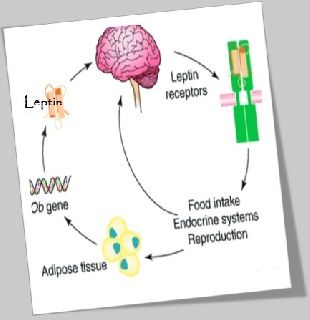
Even today, the Internet is set with sites that sell leptin supplements. Rather than taking supplements that have not been fully proven to help, overweight people have other options to aid leptin functioning. Leptin is a protein that is produced in the fat cells, circulates in the bloodstream, and would go to mental performance. Leptin could be the way fat cells inform our brain that our particular energy thermostat is defined right. Leptin tells our head which we have enough energy stored in fat cells to engage in normal, relatively expensive metabolic processe. In short, when leptin levels have reached a particular threshold for everybody, it is probably genetically set as soon as human leptin level is above that threshold, our head senses that we have energy sufficiency, and that means we can burn energy at a normal rate, eat food at a normal amount, take part in exercise with a normal rate, and we will take part in expensive processes, like puberty and pregnancy. But when people diet, they consume less as well as their fat cells lose some fat, which then lessens the amount of leptin produced. Then several processes begin within human body to operate a vehicle leptin levels back. One includes stimulation of the vagus nerve, which runs between brain and the abdomen.
The vagus nerve is acting as our energy storage nerve. Now the vagus nerve is turned on, so that we get hungrier. Everything the vagus nerve does meant to allow us to take up extra energy and store it with our fat. This happens to create more leptin which means our leptin can re-establish its personal leptin threshold. It makes us eat and it makes us bring the leptin to the level where it belongs. First fact is that our GI tract cannot absorb leptin as it is protein so get digested, so although We may could find a food rich in leptin it would not help and we should forget about finding foods full of leptin. The body has to create it is own leptin production or it is possible to make it by recombinant DNA technology but we have to take it by injection like insulin. Second fact is that we do not actually want high leptin levels in our blood, what we look for is made for body to respond to leptin more efficiently so ultimately causing LOWER leptin level. Leptin acts to curb appetite also to increase metabolism. So it would appear that we wish to increase leptin levels. But as time passes, high leptin levels inside our blood eventually results in leptin insensitivity, much like diabetes.
Hormones play an essential role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction. One of these hormones, leptin, is a starvation hormone that helps to regulate energy balance in the body. Leptin is produced by adipose tissue and signals the brain to reduce appetite and increase energy expenditure. However, in some cases, leptin resistance can occur, leading to obesity. In this essay, we will explore the facts about the hormone leptin, its role in regulating energy balance, and its link to obesity.
What is Leptin?
Leptin is a hormone that is primarily produced by adipose tissue, or fat cells, in the body. Its main function is to regulate energy balance in the body by sending signals to the brain to reduce appetite and increase energy expenditure. Leptin is released into the bloodstream and travels to the hypothalamus, a region of the brain that controls appetite and metabolism. Once in the hypothalamus, leptin binds to receptors on specific neurons, signaling the brain to reduce appetite and increase energy expenditure.
Leptin also plays a role in other bodily functions, such as the regulation of glucose metabolism, the immune system, and reproductive function. In addition, leptin levels can vary depending on factors such as gender, age, and body mass index (BMI).
Role of Leptin in Energy Balance
Leptin plays a crucial role in regulating energy balance in the body. When energy stores in the body are low, such as during periods of starvation, leptin levels decrease. This signals the hypothalamus to increase appetite and decrease energy expenditure, leading to a reduction in metabolism and energy usage.
Conversely, when energy stores in the body are high, such as after a meal, leptin levels increase. This signals the hypothalamus to reduce appetite and increase energy expenditure, leading to an increase in metabolism and energy usage.
Leptin Resistance and Obesity
While leptin plays an essential role in regulating energy balance, in some cases, leptin resistance can occur. Leptin resistance occurs when the brain becomes less responsive to the signals sent by leptin, leading to a disruption in the regulation of energy balance.
Leptin resistance can be caused by several factors, including genetic predisposition, inflammation, and environmental factors such as a high-fat diet. When leptin resistance occurs, the brain no longer receives signals to reduce appetite and increase energy expenditure, leading to an increase in appetite and a decrease in energy usage. This can lead to a positive energy balance, where more calories are consumed than expended, leading to weight gain and obesity.
Obesity is a complex condition that is influenced by numerous factors, including genetics, environmental factors, and lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity levels. However, leptin resistance is believed to play a significant role in the development of obesity. When leptin resistance occurs, it can lead to an increase in appetite, a decrease in metabolism, and an increase in fat storage, leading to weight gain and obesity.
Leptin and Weight Loss
While leptin resistance can contribute to weight gain and obesity, increasing leptin levels is not a guaranteed way to achieve weight loss. In fact, studies have shown that obese individuals often have higher levels of leptin than non-obese individuals, indicating that their bodies are producing sufficient levels of leptin, but are not responding to its signals.
Additionally, while increasing leptin levels can reduce appetite and increase energy expenditure in some individuals, others may not respond to these signals. This can be due to a variety of factors, including genetics, inflammation, and environmental factors.
Conclusion
Leptin is a crucial hormone that plays a significant role in regulating energy balance in the body. Its signals to the brain to reduce appetite and increase energy expenditure are essential for maintaining a healthy body weight. However, when leptin resistance occurs, it can disrupt the regulation of energy balance, leading to weight gain and obesity.
While leptin resistance is a complex condition that is influenced by numerous factors, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing leptin resistance and obesity. These steps include maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle, reducing inflammation in the body, and increasing physical activity levels.
In addition, research into the role of leptin in the regulation of energy balance is ongoing, and new treatments and therapies may become available in the future to address leptin resistance and obesity. These may include medications that target specific receptors in the brain or lifestyle interventions that promote healthy eating habits and physical activity.
Overall, the hormone leptin is a crucial factor in regulating energy balance in the body, and its role in the development of obesity highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle. By taking steps to reduce the risk of leptin resistance and obesity, individuals can improve their overall health and reduce the risk of developing related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.