The Expanding Role of Robotic Surgery in Oncology Treatments
Introduction
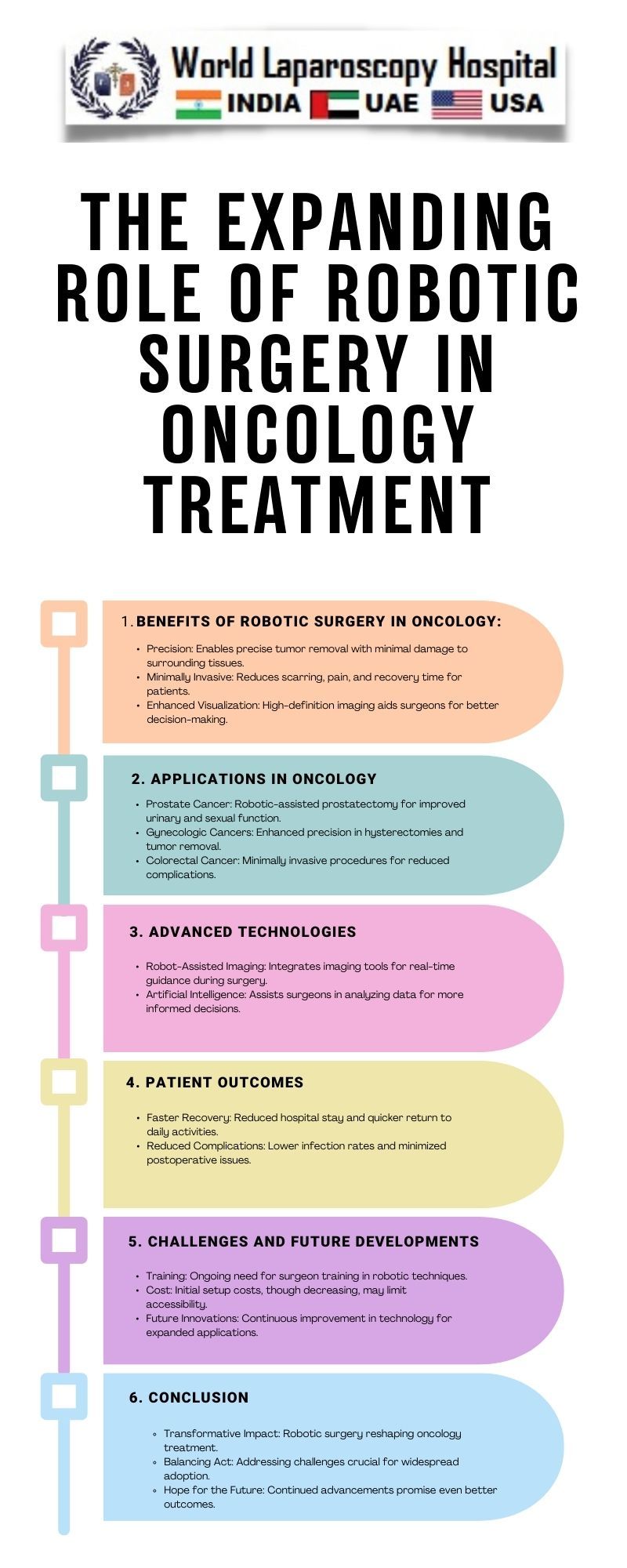
In the ever-evolving landscape of medical technology, one innovation is standing out as a game-changer in the field of oncology treatments - robotic surgery. Over the past few decades, robotic-assisted procedures have become increasingly prevalent, reshaping the way surgeons approach and manage cancer cases. This article explores the expanding role of robotic surgery in oncology treatments, delving into the technological advancements, applications, benefits, and future potential of this groundbreaking approach.
Technological Advancements in Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, involves the use of robotic systems to aid surgeons in performing intricate procedures with enhanced precision. The evolution of this technology has been remarkable, with continuous improvements in robotic platforms, imaging systems, and surgical instruments. The da Vinci Surgical System, a pioneer in robotic surgery, paved the way for subsequent innovations, enabling surgeons to operate with greater dexterity and control.
Key components of modern robotic surgical systems include robotic arms equipped with specialized instruments, a console where the surgeon controls the robotic arms, and a high-definition 3D vision system. These components work in tandem to provide a magnified, detailed view of the surgical site, allowing for meticulous and minimally invasive interventions.
Applications in Oncology
The application of robotic surgery in oncology has expanded across various cancer types, demonstrating efficacy in both diagnostic and therapeutic interventions. Common oncological procedures using robotic assistance include prostatectomies, hysterectomies, colorectal surgeries, and thoracic surgeries. The precision offered by robotic systems is particularly advantageous in delicate and hard-to-reach areas, contributing to improved patient outcomes.
Prostate Cancer:
Robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy has become a standard approach for treating localized prostate cancer. The da Vinci system's precise movements enable surgeons to navigate the narrow pelvic anatomy with increased accuracy, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues and reducing the risk of complications.
Gynecological Cancers:
In gynecologic oncology, robotic surgery is utilized for procedures such as hysterectomies and lymph node dissections. The minimally invasive nature of robotic-assisted surgeries translates to reduced blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times for patients undergoing these treatments.
Colorectal Cancer:
Robotic surgery is increasingly employed in colorectal cancer procedures, including colectomies and rectal resections. The ability to navigate tight spaces and perform intricate suturing enhances the surgeon's capabilities, leading to improved outcomes in terms of cancer removal and functional results.
Thoracic Surgery:
For thoracic malignancies, such as lung cancer, robotic-assisted procedures offer a less invasive alternative to traditional open surgery. Surgeons can access the thoracic cavity with smaller incisions, resulting in decreased pain, quicker recovery, and reduced postoperative complications.
Benefits of Robotic Surgery in Oncology
The adoption of robotic surgery in oncology brings forth a multitude of benefits for both surgeons and patients.
Precision and Accuracy:
Robotic systems provide surgeons with an unparalleled level of precision and accuracy. The robotic arms can mimic the surgeon's hand movements with greater control, enabling meticulous procedures even in challenging anatomical locations.
Minimally Invasive Approach:
One of the primary advantages of robotic surgery is its minimally invasive nature. Smaller incisions lead to reduced blood loss, decreased postoperative pain, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
Enhanced Visualization:
The high-definition 3D vision systems of robotic platforms offer superior visualization of the surgical field. This heightened clarity allows surgeons to identify and navigate critical structures with greater confidence, minimizing the risk of inadvertent damage.
Shorter Hospital Stays:
Patients undergoing robotic-assisted procedures often experience shorter hospital stays. The quicker recovery, coupled with reduced postoperative complications, contributes to a more efficient healthcare process.
Reduced Complications:
The precision and minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery contribute to a lower incidence of complications such as infections, bleeding, and wound-related issues. This is particularly significant in oncology, where patient recovery plays a pivotal role in overall treatment success.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the benefits of robotic surgery in oncology are evident, challenges and considerations persist. Cost implications, the learning curve for surgeons, and the need for specialized training are among the factors influencing the widespread adoption of this technology. Additionally, ongoing research focuses on expanding the applications of robotic surgery in complex oncological cases and integrating artificial intelligence to further enhance decision-making during procedures.
Cost Considerations:
The initial costs associated with acquiring and maintaining robotic surgical systems can be substantial. As a result, some healthcare institutions face challenges in justifying the investment, especially in regions with limited financial resources.
Surgeon Training:
Mastery of robotic surgery requires dedicated training for surgeons. The learning curve can be steep, and ensuring that healthcare professionals receive comprehensive training is essential for maximizing the benefits of this technology.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence:
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into robotic surgery holds great promise for the future. AI algorithms can assist surgeons in real-time decision-making, analyze imaging data, and enhance procedural outcomes. Ongoing research aims to leverage AI to further refine and expand the capabilities of robotic-assisted surgery.
Patient Selection Criteria:
Identifying the most suitable candidates for robotic surgery remains an essential consideration. Patient factors, tumor characteristics, and the surgeon's expertise all play a role in determining the appropriateness of robotic-assisted interventions.
Conclusion
The expanding role of robotic surgery in oncology is reshaping the landscape of cancer treatment. With continuous technological advancements, robotic systems offer surgeons unprecedented precision, enabling intricate procedures with minimal invasiveness. The benefits extend to patients, who experience shorter recovery times, reduced complications, and improved overall outcomes. As challenges are addressed and technology continues to evolve, the future holds exciting possibilities for the integration of robotic surgery in a broader range of oncological interventions, ultimately advancing the standard of care in cancer treatment.
