Safety First: Comparing Complication Rates in Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgeries
Introduction
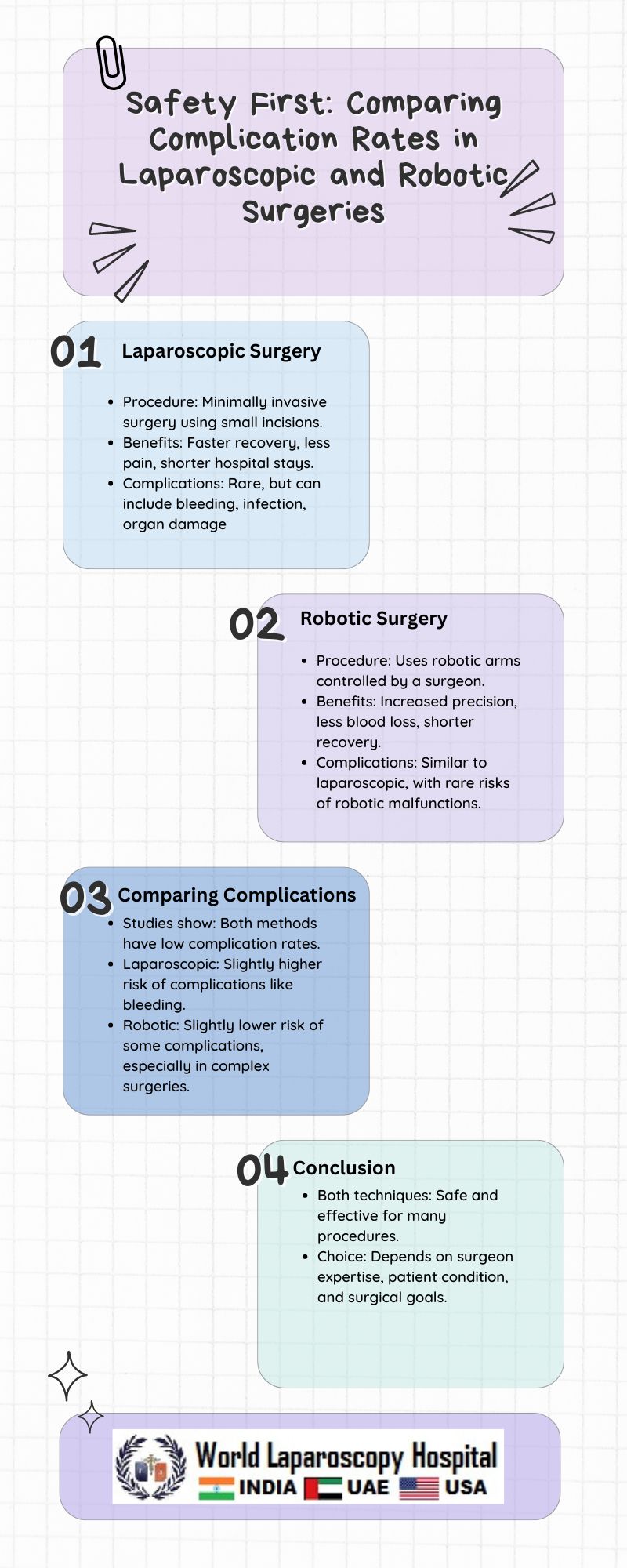
In recent years, advancements in surgical technology have revolutionized the field of surgery. Laparoscopic and robotic surgeries, in particular, have gained popularity due to their minimally invasive nature and potential benefits for patients. One of the key considerations for any surgical procedure is the rate of complications associated with it. Understanding and comparing the complication rates of laparoscopic and robotic surgeries is crucial for making informed decisions about surgical approaches. This article explores the safety profiles of these two techniques, examining their respective complication rates and factors that may influence them.
Laparoscopic Surgery: A Brief Overview
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, involves making small incisions in the abdomen through which specialized surgical instruments and a camera are inserted. The camera provides a high-definition view of the internal organs, allowing the surgeon to perform the procedure with precision. Laparoscopic surgery is commonly used for procedures such as gallbladder removal, hernia repair, and appendectomy.
Robotic Surgery: An Introduction
Robotic surgery is a type of minimally invasive surgery that utilizes robotic arms to perform surgical procedures. The surgeon controls the robotic arms from a console, manipulating the instruments with greater dexterity and precision than is possible with traditional laparoscopic instruments. Robotic surgery is used in a variety of procedures, including prostatectomy, hysterectomy, and colorectal surgery.
Comparing Complication Rates
Several studies have compared the complication rates of laparoscopic and robotic surgeries across various procedures. Overall, the consensus is that both techniques have comparable complication rates, with some variations depending on the specific procedure and patient population.
Gallbladder Removal
One study comparing laparoscopic and robotic gallbladder removal found no significant difference in complication rates between the two techniques. Both laparoscopic and robotic approaches were associated with low rates of complications such as bile duct injury and surgical site infection.
Hernia Repair
For hernia repair, a systematic review and meta-analysis found that robotic-assisted hernia repair was associated with a lower risk of surgical site infection compared to laparoscopic hernia repair. However, other complications such as hernia recurrence did not show significant differences between the two techniques.
Prostatectomy
In the case of prostatectomy, studies have shown comparable complication rates between laparoscopic and robotic approaches. Both techniques have been associated with low rates of complications such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction.
Factors Influencing Complication Rates
Several factors may influence the complication rates of laparoscopic and robotic surgeries. These include the surgeon's experience and skill level, patient characteristics such as age and overall health, and the complexity of the procedure being performed. Additionally, the specific technology and equipment used in robotic surgery can also impact complication rates.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both laparoscopic and robotic surgeries are associated with low rates of complications across various procedures. While some studies suggest that robotic surgery may offer certain advantages, such as lower rates of surgical site infection in hernia repair, overall complication rates between the two techniques are comparable. Factors such as surgeon experience, patient characteristics, and procedure complexity play a significant role in determining complication rates. Ultimately, the choice between laparoscopic and robotic surgery should be based on a thorough evaluation of these factors, weighing the potential benefits and risks for each individual patient.