
About 1-2% of all pregnancies may be ectopic which is a very risky and possibly life-threatening condition. Of these, 95-97% occur in the fallopian tubes. Recent advanced techniques in diagnosis and management have reduced the mortality rates by almost half.
Laparoscopic management is offered when:
1. patient is hemodynamically stable
2. beta HCG >10,000 mUI/ml
3. mean sac diameter>=4cm
4. contraindication to medical management by methotrexate
5. patient cannot be followed up adequately post medical management


Steps:
1. Veress needle checked for spring action and patency. Other instruments were also checked for proper functioning.
2. Patient in the supine position
3. General anaesthesia given
4. Painting and draping done
5. Umbilicus everted with Allis after selecting the port site:
a.Intra umbilical in obese patients
b.Supra umbilical in patients with previous surgery
c.Inferior crease of umbilicus in all other patients
6. With the aid of a No.11 blade, a stab wound was given of approximately 2mm in the selected port site..
7. Lift the loose part of the abdomen using thenar, hypothenar, and all fingers of both surgeon and assistant.
8. Hold the veress like a dart by shielding it at a distance of abdominal wall thickness plus 4cm and insert it.
9. Hear the two clicks. First of the piercing of the rectus sheath and second of the piercing of the peritoneum.
10. Confirm correct placement of the veress needle by:
(a)Irrigation test
(b)Suction test
(c)Hanging drop test
(d)Plunging test
11. Connect the insufflation cable to veress and create pneumoperitoneum with a set pressure of 12-15mmHg.
12. Check the pneumoperitoneum by:
(a)liver dullness
(b)distention of abdomen
(c)Actual flow rate of ‘0’
While keeping a watch on the patient’s EtCO2.
13. Remove the veress needle.
14. Make a marking of 10mm trocar and then increase the incision up to 11-12mm.
15. Dilate the urachus with artery forceps as per the Scandinavian technique
16. Insert the 10mm trocar with cannula held like a piston with the index finger pointing to control the depth of insertion, head of the trocar on the thenar eminence, and middle finger wrapped around the gas channel with screwing motion of the wrist while lifting the abdominal wall till give away feeling and then change the direction towards the pelvis. At this point, a hissing sound is heard of the air leaking out.
17. Remove the trocar.
18. Clean the cannula with a gauze held in a grasper for clear passage of the telescope.
19. Check for any injury during the passage of the veress and trocar and get a general view of the pelvis.
20. Look for any sign of ruptured ectopic pregnancy:
(a)presence of hematoma
(b)presence of clots
21. Decide the target of the surgery by inspecting bilateral tubes.
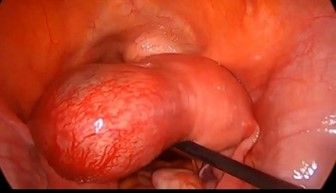
22. Using the baseball diamond concept, make a secondary port 7.5cm away from the primary port on the same arc under vision by transilluminating the area over the ectopic.
23. Using an atraumatic grasper in the secondary port and the telescope in the primary port, perform a diagnostic lap inspecting the following:
a. Right iliac fossa
b. Caecum
c. Appendix
d. Right hypochondrium
e. Ascending colon
f. Hepatic flexure of colon
g. Anterior pouch
h. Bladder
i. UV fold of peritoneum
j. Median ligament
k. Medial ligament
l. Cooper ligament
m. Posterior pouch
n. Uterosacral ligament
o. Rectum
p. Uterus- fundus, anterior and posterior surface
q. Bilateral adnexal- ovaries, tubes, round ligament, IP ligament, ovarian
fossa, and ligaments
r. Sacral promontory
s. Right and left pelvic sidewalls, deep ring, ureter, the triangle of doom,
trapezoid of disaster
t. Right lobe of the liver
u. Gall bladder
v. Stomach
w.Falciform ligament
x. Left lobe of the liver and left hypochondrium
y. Spleen
z. Left iliac fossa and sigmoid colon
24. Another port is inserted along the same arc, 7.5cm lateral to the secondary port to achieve two ipsilateral ports under vision.
25. Identify the diseased fallopian tube with the aid of an atraumatic grasper and a Maryland.
26. Contralateral tube inspection is also done.
27. Affected tube is mobilized by dissection of the mesosalpinx using a bipolar or harmonic if needed. Retraction of the fallopian tube in anterior and medial direction is done to give adequate space for dissection and to avoid injury to the pelvic wall. Avoid injury to the ovarian artery (causes devascularisation of ovaries).
28. Five units of vasopressin in 20ml normal saline are injected to minimize bleeding with a 20 gauge spinal needle in the area of the tubal segment containing trophoblastic tissue and the uterine surface adjacent to it. Notice the blanching of the tissue.
29. Stabilize tube with a grasper in the left hand.
30. Circumfentially incise around the cornua containing the ectopic pregnancy. Traction and counter traction is maintained to develop a plane of dissection.
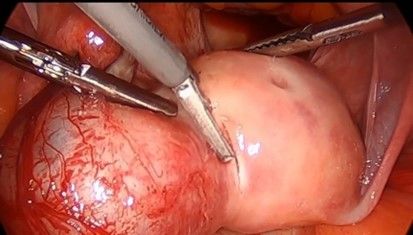
31. The products of conception are placed in the posterior cul de sac for removal later.
32. The defect is repaired in multiple layers. Usually, two layers of the myometrium and then the third layer of serosa is repaired separately.
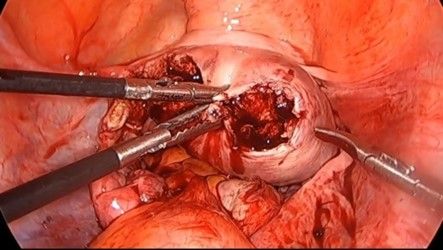
33. Close inner myometrium by continuous suturing using barbed suture or 2-0 vicryl.
34. Outer myometrium is closed by baseball suturing with 1-0 vicryl or absorbable braided suture.
35. Serosa is repaired by baseball suturing.
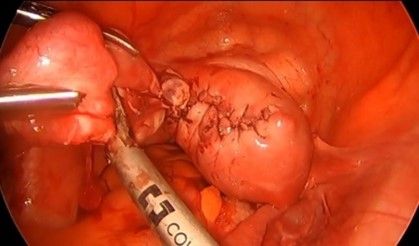
36. Salpingectomy is done with the help of bipolar and scissors successively of the affected tube since the cornua were resected and hence the fallopian tube will not be normal. The mesosalpinx and meso ovarian are coagulated and cut with the right hand while the left-hand holds the fallopian tube with an atraumatic grasper. This dissection must be from the lateral to the medial side.
36. The products and tube are removed by either pulling through the 10mm port site by aligning the tissue longitudinally or by using an endo bag.
37. Hemostasis is achieved.
38. Suction and irrigation are done if there is any spillage of blood.
39. Final inspection of the tube is done.
40.10mm port is closed using a veress needle or cobbler needle.
41. All ports are removed slowly to avoid any fascial injury or entrapment of the omentum or bowel.
42. Superficial closure of all port sites is done.
43. Abdomen is cleaned.
44. Antiseptic dressing done
45. Post-op vitals are noted and the patient is shifted to the recovery room.
46. Tissue that is retrieved is sent for histopathology.
Elaborated Steps
Position the patient in the supine position with both arms tucked.
Administer general anesthesia.
Place a Foley catheter to empty the bladder.
Preoperative antibiotics are administered.
Place a uterine manipulator to manipulate the uterus.
Insufflate the abdomen using CO2.
The laparoscope is inserted through a 10mm port at the umbilicus.
Place 2-3 additional trocars as required.
Identify the round ligament and fallopian tube.
Dissect the round ligament to enter the broad ligament.
Identify the interstitial portion of the fallopian tube.
Place a uterine artery clamp across the proximal part of the tube.
Divide the tube proximal to the clamp.
Remove the products of conception from the interstitial space.
Use suction to remove the contents of the pregnancy.
Inspect the tube and cornual area for bleeding.
Control bleeding by electrocoagulation or suturing.
Use suction to clear any remaining blood clots.
Inspect the surrounding structures for any additional bleeding.
Place a drain to monitor any potential bleeding or fluid accumulation.
Remove the uterine manipulator.
Remove the laparoscope.
Close the ports.
Deflate the abdomen.
Remove the trocars.
Close the incisions with sutures or staples.
Apply sterile dressing to the incisions.
The patient is awakened from anesthesia.
Extubate the endotracheal tube.
Move the patient to the post-anesthesia care unit.
Administer analgesics for pain management.
Monitor vital signs and urine output.
Check the dressing for bleeding or drainage.
Observe the patient for any signs of infection or complications.
Advise the patient to avoid strenuous activity for 2-4 weeks.
Advise the patient to avoid intercourse for 2-4 weeks.
Schedule a follow-up appointment.
Evaluate the patient's postoperative course.
Monitor for any complications, such as bleeding or infection.
Evaluate the patient's recovery of bowel and bladder function.
Elaborated Steps
Position the patient in the supine position with both arms tucked.
Administer general anesthesia.
Place a Foley catheter to empty the bladder.
Preoperative antibiotics are administered.
Place a uterine manipulator to manipulate the uterus.
Insufflate the abdomen using CO2.
The laparoscope is inserted through a 10mm port at the umbilicus.
Place 2-3 additional trocars as required.
Identify the round ligament and fallopian tube.
Dissect the round ligament to enter the broad ligament.
Identify the interstitial portion of the fallopian tube.
Place a uterine artery clamp across the proximal part of the tube.
Divide the tube proximal to the clamp.
Remove the products of conception from the interstitial space.
Use suction to remove the contents of the pregnancy.
Inspect the tube and cornual area for bleeding.
Control bleeding by electrocoagulation or suturing.
Use suction to clear any remaining blood clots.
Inspect the surrounding structures for any additional bleeding.
Place a drain to monitor any potential bleeding or fluid accumulation.
Remove the uterine manipulator.
Remove the laparoscope.
Close the ports.
Deflate the abdomen.
Remove the trocars.
Close the incisions with sutures or staples.
Apply sterile dressing to the incisions.
The patient is awakened from anesthesia.
Extubate the endotracheal tube.
Move the patient to the post-anesthesia care unit.
Administer analgesics for pain management.
Monitor vital signs and urine output.
Check the dressing for bleeding or drainage.
Observe the patient for any signs of infection or complications.
Advise the patient to avoid strenuous activity for 2-4 weeks.
Advise the patient to avoid intercourse for 2-4 weeks.
Schedule a follow-up appointment.
Evaluate the patient's postoperative course.
Monitor for any complications, such as bleeding or infection.
Evaluate the patient's recovery of bowel and bladder function.