Introduction
In the realm of modern surgery, two groundbreaking techniques have emerged as leaders in minimally invasive procedures: laparoscopic and robotic-assisted surgeries. These techniques have revolutionized the field, offering patients less pain, shorter recovery times, and improved outcomes compared to traditional open surgeries. However, each method has its own set of advantages and limitations. In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of laparoscopic and robotic techniques, shedding light on their impact on the future of surgery.
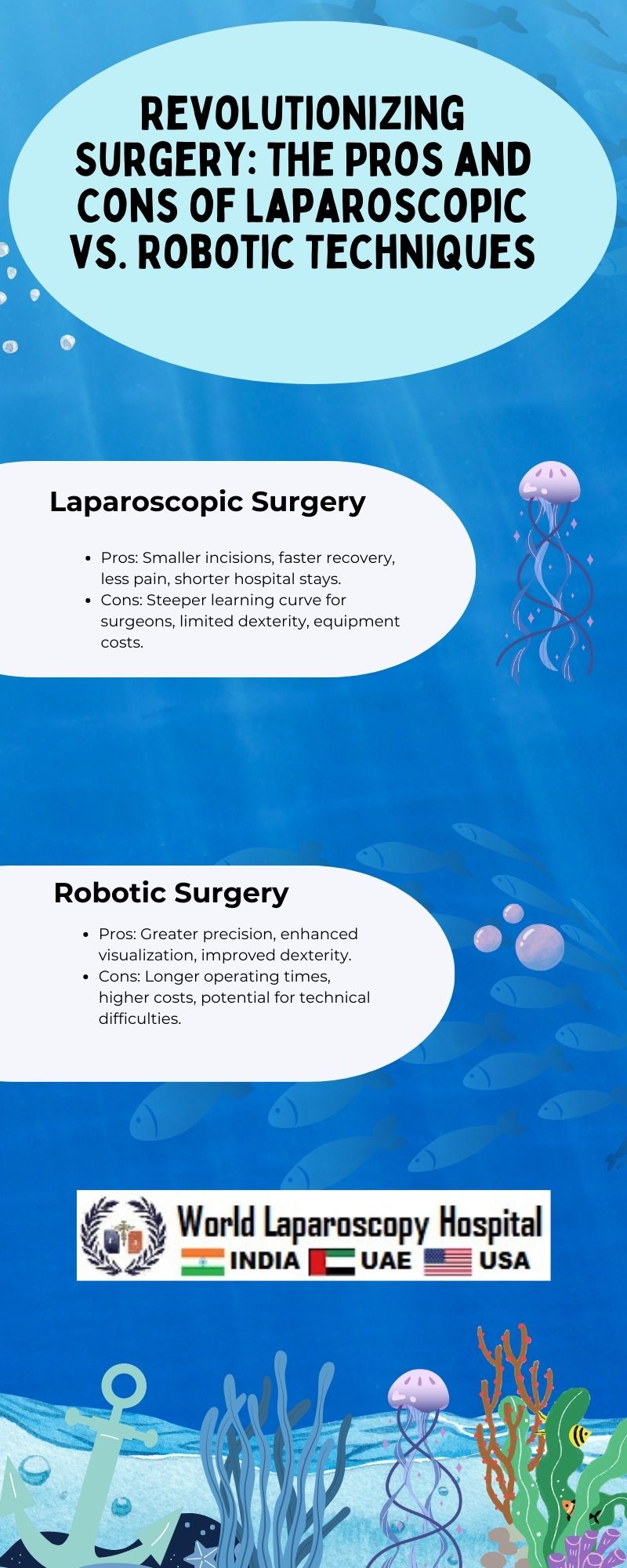
Laparoscopic Surgery:
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery (MIS) or keyhole surgery, involves making small incisions (usually 0.5 to 1.5 cm) in the abdomen through which specialized instruments and a camera (laparoscope) are inserted. The camera provides a high-definition view of the surgical site, allowing the surgeon to perform the procedure with precision.
Pros:
Minimal Scarring:
One of the most significant advantages of laparoscopic surgery is the minimal scarring it leaves. Compared to traditional open surgeries that require larger incisions, laparoscopic incisions are small and often result in less visible scars.
Faster Recovery:
Patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery typically experience shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times compared to open surgery. This is due to the reduced trauma to the body's tissues and organs.
Reduced Pain and Discomfort:
The smaller incisions and less invasive nature of laparoscopic surgery result in reduced postoperative pain and discomfort for patients.
Lower Risk of Infection:
Since laparoscopic surgery involves smaller incisions, there is a lower risk of infection compared to open surgery, where larger incisions are made.
Quicker Return to Normal Activities:
Patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery often find that they can return to their normal activities sooner than those who have had open surgery.
Cons:
Limited Range of Motion:
The instruments used in laparoscopic surgery have a limited range of motion compared to the human hand, which can make certain maneuvers challenging for the surgeon.
Steep Learning Curve:
Laparoscopic surgery requires specialized training for surgeons due to the unique skills and hand-eye coordination required to perform procedures using long instruments and a video monitor.
Risk of Complications:
While laparoscopic surgery is generally safe, there is a risk of complications such as bleeding, organ damage, and infection, as with any surgical procedure.
Cost:
Laparoscopic surgery can be more expensive than open surgery due to the need for specialized equipment and training.
Robotic Surgery:
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, is a form of minimally invasive surgery that utilizes robotic systems to assist surgeons in performing procedures with enhanced precision and control. The surgeon controls the robotic arms from a console, which provides a 3D view of the surgical site.
Pros:
Enhanced Precision:
Robotic systems offer surgeons greater precision and control than traditional laparoscopic instruments, allowing for more complex and delicate procedures to be performed.
Improved Visualization:
The 3D, high-definition view provided by the robotic system allows for better visualization of the surgical site, enhancing the surgeon's ability to perform precise movements.
Reduced Fatigue:
Robotic surgery can be less physically demanding for surgeons compared to traditional laparoscopic surgery, as the robotic arms can filter out hand tremors and provide ergonomic benefits.
Shorter Hospital Stays:
Patients undergoing robotic surgery often experience shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times compared to open surgery, similar to laparoscopic surgery.
Less Blood Loss:
Robotic surgery can result in less blood loss during procedures compared to open surgery, which can lead to a reduced need for blood transfusions.
Cons:
Cost:
Robotic surgery can be significantly more expensive than both laparoscopic and open surgery due to the high cost of robotic systems and the need for specialized training.
Limited Haptic Feedback:
One of the drawbacks of robotic surgery is the limited haptic feedback (sense of touch) experienced by the surgeon, which can make it challenging to detect subtle changes in tissue texture and stiffness.
Risk of Technical Failures:
Robotic systems are complex machines that can experience technical failures, such as system errors or malfunctions, which could potentially disrupt or delay surgery.
Steep Learning Curve:
Like laparoscopic surgery, robotic surgery requires specialized training for surgeons to become proficient in using the robotic system, which can be time-consuming.
Conclusion:
Both laparoscopic and robotic-assisted surgeries have revolutionized the field of surgery, offering patients less invasive options with faster recovery times and improved outcomes. While each technique has its own set of advantages and limitations, the choice between laparoscopic and robotic surgery often depends on the specific needs of the patient, the complexity of the procedure, and the surgeon's expertise. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in minimally invasive surgery, leading to even better outcomes for patients.