Introduction
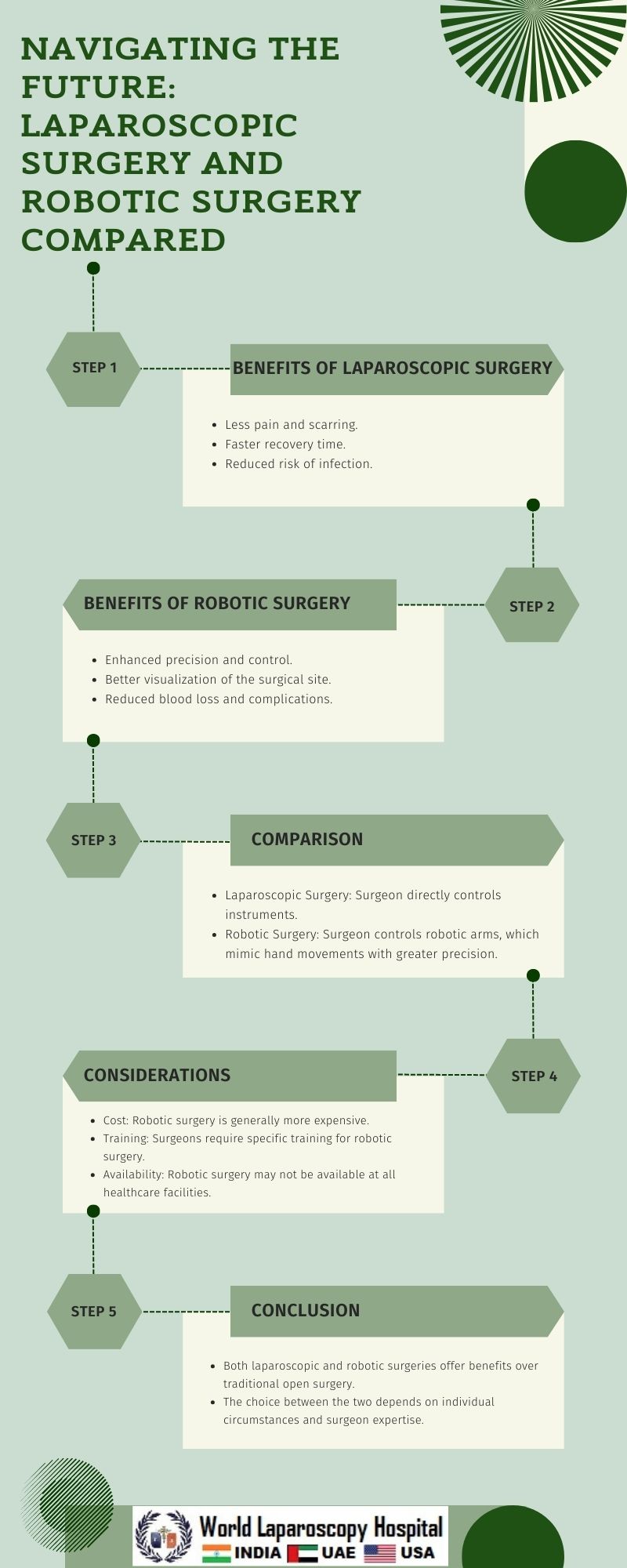
In the world of surgery, technological advancements have revolutionized traditional methods, offering patients less invasive options with potentially quicker recovery times. Two such methods, laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery, have gained popularity for their precision and minimal invasiveness. This article aims to compare these two techniques, highlighting their differences, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
Laparoscopic Surgery: A Brief Overview
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery (MIS) or keyhole surgery, involves making small incisions through which specialized surgical instruments and a camera are inserted. The camera provides a magnified view of the internal organs on a monitor, allowing the surgeon to perform the procedure with precision.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
Reduced trauma: Smaller incisions lead to less trauma to surrounding tissues, resulting in less pain and faster recovery.
Shorter hospital stays: Patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery typically spend less time in the hospital compared to traditional open surgery.
Quicker recovery: Due to reduced trauma, patients often recover more quickly and can resume normal activities sooner.
Less scarring: The small incisions in laparoscopic surgery result in minimal scarring compared to traditional surgery.
Drawbacks of Laparoscopic Surgery
Limited dexterity: The instruments used in laparoscopic surgery have limited range of motion compared to the human hand, which can sometimes limit the surgeon's dexterity.
Steep learning curve: Laparoscopic surgery requires specialized training, and not all surgeons may be proficient in this technique.
Equipment costs: The specialized instruments and equipment required for laparoscopic surgery can be expensive.
Robotic Surgery: A Brief Overview
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, involves the use of a robotic system to perform surgical procedures. The surgeon controls the robotic arms from a console, which provides a 3D view of the surgical site and allows for precise movements.
Benefits of Robotic Surgery
Enhanced precision: The robotic system allows for more precise movements compared to traditional laparoscopic instruments, leading to better surgical outcomes.
Improved dexterity: The robotic arms can mimic the movements of the human hand, allowing for greater dexterity during surgery.
Reduced fatigue: The ergonomic design of the console reduces surgeon fatigue during long procedures.
Minimal invasiveness: Like laparoscopic surgery, robotic surgery requires small incisions, resulting in less trauma to the patient's body.
Drawbacks of Robotic Surgery
Cost: The initial cost of purchasing and maintaining a robotic surgical system can be high, which may lead to increased healthcare costs for patients.
Learning curve: Robotic surgery requires specialized training, and surgeons need to become proficient in using the robotic system.
Limited tactile feedback: The lack of direct contact with the surgical site can limit the surgeon's ability to feel tissue characteristics, which may affect surgical decision-making.
Comparison of Laparoscopic Surgery and Robotic Surgery
Precision: Robotic surgery offers enhanced precision compared to laparoscopic surgery, thanks to the robotic system's ability to mimic the surgeon's movements with greater accuracy.
Dexterity: While both techniques offer improved dexterity compared to traditional surgery, robotic surgery's ability to mimic the human hand gives it an edge in delicate procedures.
Learning curve: Both laparoscopic and robotic surgery require specialized training, but the learning curve for robotic surgery may be steeper due to the complexity of the robotic system.
Cost: Laparoscopic surgery is generally more cost-effective than robotic surgery, as it does not require the purchase and maintenance of expensive robotic systems.
Tactile feedback: Laparoscopic surgery provides direct tactile feedback to the surgeon, which can be beneficial in certain procedures where tissue characteristics are important.
Conclusion
Both laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery offer significant advantages over traditional open surgery, including reduced trauma, quicker recovery times, and less scarring. However, each technique has its own set of benefits and drawbacks, and the choice between the two depends on various factors, including the surgeon's expertise, the complexity of the procedure, and the patient's individual needs. As technology continues to advance, both laparoscopic and robotic surgery are likely to play an increasingly important role in the future of surgery, offering patients more options for minimally invasive procedures.
Laparoscopic surgery, celebrated for its minimal invasiveness, emerges as a cornerstone of modern surgical practice. Its advantages, from reduced trauma to quicker recovery, underscore its transformative impact on patient outcomes. Yet, challenges such as limited dexterity and the learning curve temper its ascent.
In the symphony of surgical innovation, robotic surgery emerges as a virtuoso, offering unparalleled precision and dexterity. Its ability to navigate complexities with ease, coupled with reduced fatigue and minimal invasiveness, heralds a new era in patient-centered care. However, the cost and learning curve cast a shadow on its widespread adoption.
As surgeons navigate the crossroads of technique selection, this article provides a compass, delineating the nuanced differences. While robotic surgery shines in precision and dexterity, laparoscopic surgery stands as a stalwart of affordability and tactile feedback. The journey forward demands a balanced consideration of these factors, ensuring optimal patient outcomes in the ever-evolving landscape of surgical excellence.