Introduction
The field of surgery has witnessed remarkable innovations over the years, transforming the way medical professionals approach complex procedures. One such innovation that has revolutionized colorectal surgery is laparoscopic splenic flexure resection. This minimally invasive technique has gained prominence in recent years for its ability to treat various colorectal conditions while offering numerous benefits to patients. In this article, we will delve into the world of laparoscopic splenic flexure resection, exploring its history, techniques, benefits, challenges, and its role in modern colorectal surgery.
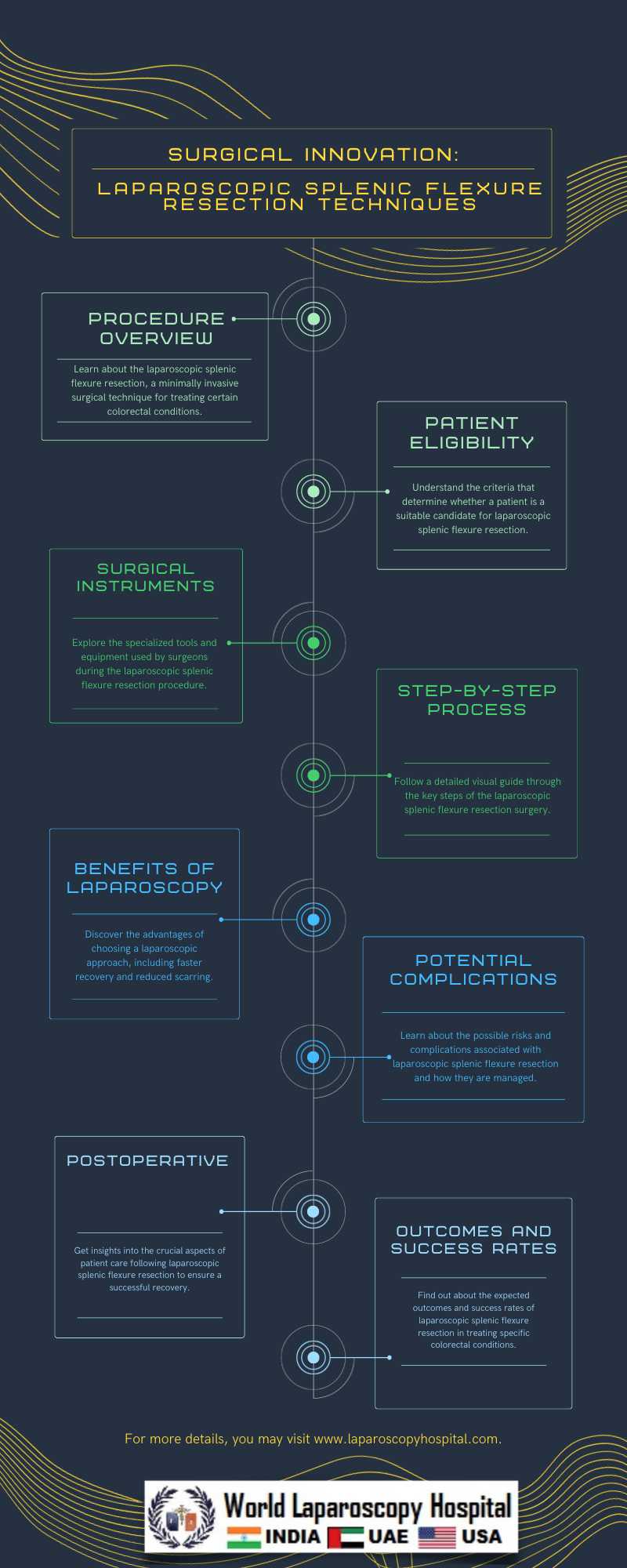
The Evolution of Colorectal Surgery
Colorectal surgery has a long history dating back to ancient times when surgical interventions were often crude and associated with high morbidity and mortality rates. Over the centuries, surgical techniques have evolved significantly, leading to safer and more effective procedures. The advent of laparoscopic surgery in the late 20th century marked a major milestone in the field of colorectal surgery.
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, involves making small incisions and using specialized instruments to access and operate within the abdominal cavity. The benefits of this approach over traditional open surgery include reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery times, and smaller scars. Laparoscopy rapidly gained popularity in various surgical specialties, including colorectal surgery.
Understanding Laparoscopic Splenic Flexure Resection
Laparoscopic splenic flexure resection is a specific laparoscopic procedure used to treat various colorectal conditions, including cancer, diverticulitis, and inflammatory bowel disease, among others. The splenic flexure is the bend between the transverse colon and the descending colon, and resecting this area may be necessary in cases of disease or obstruction. This procedure involves the removal of a segment of the colon, which is then reconnected to restore normal bowel continuity.
Techniques and Procedure
The laparoscopic splenic flexure resection procedure involves several key steps:
1. Patient Preparation: The patient is prepared for surgery, which may include bowel cleansing and fasting.
2. Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient is comfortable and pain-free throughout the procedure.
3. Incisions: Small incisions are made in the abdominal wall to allow access for laparoscopic instruments and a camera.
4. Insufflation: Carbon dioxide gas is introduced into the abdominal cavity to create space for the surgeon to work.
5. Visualization: A laparoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a camera on the end, is inserted through one of the incisions to provide a clear view of the surgical area.
6. Dissection and Resection: The surgeon carefully dissects the tissue around the splenic flexure and resects the affected portion of the colon.
7. Anastomosis: The remaining sections of the colon are rejoined (anastomosed) to restore normal bowel continuity.
8. Closure: The incisions are closed, and the procedure is complete.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Splenic Flexure Resection
Laparoscopic splenic flexure resection offers several advantages over traditional open surgery:
1. Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions result in less trauma to the abdominal muscles and tissues.
2. Faster Recovery: Patients typically experience less pain and can return to their regular activities sooner.
3. Shorter Hospital Stays: The need for extended hospitalization is reduced.
4. Reduced Scarring: Small incisions result in less visible scarring compared to a large abdominal incision.
5. Improved Cosmesis: Patients often appreciate the aesthetic benefits of smaller scars.
6. Lower Risk of Infections: Smaller wounds are less prone to postoperative infections.
7. Enhanced Surgical Precision: Laparoscopic instruments provide excellent visualization and maneuverability.
Indications for Laparoscopic Splenic Flexure Resection
Laparoscopic splenic flexure resection is indicated for a range of colorectal conditions, including:
1. Colorectal Cancer: Removal of cancerous growths in the splenic flexure.
2. Diverticulitis: Treatment of inflammation and complications caused by diverticulosis.
3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Management of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
4. Benign Polyps: Removal of noncancerous growths that cause symptoms or complications.
5. Colonic Volvulus: Correction of a twisted colon.
6. Ischemic Bowel Disease: Treatment of reduced blood flow to the colon.
7. Bowel Obstruction: Relief of blockages in the colon.
The specific indication for the procedure will vary based on the patient's condition and the surgeon's assessment.
Challenges and Considerations
While laparoscopic splenic flexure resection offers numerous benefits, it is not without challenges. Surgeons must carefully consider several factors, including:
1. Patient Selection: Not all patients are suitable candidates for laparoscopic surgery, and individual factors must be assessed.
2. Experience: Surgeons require specialized training and experience in laparoscopic techniques.
3. Complexity: The procedure can be technically challenging, especially in cases of extensive disease.
4. Complications: As with any surgery, complications such as bleeding, infection, and anastomotic leaks are possible.
5. Conversion to Open Surgery: In some cases, the laparoscopic approach may need to be converted to open surgery due to unforeseen difficulties.
Outcomes and Success Rates
The success of laparoscopic splenic flexure resection depends on various factors, including the patient's overall health, the indication for surgery, and the surgeon's expertise. However, studies have shown promising outcomes, including:
1. Low Morbidity: Laparoscopic procedures are associated with lower complication rates compared to open surgery.
2. Shorter Hospital Stays: Patients typically spend less time in the hospital after laparoscopic surgery.
3. Improved Quality of Life: Reduced pain and faster recovery contribute to an improved postoperative quality of life.
4. Comparable Oncologic Outcomes: For colorectal cancer, laparoscopic resection has shown comparable oncologic outcomes to open surgery.
Conclusion:
Laparoscopic splenic flexure resection represents a significant advancement in modern colorectal surgery. This minimally invasive approach offers multiple advantages, including reduced pain, faster recovery, and improved cosmesis. While it presents challenges and considerations, the procedure has proven to be a valuable option for patients with various colorectal conditions.
As technology continues to advance and surgical techniques evolve, laparoscopic splenic flexure resection is likely to play an increasingly vital role in the management of colorectal diseases. Surgeons and patients alike can look forward to the continued refinement of this innovative approach, enhancing the outcomes and quality of life for individuals facing colorectal surgery.