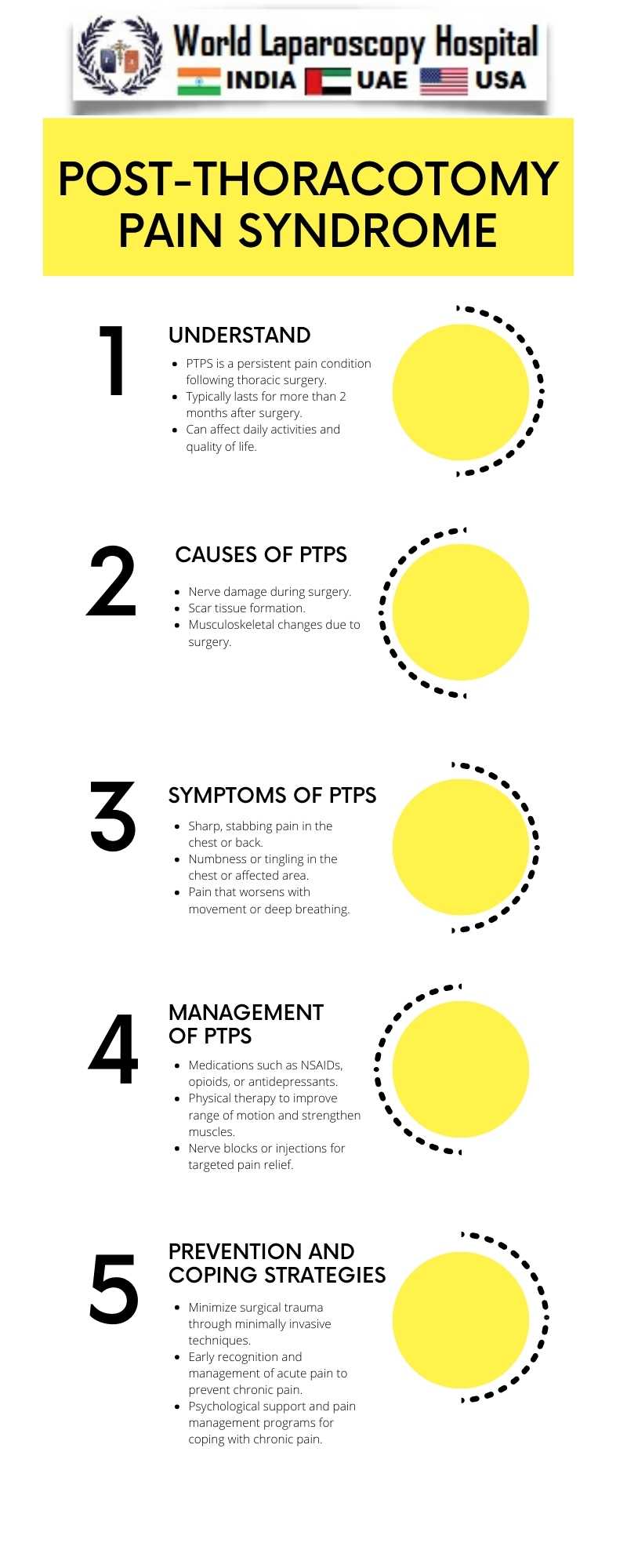
Thoracic surgery is a specialized field of surgery that deals with procedures involving the chest cavity, including the lungs, esophagus, and heart. While these surgeries are often life-saving, they can also lead to a significant complication known as post-thoracotomy pain syndrome (PTPS). PTPS is characterized by chronic pain that persists long after the surgical incision has healed, often lasting for months or even years. This essay explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of PTPS.
Causes of PTPS:
The exact cause of PTPS is not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development. One of the primary causes is damage to the intercostal nerves during surgery. These nerves run along the ribs and are responsible for transmitting sensation from the chest wall to the brain. When these nerves are injured or irritated during surgery, they can become hypersensitive, leading to chronic pain. Other potential causes include inflammation, scar tissue formation, and psychological factors such as anxiety and depression.
Symptoms of PTPS:
The hallmark symptom of PTPS is chronic pain in the chest wall or rib area that persists for more than three months after surgery. The pain is often described as sharp, stabbing, or burning and may be aggravated by movement or deep breathing. In addition to pain, patients may also experience numbness, tingling, or sensitivity to touch in the affected area.
Diagnosis of PTPS:
Diagnosing PTPS can be challenging, as there are no specific tests or imaging studies that can definitively confirm the condition. Instead, diagnosis is based on a thorough medical history, physical examination, and exclusion of other possible causes of pain. Imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI may be used to rule out other conditions, such as rib fractures or pneumonia.
Management of PTPS:
The management of PTPS is multidisciplinary and often requires a combination of approaches to effectively control pain and improve quality of life. Treatment options may include:
1. Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, may be used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. In some cases, antidepressants or anticonvulsants may be prescribed to help manage nerve-related pain.
2. Physical Therapy: Physical therapy techniques, such as stretching exercises, massage, and heat therapy, can help improve flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and alleviate pain.
3. Nerve Blocks: In some cases, a nerve block may be performed to temporarily numb the affected nerves and provide pain relief. This procedure is typically done using a local anesthetic injected into the area around the nerves.
4. Psychological Support: PTPS can have a significant impact on a patient's mental health, leading to anxiety, depression, and decreased quality of life. Psychological support, such as counseling or cognitive behavioral therapy, may be beneficial in managing these aspects of the condition.
5. Surgical Interventions: In rare cases where conservative treatments are ineffective, surgical interventions such as nerve ablation or neuromodulation may be considered to alleviate pain.
Conclusion:
Post-thoracotomy pain syndrome is a complex and challenging condition that can significantly impact patients' quality of life. Early recognition and appropriate management are essential to minimize the impact of PTPS on patients' lives. A multidisciplinary approach involving pain specialists, surgeons, physical therapists, and psychologists is often necessary to provide comprehensive care for patients with PTPS. Further research is needed to better understand the underlying mechanisms of PTPS and develop more effective treatment strategies.