Introduction
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) has revolutionized the field of surgery, offering patients shorter recovery times, less pain, and smaller incisions compared to traditional open surgery. Two main techniques dominate the landscape of MIS: laparoscopic surgery and robotic-assisted surgery. Both approaches have their strengths and weaknesses, and as technology advances, the future of minimally invasive surgery promises even greater precision and efficiency. In this article, we will explore the current state of laparoscopic and robotic surgery, their differences, and the potential future developments in this field.
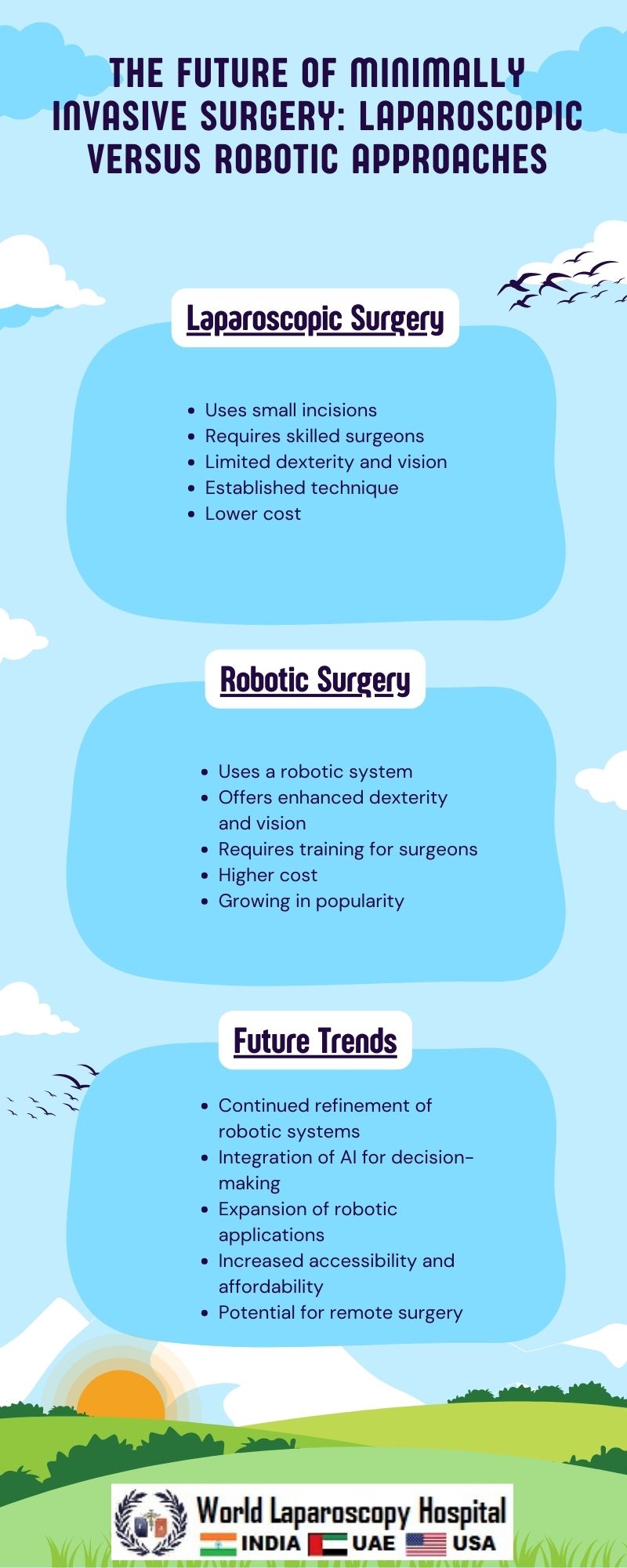
Laparoscopic Surgery: A Pioneer in Minimally Invasive Techniques
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as keyhole surgery, has been a cornerstone of minimally invasive surgery for decades. It involves making small incisions in the abdomen through which a camera (laparoscope) and specialized surgical instruments are inserted. The surgeon uses these instruments to perform the surgery while viewing a magnified image of the internal organs on a monitor.
One of the key advantages of laparoscopic surgery is its minimally invasive nature, resulting in less trauma to the surrounding tissues and faster recovery times for patients. It is commonly used for procedures such as gallbladder removal, appendectomy, and hernia repair.
Despite its advantages, laparoscopic surgery has limitations. The use of rigid instruments limits the range of motion and dexterity of the surgeon, making complex procedures challenging. Additionally, the two-dimensional image provided by the camera can make depth perception difficult, leading to a steep learning curve for surgeons.
Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Enhancing Precision and Dexterity
Robotic-assisted surgery represents the next evolution in minimally invasive techniques. It combines the advantages of laparoscopic surgery with enhanced precision and dexterity provided by robotic technology. The da Vinci Surgical System, developed by Intuitive Surgical, is the most well-known robotic surgical system used worldwide.
In robotic-assisted surgery, the surgeon sits at a console and controls the robotic arms, which are equipped with surgical instruments. The system translates the surgeon's hand movements into precise movements of the instruments inside the patient's body. The robotic system also provides a three-dimensional, high-definition view of the surgical site, enhancing depth perception.
Robotic-assisted surgery offers several advantages over laparoscopic surgery. The articulating instruments provide greater range of motion and precision, making complex procedures more manageable. The ergonomic console allows the surgeon to operate in a more comfortable position, reducing fatigue during long surgeries. Additionally, the three-dimensional view provides a more immersive surgical experience, enhancing the surgeon's spatial awareness.
The Future of Minimally Invasive Surgery: Advances in Technology
As technology continues to advance, the future of minimally invasive surgery looks promising. One area of development is the miniaturization of robotic systems, allowing for even smaller incisions and greater precision. Researchers are also exploring the use of flexible robotic instruments, which could further enhance the range of motion and dexterity of robotic-assisted surgery.
Another area of development is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms into robotic surgical systems. These algorithms can analyze data from previous surgeries to provide real-time guidance to the surgeon, helping to improve surgical outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
In addition to technological advancements, the future of minimally invasive surgery will also see improvements in surgical training and education. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies are being used to create realistic surgical simulations, allowing surgeons to practice complex procedures in a safe environment.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the potential benefits of robotic-assisted surgery, there are challenges and considerations that need to be addressed. One concern is the cost of robotic systems, which can be significant. This cost may limit access to robotic surgery for some patients and healthcare institutions.
Another consideration is the learning curve associated with robotic-assisted surgery. Surgeons need to undergo specialized training to become proficient in using the robotic system, which can take time and resources.
Additionally, there is a need for further research to evaluate the long-term outcomes of robotic-assisted surgery compared to laparoscopic surgery and open surgery. While short-term studies have shown promising results, more data is needed to fully understand the benefits and risks of robotic-assisted surgery.
Conclusion
The future of minimally invasive surgery is bright, with laparoscopic and robotic-assisted approaches leading the way. Both techniques offer advantages over traditional open surgery, including faster recovery times, less pain, and smaller incisions. As technology continues to advance, the field of minimally invasive surgery will likely see further improvements in precision, dexterity, and surgical outcomes. However, challenges such as cost and training need to be addressed to ensure that these innovations benefit patients and healthcare systems worldwide.