MBBS, MS OBG, FRM, Fellowship in Obs Scan (Mediscan), FMAS
Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh
Introduction:
Proximal tubal disease accounts for approximately 15% of cases of tubal factor infertility. Under laparoscopic guidance, the hysteroscopic approach enables tubal cannulation and evaluation of the entire pelvis. Treatment of additional problems affecting the fallopian tubes, particularly adhesions and endometriosis is possible. Moreover laparoscopy helps to monitor the procedure and offers to assess tubal patency, leading to the ability to observe the utero-tubal junctions (UTJs) directly by hysteroscopy and to provide an excellent approach for tubal cannulation.

The relatively higher success rate of recanalizing tubes : 1) accurate visualization of both ostia before passing catheter, which definitely facilitated the successful cannulation, 2 ) hydrotubation. The total pregnancy rate per patient after was 48.9% thus minimising the requirement of ivf. Ectopic pregnancy has been reported in 5%.
Indication:
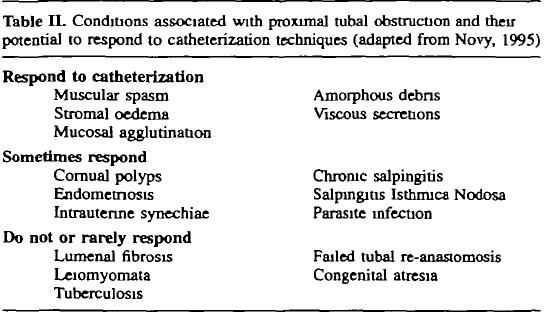
HSG showing cornual tubal block which can be due to spasm, debris , cornual polyps, synaechae, mucus agglutination
Contraindications
Active infection, Menstruation, Recent Trauma
Complications:
Damage to normal tube: dissection, perforation
Ectopic pregnancy
Anatomy:
Fallopian tube measures 8 -12 cm long. It has 4 parts: intramural, isthmus, ampulla and infundibulum. Intramural portion of tube is 1 -2 cm in length mostly tortuous .The direction of mucosal folds is towards uterine tube , it has a sphincter at this junction made of smooth muscle which can close. Ampulla measures 7 - 8cm and isthmus 4 cm . Ampulla is the widest part and intramural part is the narrowest.
Preoperative preparations:
- Diagnostic Laparoscopy with hysteroscopic tubal cannulation and chrompertubation must be performed between day 6 - 12 of periods
- Required Blood tests and Pre anesthetic check up
- Informed consent
- 400 mcg vaginal misoprostol for cervical dilatation 2 hrs - 4 hrs prior if nullipara
- Antibiotic
Surgeon, Assistant, Anaesthesian, Scrub nurse, OT technician, Instruments Required
Laparoscopic Instruments:
Insufflator, CO2 gas, 2 alleys, no 11 size blade, BPL handle, 10 ml syringe with saline, 10 ml syringe with 2 % xylocaine
Veress needle, 10 mm port, 1 or 2 5 mm port, 30 degree 10 mm telescope, Atraumatic grasper, 5 mm suction and irrigation apparatus. Methylene blue dye, 10 ml syringe, Rubins cannula
Hysteroscopic Instruments:
Sims speculum, Vulsellum, Alleys forceps, Uterine sound, Hegars dilator, 30 degree 4 mm Telescope, 4 channel diagnostic sheath
IV line, Normal saline, 2 Monitors, Light source , CCD each
Procedural Steps:
- Diagnostic laparoscopy with tubal patency test
- Diagnostic hysterscopy
- Selective Tubal Cannulation
- Selective chrompertubation
Executional steps:
Patient position:
Modified lithotomy with head end low by 15 degree and the vagina of patient should be at level of surgeons elbow
General anesthesia is given along with local anesthesia at port sites with 2 % xylocaine.
Position of personnel:
Surgeon on the left side of patient, in coaxial line with target and monitor. Height of table to be 0.49 x ht of surgeon in cm, monitor to be at distance that equals to 5 times the diagonal length of monitor. Camera assistant on right of surgeon. Assistant in between legs of patient. Anaesthetist on the cephalad position.
Parts are cleaned with antiseptic and draped.
Port Position:
Two ports: Optical port in inferior umbilical crease.
For diagnostic: one 5mm lateral port in left iliac fossa or suprapubic port (3 -5 cm above pubic symphysis in midline)
In case of operative: 2 lateral ports by base ball diamond concept
Diagnostic Laparoscopy
- Make a transverse stab wound with size11 blade at the inferior crease of umbilicus
- Check the spring of veress needle as well as patency with saline in 10mm syringe
- Hold the entire thickness of the infra-umbilical abdomen wall in middle to measure the thickness of abdominal wall then hold the veress needle like a dart at a distance equal to 4cm plus abdominal wall thickness
- Insert the Veress needle perpendicular to abdominal wall and 45 degrees to the body of patient, pointing towards anus until 2 clicks are felt
- Push 5 ml normal saline and suck back : in intraperitoneal placement there is free flow of saline into abdominal cavity and air bubbles are sucked out.
- Hang a drop of saline on veress and pull abdominal wall then drop goes into abdominal cavity.
- Switch on the insufflator, let air flow start then connect the tube to veress needle with flow rate of 1L/min. observe the monitor, once 500 ml of C02 is in then increase the flow rate to 2.5 lt /min till 1.5 lt of gas is in, at this point of time, a preset pressure of 12 -15 mm hg is reached.
- Increase the size of skin incision by 11 blade to make a smiley in the infra umbilical crease, to fit a 10mm port. This can be pre-checked by placing 10mm port for estimation of incision.
- With artery forceps open obliterated vitellointestine duct till rectus sheath & insert 10mm port holding it like a Gun with tip of index finger at half way distance from piercing end, middle finger wrapping gas port & then thenar eminence pressing trochar against cannula.
- With screwing movement enter abdominal cavity perpendicularly & hear for single click. Take out cannula & hear for hissing sound of gas which confirm intraperitoneal placement.
- Inserts the telescope after white balancing and focussing at a distance of 10 cm and confirm intraperitoneal position.
- Insert the 5mm lateral port under direct vision in left iliac fossa avoiding vessels after giveing skin incision
- Inserts atraumatic grasper through 5mm port.
- Surgeon can hold both the telescope and working instrument for diagnostic laparoscopy
- In case of operative laparoscopy, camera person can hold the telescope
- Inspect the entire abdomen in clockwise direction
- With patient in steep trendelenberg position ( 30 degree head down )
- First visualise structures just below umbilicus then caecum, appendix, right ascending colon.
- In reverse trendelenberg position :withdraw the telescope little bit to see the right lobe of liver, gall bladder, stomach, left lobe of liver, spleen, left colon then pelvic cavity.
- Inspects pelvis : trendelenberg position with uterus lifted anteriorly with vaginal hegars dilator. Push the bowel above sacral promontory.
- See the uterus , ovaries , both tubes, bladder ,cul de sac, sacral promontory.
- Can watch persistalsis of ureter , iliac vessels , triangle of doom ,triangle of pain and trapezoid of disaster.
- Inspect the medial umbilical ligament, median umbilical ligament ,broad ligament, round ligament , infundibulo pelvic ligament and deep inguinal ring.
- Mobilise the sigmoid colon to visualise left side of pelvis.
- Always first inspect the upper abdomen then only inspect pelvic cavity
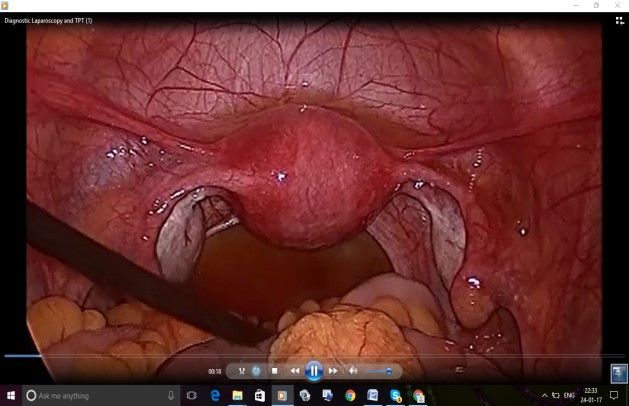
Tubal patency test:
- Assistant in between the legs will fix the rubins cannula to cervix and inject the diluted methylene blue dye into uterine cavity and the surgeon looks for free flow of dye through bilateral fimbrial ends with help of atraumatic grasper supporting the tube from behind and lifting the tube anteriorly to visualise the fimbrial end
- If there is a leak of dye from cervix , can reduce by grasping the cervix with alleys to avoid false negative tubal patency test. Some times can block the contralateral tube by atruamtic grasper so that dye enters ipsilateral tube to check patency.
- Suck all the methylene blue dye from cul de sac after completion of patency test.
- Laparoscopy must be done first so that cervical dilatation can be done under vision to avoid uterine perforation.
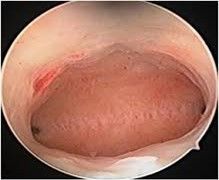
Diagnostic Hysteroscopy:
- Check the 4mm 30 degree rigid telescope and clean the eye piece of telescope with gauge
- Attach the telescope to 7 mm, 4 channel operative sheath after removing the obturator (lines on telescope , diagnostic sheath must be parallel and turn and lock it).
- Surgeon sits in between the legs
- Insert the vaginal sims speculum into vagina
- Hold the cervix with vulsellum and dilate the cervix upto 10 hegar
- Attach warm normal saline to inflow of 4 channel operative sheath .
- Do the white balancing and focusing at 4 cm distance
- CCD cable must be at 6 o clock position and light source should be at 12 o clock to see the posterior wall of uterus, rotate only the light source to 6 o clock to see the anterior wall of uterus and keep the light source to left to see right of uterine cavity and vice versa.
- An arrow mark on monitor also shows us the position of light cable.
- Insert slowly and smoothly the hysteroscope with inflow on and light source on into the uterine cavity through the cervical canal.
- Insert the hysteroscope till fundus is seen then await till normal saline distends the uterine cavity and becomes clear.
- Some endometrial flakes and blood clots might be there.
- Systemically visualize the endometrium on fundus, anterior wall , posterior wall, both lateral walls of uterine cavity and both tubal ostia for normalcy or any lesions. Inspect the shape and size of uterine cavity.
- Air bubbles will be seen near tubal ostia if tubes are patent
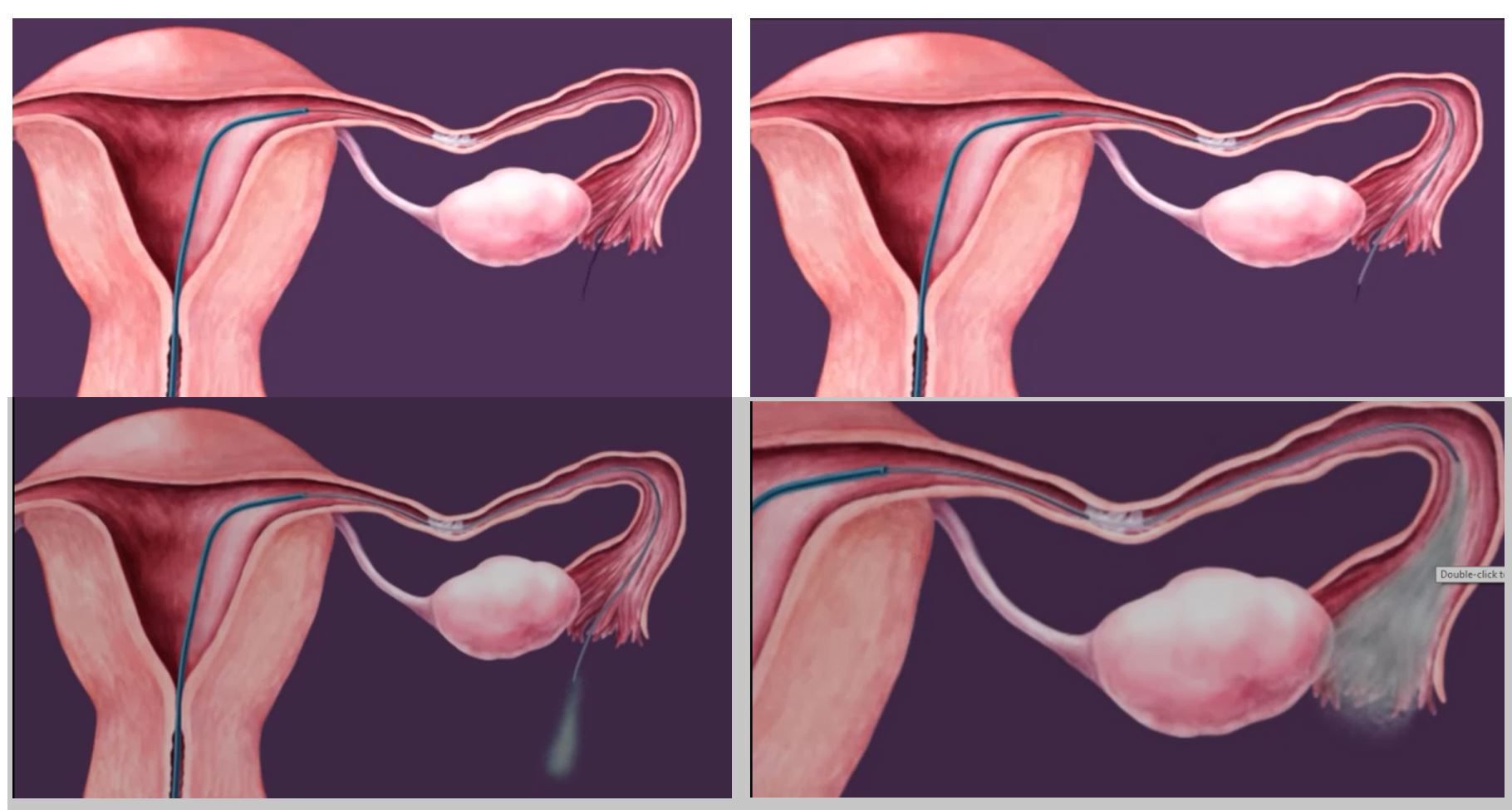
- Take a 60 cm coaxial Novy catheters (3-Fr catheter with 1 cm markings, 5-Fr catheter and an intraluminal guidewire <0.5mm in diameter)
- Insert 5 fr catheter directly into the 2mm working channel of operative hysteroscope and selectively bent or steered to a position in apposition to the tubal opening.
- Inject Diluted methylene blue through the catheter into the Fallopian tube and observe the laparoscopic appearance of the proximal and distal Fallopian tube Identify the presence of expelled mucus plugs from the fimbriae
- If proximal occlusion is not relieved during selective injection of dye, the inner catheter is then introduced through 5 fr catheter with guide wire.
- The tube is cannulated first with the wire guide ( soft tip goes into fallopian tube), and then the inner catheter is brought over it.
- The wire and cannula will be advanced until the surgeon could identify the wire and cannula within the tube, or until it was clear the tube could not be cannulated.
- The tube always was cannulated beyond the previously identified area of obstruction as seen on HSG.
- The surgeon can manipulate the tube to decrease the angle between the isthmus and the cornu to facilitate the cannulation.
- Upon withdrawal of the wire guide, selective injection of dye will verify successful recanalization of the Fallopian tube under laparoscopic observation.
- If dye is observed to spill from fimbrial end: tube is patent
- Same procedure is repeated on opposite side if it has proximal obstruction.
- Remove the hysteroscope , stop the saline inflow
- Remove the 5mm port under direct vision and then 10mm port is removed first followed by telescope.
- Deflate the abdomen and close 10mm port
- No need to close rectus of any ports if it is all 5mm, only dressing and bandage application is enough
- Patient and attenders to be explained the intraoperative findings and the Copy of edited video of the surgery must be given to them