An Analysis of Current Trends in the Use of Laparoscopy Across Different Surgical Procedures
Thesis Statement: The use of laparoscopic procedures has seen a substantial increase in the last decade, with the technique now being used in a significant percentage of various surgical procedures including bariatric surgery, antireflux surgery, appendectomy, cholecystectomy, colectomy, ventral hernia repair, and rectal resection. The varied rate of laparoscopic adoption across these procedures indicates a significant shift in surgical practice towards minimally invasive techniques, but also highlights the challenges and constraints in implementing these techniques in certain procedures.
Introduction:
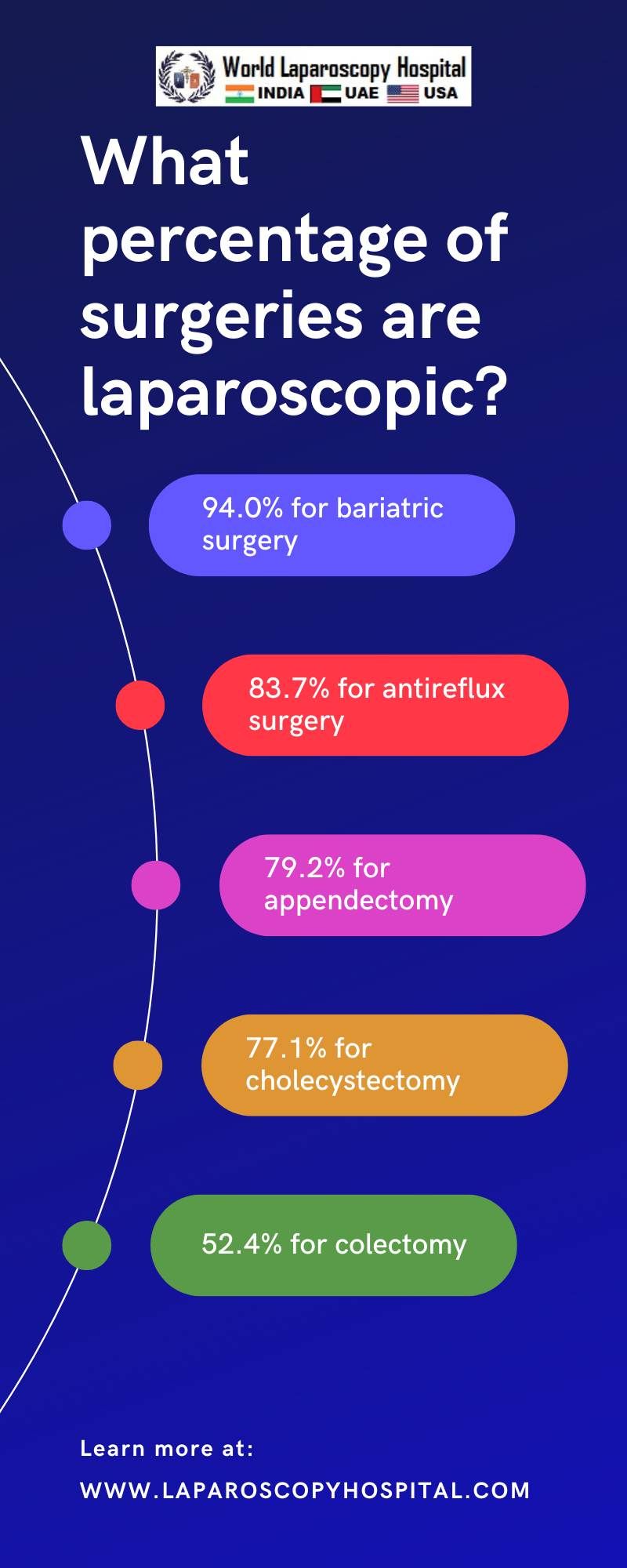
The thesis explores the current rates of laparoscopic use in different surgical procedures. Based on recent data, 94.0% of bariatric surgeries, 83.7% of antireflux surgeries, 79.2% of appendectomies, 77.1% of cholecystectomies, 52.4% of colectomies, 28.1% of ventral hernia repairs, and 18.3% of rectal resections are now performed using laparoscopic techniques. These statistics reveal a paradigm shift towards minimally invasive surgical techniques but also suggest a varying rate of adoption across different procedures.
The percentage of general surgery procedures performed laparoscopically has increased significantly in recent years. In 2000, only about 10% of general surgery procedures were performed laparoscopically. By 2018, this number had increased to over 60%. This increase is due to a number of factors, including the development of new laparoscopic techniques, the increasing availability of laparoscopic equipment, and the growing body of evidence supporting the safety and efficacy of laparoscopic surgery.
Here are some of the most common general surgery procedures that are now performed laparoscopically:
In contrast, the lower rates of laparoscopic use in procedures such as colectomy, ventral hernia repair, and rectal resection will be examined in detail. Factors potentially contributing to these lower rates may include the complexity of these procedures, the need for extensive surgical experience and skills in laparoscopic techniques, and the potential risks and complications associated with the laparoscopic approach in these cases.
Discussion:
The current state of laparoscopic use across various surgical procedures presents a compelling narrative about the evolution of the surgical practice. As evidenced by recent data, laparoscopy has found widespread acceptance and application, particularly in bariatric surgery (94.0%), antireflux surgery (83.7%), appendectomy (79.2%), and cholecystectomy (77.1%). However, its adoption is comparatively lower in colectomy (52.4%), ventral hernia repair (28.1%), and rectal resection (18.3%).
This stark contrast in the usage of laparoscopy can be attributed to multiple factors, including the nature of the surgery, patient-specific conditions, the surgeon's expertise, and the perceived benefits and risks associated with the laparoscopic approach.
Bariatric and antireflux surgeries have the highest rates of laparoscopic use. These procedures are typically performed on the upper gastrointestinal tract, which is easily accessible via the laparoscopic approach. Moreover, these procedures often involve obese patients, for whom the benefits of laparoscopy—such as shorter recovery time, reduced postoperative pain, and minimized scarring—are particularly pronounced. The widespread use of laparoscopy in these procedures can also be attributed to the extensive training and familiarity that surgeons have with laparoscopic techniques in this context.
Appendectomies and cholecystectomies also exhibit high rates of laparoscopic use. Over the past few decades, laparoscopic appendectomy and cholecystectomy have been proven safe and effective, often preferred due to their associated shorter hospital stays and quicker return to normal activity.
On the other hand, the adoption of laparoscopy in colectomy, ventral hernia repair, and rectal resection is notably lower. This may be due to several reasons. These procedures are often more complex and require a high degree of surgical skill and experience. Additionally, the associated anatomical regions may be more challenging to navigate laparoscopically, particularly in patients with previous surgeries or those with complex medical conditions. Furthermore, these procedures may carry a higher risk of complications, which might deter some surgeons from adopting the laparoscopic approach.
Despite these challenges, there is a steady increase in the use of laparoscopy in these procedures. Advances in technology, surgeon training, and the establishment of clear guidelines have made laparoscopy a viable option in an increasing number of cases. Still, further research and development are necessary to overcome the existing barriers and broaden the application of laparoscopy.
It's worth noting that the decision to use laparoscopy should always be patient-centered. While laparoscopy has many benefits, it is not suitable for every patient or every condition. The surgeon must consider the individual patient's health, the nature of the disease, the potential benefits and risks of the laparoscopic approach, and their own skill and comfort level with the technique.
In conclusion, the high percentage of laparoscopic use in several surgical procedures signifies a major shift in surgical practice towards minimally invasive techniques. However, the variable rate of adoption across different procedures underscores the challenges inherent in implementing these techniques universally. As we continue to advance technologically and clinically, it is hoped that the use of laparoscopic techniques will become increasingly common, improving patient outcomes across a broader range of surgical procedures.
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, has revolutionized the field of medicine over the past few decades. Its benefits such as shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery times, and fewer postoperative complications have made it increasingly popular among both physicians and patients. However, the economic aspects of laparoscopic surgery are complex and multifaceted, including upfront costs of equipment and training, cost savings from quicker patient recovery, and long-term impacts on healthcare systems. This essay explores the future economic aspects of laparoscopic surgery, considering trends in technology, healthcare policy, and patient expectations.
The Upfront Costs and Long-Term Savings
The initial costs associated with laparoscopic surgery can be high, primarily due to the need for specialized equipment and the training required for surgeons. Advanced laparoscopic equipment like high-definition monitors, insufflators, and specialized surgical instruments represent significant capital investments for healthcare facilities. Additionally, the technical skill required for laparoscopic procedures necessitates comprehensive training programs, which are both time-consuming and costly.
However, these upfront costs must be balanced against the potential long-term savings. Laparoscopic procedures often result in shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery times, which can significantly reduce the overall cost of care. Furthermore, the minimization of postoperative complications not only improves patient outcomes but can also lead to substantial cost savings for healthcare systems.
The Role of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are likely to play a crucial role in the economic aspects of laparoscopic surgery. As technology continues to evolve, it is anticipated that the cost of laparoscopic equipment will decrease, making it more accessible to a wider range of healthcare facilities, including those in low and middle-income countries. Moreover, advancements such as robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery, while currently expensive, may become more affordable in the future, potentially offering even greater precision and control during procedures.
Healthcare Policy and Reimbursement Models
Future healthcare policies and reimbursement models will also significantly impact the economics of laparoscopic surgery. As the cost-effectiveness of laparoscopic surgery becomes more evident, healthcare policymakers may be incentivized to promote its use. Reimbursement models could shift to favor minimally invasive procedures, reflecting their benefits in terms of patient outcomes and cost savings.
Patient Expectations and Quality of Life
Finally, it's essential to consider the economic impact of improved quality of life for patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. The less invasive nature of these procedures often leads to less postoperative pain, quicker return to work, and overall improved patient satisfaction. These factors can have significant economic implications in terms of increased productivity and decreased indirect costs related to recovery.
In the future, the economic aspects of laparoscopic surgery will be influenced by a multitude of factors including technological advancements, evolving healthcare policies, and changing patient expectations. Despite the high initial costs, the long-term savings, coupled with improved patient outcomes, make laparoscopic surgery a promising investment for healthcare systems globally. However, to fully realize its potential, there is a need for strategic planning, investment in training, and the development of policies that promote the accessibility and affordability of laparoscopic procedures.
Conclusion:
While the overall trend towards laparoscopic procedures is evident, it is important to understand the varying rates of its adoption in different surgical procedures. This understanding will provide insights into the challenges and opportunities for further advancement in the field of minimally invasive surgery. The thesis aims to provoke thought and encourage further research into ways of increasing the percentage of laparoscopic use in procedures where its adoption has been slower.
Introduction:
The thesis explores the current rates of laparoscopic use in different surgical procedures. Based on recent data, 94.0% of bariatric surgeries, 83.7% of antireflux surgeries, 79.2% of appendectomies, 77.1% of cholecystectomies, 52.4% of colectomies, 28.1% of ventral hernia repairs, and 18.3% of rectal resections are now performed using laparoscopic techniques. These statistics reveal a paradigm shift towards minimally invasive surgical techniques but also suggest a varying rate of adoption across different procedures.
The percentage of general surgery procedures performed laparoscopically has increased significantly in recent years. In 2000, only about 10% of general surgery procedures were performed laparoscopically. By 2018, this number had increased to over 60%. This increase is due to a number of factors, including the development of new laparoscopic techniques, the increasing availability of laparoscopic equipment, and the growing body of evidence supporting the safety and efficacy of laparoscopic surgery.
Here are some of the most common general surgery procedures that are now performed laparoscopically:
- Appendectomy
- Cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal)
- Hernia repair
- Nissen fundoplication (for gastroesophageal reflux disease)
- Hiatal hernia repair
- Inguinal hernia repair
- Umbilical hernia repair
- Varicose vein stripping
- Thyroidectomy
- Adrenalectomy
- Splenectomy
- Colectomy (colon removal)
- Gastrectomy (stomach removal)
- Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy)
- Smaller incisions, leads to less pain and scarring
- Faster recovery time
- Shorter hospital stay
- Reduced risk of infection
- Improved cosmetic results
- The procedure is more complex and time-consuming than traditional open surgery
- There is a risk of complications, such as bleeding and injury to internal organs
- The cost of laparoscopic surgery is typically higher than traditional open surgery

The percentage of surgery done by laparoscopy in gynecology varies depending on the procedure. For example, laparoscopy is used in about 90% of cases for the removal of ovarian cysts, but only about 20% of cases for hysterectomy.
Here is a table of the percentage of surgery done by laparoscopy in gynecology for various procedures:
Procedure Percentage of Surgery Done by Laparoscopy
- Ovarian cyst removal 90%
- Hysterectomy 20%
- Myomectomy 60%
- Endometriosis surgery 70%
- Infertility surgery 50%
- Pelvic organ prolapse surgery 40%
It is important to note that these percentages are just estimates and may vary depending on the surgeon and the patient's individual circumstances.
Here are some of the benefits of laparoscopic surgery:
Smaller incisions, leads to less pain and scarring
- Faster recovery time
- Shorter hospital stay
- Reduced risk of infection
- Improved cosmetic results
- Here are some of the risks of laparoscopic surgery:
Complications associated with general anesthesia
- Injury to internal organs
- Bleeding
- Infection
Overall, laparoscopic surgery is a safe and effective procedure that offers many benefits over traditional open surgery. If you are considering gynecologic surgery, talk to your doctor about whether laparoscopic surgery is an option for you.
The thesis will further delve into the reasons behind the high percentage of laparoscopic use in bariatric and antireflux surgeries, exploring factors such as the nature of these procedures, their suitability for the laparoscopic approach, and the benefits that this method offers in terms of recovery time, postoperative pain, and cosmetic results.In contrast, the lower rates of laparoscopic use in procedures such as colectomy, ventral hernia repair, and rectal resection will be examined in detail. Factors potentially contributing to these lower rates may include the complexity of these procedures, the need for extensive surgical experience and skills in laparoscopic techniques, and the potential risks and complications associated with the laparoscopic approach in these cases.
Discussion:
The current state of laparoscopic use across various surgical procedures presents a compelling narrative about the evolution of the surgical practice. As evidenced by recent data, laparoscopy has found widespread acceptance and application, particularly in bariatric surgery (94.0%), antireflux surgery (83.7%), appendectomy (79.2%), and cholecystectomy (77.1%). However, its adoption is comparatively lower in colectomy (52.4%), ventral hernia repair (28.1%), and rectal resection (18.3%).
This stark contrast in the usage of laparoscopy can be attributed to multiple factors, including the nature of the surgery, patient-specific conditions, the surgeon's expertise, and the perceived benefits and risks associated with the laparoscopic approach.
Bariatric and antireflux surgeries have the highest rates of laparoscopic use. These procedures are typically performed on the upper gastrointestinal tract, which is easily accessible via the laparoscopic approach. Moreover, these procedures often involve obese patients, for whom the benefits of laparoscopy—such as shorter recovery time, reduced postoperative pain, and minimized scarring—are particularly pronounced. The widespread use of laparoscopy in these procedures can also be attributed to the extensive training and familiarity that surgeons have with laparoscopic techniques in this context.
Appendectomies and cholecystectomies also exhibit high rates of laparoscopic use. Over the past few decades, laparoscopic appendectomy and cholecystectomy have been proven safe and effective, often preferred due to their associated shorter hospital stays and quicker return to normal activity.
On the other hand, the adoption of laparoscopy in colectomy, ventral hernia repair, and rectal resection is notably lower. This may be due to several reasons. These procedures are often more complex and require a high degree of surgical skill and experience. Additionally, the associated anatomical regions may be more challenging to navigate laparoscopically, particularly in patients with previous surgeries or those with complex medical conditions. Furthermore, these procedures may carry a higher risk of complications, which might deter some surgeons from adopting the laparoscopic approach.
Despite these challenges, there is a steady increase in the use of laparoscopy in these procedures. Advances in technology, surgeon training, and the establishment of clear guidelines have made laparoscopy a viable option in an increasing number of cases. Still, further research and development are necessary to overcome the existing barriers and broaden the application of laparoscopy.
It's worth noting that the decision to use laparoscopy should always be patient-centered. While laparoscopy has many benefits, it is not suitable for every patient or every condition. The surgeon must consider the individual patient's health, the nature of the disease, the potential benefits and risks of the laparoscopic approach, and their own skill and comfort level with the technique.
In conclusion, the high percentage of laparoscopic use in several surgical procedures signifies a major shift in surgical practice towards minimally invasive techniques. However, the variable rate of adoption across different procedures underscores the challenges inherent in implementing these techniques universally. As we continue to advance technologically and clinically, it is hoped that the use of laparoscopic techniques will become increasingly common, improving patient outcomes across a broader range of surgical procedures.
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, has revolutionized the field of medicine over the past few decades. Its benefits such as shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery times, and fewer postoperative complications have made it increasingly popular among both physicians and patients. However, the economic aspects of laparoscopic surgery are complex and multifaceted, including upfront costs of equipment and training, cost savings from quicker patient recovery, and long-term impacts on healthcare systems. This essay explores the future economic aspects of laparoscopic surgery, considering trends in technology, healthcare policy, and patient expectations.
The Upfront Costs and Long-Term Savings
The initial costs associated with laparoscopic surgery can be high, primarily due to the need for specialized equipment and the training required for surgeons. Advanced laparoscopic equipment like high-definition monitors, insufflators, and specialized surgical instruments represent significant capital investments for healthcare facilities. Additionally, the technical skill required for laparoscopic procedures necessitates comprehensive training programs, which are both time-consuming and costly.
However, these upfront costs must be balanced against the potential long-term savings. Laparoscopic procedures often result in shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery times, which can significantly reduce the overall cost of care. Furthermore, the minimization of postoperative complications not only improves patient outcomes but can also lead to substantial cost savings for healthcare systems.
The Role of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are likely to play a crucial role in the economic aspects of laparoscopic surgery. As technology continues to evolve, it is anticipated that the cost of laparoscopic equipment will decrease, making it more accessible to a wider range of healthcare facilities, including those in low and middle-income countries. Moreover, advancements such as robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery, while currently expensive, may become more affordable in the future, potentially offering even greater precision and control during procedures.
Healthcare Policy and Reimbursement Models
Future healthcare policies and reimbursement models will also significantly impact the economics of laparoscopic surgery. As the cost-effectiveness of laparoscopic surgery becomes more evident, healthcare policymakers may be incentivized to promote its use. Reimbursement models could shift to favor minimally invasive procedures, reflecting their benefits in terms of patient outcomes and cost savings.
Patient Expectations and Quality of Life
Finally, it's essential to consider the economic impact of improved quality of life for patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. The less invasive nature of these procedures often leads to less postoperative pain, quicker return to work, and overall improved patient satisfaction. These factors can have significant economic implications in terms of increased productivity and decreased indirect costs related to recovery.
In the future, the economic aspects of laparoscopic surgery will be influenced by a multitude of factors including technological advancements, evolving healthcare policies, and changing patient expectations. Despite the high initial costs, the long-term savings, coupled with improved patient outcomes, make laparoscopic surgery a promising investment for healthcare systems globally. However, to fully realize its potential, there is a need for strategic planning, investment in training, and the development of policies that promote the accessibility and affordability of laparoscopic procedures.
Conclusion:
While the overall trend towards laparoscopic procedures is evident, it is important to understand the varying rates of its adoption in different surgical procedures. This understanding will provide insights into the challenges and opportunities for further advancement in the field of minimally invasive surgery. The thesis aims to provoke thought and encourage further research into ways of increasing the percentage of laparoscopic use in procedures where its adoption has been slower.