures. This can disrupt existing workflows and require careful planning and coordination. To overcome these challenges, hospitals can work closely with all stakeholders to develop standardized protocols and workflows for robotic surgery.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Issues
Regulatory and reimbursement issues also pose challenges for hospitals implementing robotic surgery. Regulatory agencies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), require hospitals to adhere to strict guidelines for the use of robotic systems, including reporting adverse events and ensuring patient safety. Compliance with these regulations can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Reimbursement for robotic surgery can also be complex, as payers may have different policies and coverage criteria for robotic procedures. Hospitals must navigate these reimbursement issues to ensure that they are adequately reimbursed for the cost of robotic surgery. This may require negotiating with payers and advocating for appropriate reimbursement rates.
Conclusion
While the challenges of implementing robotic surgery in hospitals are significant, they are not insurmountable. By addressing cost considerations, investing in training and credentialing, optimizing workflows, and navigating regulatory and reimbursement issues, hospitals can successfully integrate robotic surgery into their practice. The benefits of robotic surgery, including improved patient outcomes and reduced recovery times, make overcoming these challenges well worth the effort.