Assistant Professor/Lecturer
KIMS, Bangalore
Task Analysis of Laparoscopic Splenectomy
Indications
- Idiopathic Thrombocyotopenic Purport
- Autoimmune Haemolytic Anemia
- Microspherocytosis
- Benign tumours and cysts
- AIDS-related thrombocytopenia
Contra-Indications
- Massive Splenomegaly
- Portal Hypertension
- Vaccines - Pneumococcal , Haemophilus influenza, Neisseria meningitidis ideally two weeks prior to surgery or post operatively.
- Blood and platelet transfusion if needed and arrange blood.
Anaesthesia
- General anaesthesia with endotracheal intubation is required.
- Two large IV catheters.
- Foleys catheter and Nasogastric tube.
Patient Position
- Patient placed in right lateral position and left arm crossing chest and lying on right arm.
- Left hip and chest are elevated with pillows, leaving the flank area open and the left knee flexed, with a padding o blankets between the legs.
- The patients secured across the chest and hips to the table with wide adhesive tape,as the operating room table will be tilted.
- Monopolar cautery check done along with patient end plate and Hormonic scalpel checks done.
- Coaxial alignment of surgeon, target and monitor checked.
- Camera connected, white balancing and focusing done.
- Co2 cylinder checked for sufficient insuflation.
- Working status of all the lap instruments along with insulation check is properly made.
Operative Preparation
The skin is prepared from the lower chest to pubis.
Port placement
- A 10 mm camera port is inserted at the level of the umbilicus over the left mid clavicular line.
- A 2mm stab incision is placed and verses needle is inserted perpendicular to abdominal wall.
- Intrabdominal position if verses is confirmed by the suction, irrigation, hanging drop and plunger test.
- Pneumoperitoneum is created by setting the insufflator at 14 mm hg.
- Camera inserted and abdomen inspected noting the size of the spleen for working port placement.
- Two additional 5mm ports are inserted on either side of camera port at 7.5 cms according to base ball diamond concept.
- Additional epigastric port can be inserted for liver retraction in case of hepatomegaly.
Details of procedure
Dissecting free from ligaments
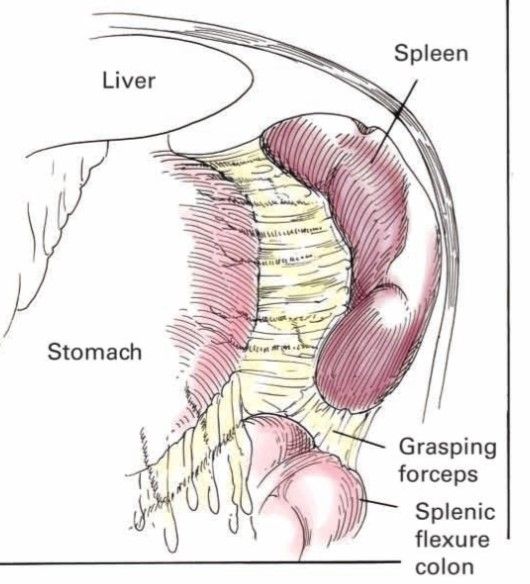
- After inspection of the abdomen the splenocolic ligament is visualised along with greater omentum.
- Splenic end of the ligament is identified and elevated with traction identifying a plane above the splenic flexure and entered using harmonic scalpel.
- Dissection continued medial to spleen to reach the gastrosplenic ligament containing short gastric vessels.
- By giving traction over the greater curvature of stomach lesser sac is entered using blunt dissection and short gastric vessels are divided 1 cm away from the gastric wall.
- The pancreas,splenic artery and vein running at the base of lesser sac are visualized.
- Short gastric are divided upto gastro oesophageal junction.
- Spleen is elevated medially and the splenorenal ligament is divided and continued till the top of spleen is free.

Dissection of splenic pedicle
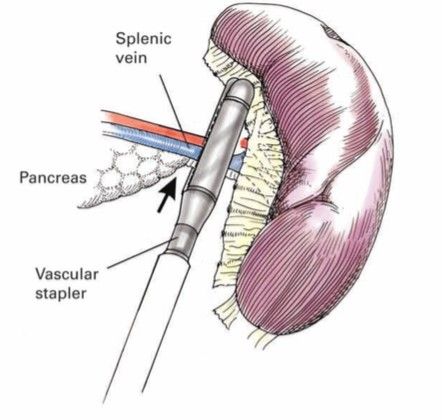
- Dissection of the medial part of spleen continued to reach the splenic pedicle.
- The area chosen should be distal to the tail of the pancreas but proximal to the trifurcation of the splenic vessels.
- A 12 mm port is required for Endo GIA Vascular stapler for the splenic pedicle.
- Dissection is performed until vessels an be safely encompassed within the jaws of the Vascular stapler.
- Care is taken to include the pedicle having splenic artery and vein in the arms of the stapler and fired .
- Alternatively artery and vein can be dissected and fired with stapler separately.
- Reinforced plastic bag is introduced and the organ is carefully placed into the bag.
- Bag is closed and partially withdrawn through the abdominal wall until the open rim of the bag is under control outside the abdomen.
- Bag is cut free from the carrier using drawstring in the end of instrument handle.
- Spleen is morcellated and extracted
- Post extraction the right upper quadrant lavaged with suction irrigator and a careful inspection is made of all cut surfaces and vessels.
- Tail of the pancreas is examined for possible injury.
- A silastic catheter drain is placed.
- All ports are closed under vision.
Post operative care
- The NG tube is removed post operatively.
- Foleys catheter is discontinued when the patient is alert enough to void.
- Clear liquids can be started within a day and diet is advanced as tolerated.