DR. A. SUDHAN KUMAR
PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT
1) assessment of type of hernia (direct or indirect), unilateral or bilateral, recurrent,complicated (features of obstruction)
2) comorbidites (DM/HTN/COPD/cardiac disease)
3) previous history of smoking, any previous surgery, weight lifting
4) pre anaesthetic evaluation
5) USG abdomen – to know type of hernia, defect size, BPH
POSITION OF PATIENT
Trendelenberg position with head low by 15 – 30 Degree
ERGONOMICS:
1) Operating surgeon, target(hernia site) and the monitor should lie on coaxial arrangement
2) The height of table should equals 0.49cm x surgeon’s height
3) The surgeon should stand on opposite site of the target (right side for left sided hernia, left side for right sided hernia)
4) Distance between surgeon and monitor should be 5 times the diagonal length of screen
5)check for insuffulators, energy sources, cable wires and insulation of instruments
PORT POSITIONING:

Based on the principles of BASEBALL DIAMOND CONCEPT
1) 10mm Optical port placed in infraumbilical region
2) two 5mm working ports placed according to baseball diamond concept
Access to peritoneal cavity:
1) close technique: (through veress needle)
• incision at inferior crease of umbilicus using 11 no. blade.
• Check the patency of veress needle, spring action before insertion
• Hold veress needle like a dart
• Lift the abdominal wall and insert the Veress needle 45o angle to the spine and perpendicular to the lifted abdominal wall. It is guided towards the anal canal as there is hollow sacral curve to prevents injury to bowel and vessels
• Insertion is confirmed by two clicks
• Entry to abdominal cavity confirmed by irrigation,aspiration and hanging drop tests.
2) open technique:
• Incision at inferior crease of umbilicus
• Scandinavian technique for safer entry to the intra-peritoneal space.
• Blunt trocar inserted and secured with lateral stay sutures
CREATION OF PNEUMOPERITONEUM
1)Insufflation via Veress needle, using CO2
2)check for uniform distension of abdomen. Insuffalation continued until preset pressure reaches12-15mmHg,
3) remove veress
4) the infraumblical incision extended to 11mm.
5)insertion of cannula with trocar by screwing movement perpendicular in direction to abdominal cavity. Once peritoneum preached, turned to the desired site of target
6) The camera is white-balanced and then focused at a distance of the focal length
7) 10mm optical port inserted under direct vision
8) insertion of two 5mm working ports by baseball diamond concept
Procedural Steps
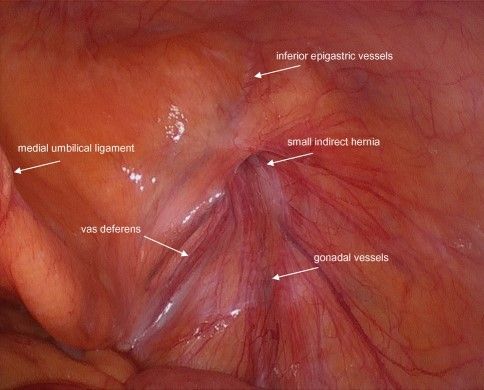

Diagnostic laparoscopy
Assessment of hernia site, three ligaments (median, two medial and two lateral umbilical ligaments), triangle of doom, triangle of pain and trapezoid of disaster.
1) Adhesiolysis in case of severe dense adhesions
2)peritoneal dissection should be started laterally about 6 cm from the outer margin of the hernia defect (right hernia – 2 o clock and left hernia – 10 o clock position)
3) dissection is from lateral to medial side and reach upto hernia site. Do not dissect over hernia sac to prevent injury.
3) rise the flap upto medial umbilical ligament which is facilitated by the entry of CO2 into preperitoneal space and further medial dissection avoided to prevent injury to bladder . fibrous strands are cut.
4) using peanut, push the fat towards the anterior abdominal wall to prevent injury to vital structures
5)medial pocket is made and cooper’s ligament (light house) is visualized. Lateral pocket is made and careful dissection should be carried over triangle of doom and triangle of pain.
6)blunt dissection of sac is done by Maryland and push the cord structures away by giving backward traction and asking assistant tohold testis in scrotum. Pseudosac (condensation of transversalis fascia) to be differentiated from sac and to be separated.
Mesh Placement:
1) polypropylene mesh – 10*15 cm mesh used
2) roll the mesh outside the abdomen and push it through 10mm port under vision using needle holder.
3) unroll the mesh. Place the mesh over myopectineal orifice of FRUCHAUD (inguinal,femoral,obturator area)
4) in bilateral hernia, single large mesh is placed covering both the defect
FIXATION OF MESH. NO FIXATION MY BE BETTER THAN FIXATION
1) Using tacker or suture
2) Fixed to cooper’s ligament in medial aspect and laterally fixed to rectus abdominis and anterior abdominal wall. Knotting is preferably done using intracorporeal surgeon’s knot.