Robotic Surgery for Colorectal Conditions: A New Hope
Introduction:
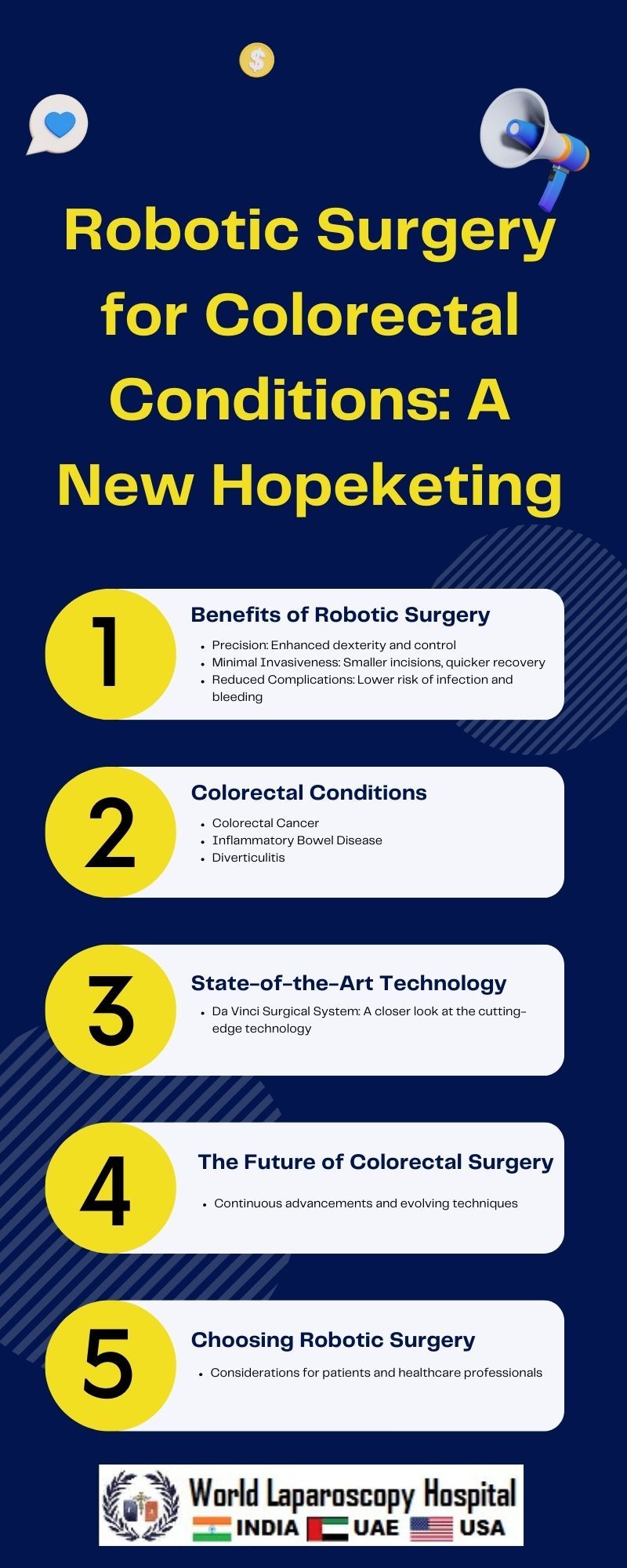
Colorectal conditions pose significant challenges to patients and healthcare professionals alike, often requiring complex surgical interventions. In recent years, a revolutionary advancement has emerged in the form of robotic surgery, offering new hope and transforming the landscape of colorectal healthcare. This article explores the intricacies of robotic surgery, its applications in treating colorectal conditions, and the potential impact it has on patient outcomes and the future of surgical care.
Understanding Colorectal Conditions:
To comprehend the significance of robotic surgery in colorectal healthcare, it is crucial to first understand the nature of colorectal conditions. Colorectal diseases encompass a spectrum of disorders, including colorectal cancer, inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), diverticulitis, and polyps. These conditions often necessitate surgical interventions to alleviate symptoms, remove tumors, or address complications.
The Evolution of Surgical Techniques:
Traditional open surgery has long been the standard approach for treating colorectal conditions. However, it comes with inherent drawbacks, such as larger incisions, increased pain, extended recovery times, and a higher risk of complications. Over time, minimally invasive techniques, including laparoscopic surgery, emerged as alternatives, offering smaller incisions and quicker recoveries. Despite these advantages, laparoscopy has its limitations, particularly in terms of dexterity and precision.
Robotic Surgery: A Technological Breakthrough:
Robotic surgery represents a paradigm shift in the field of colorectal surgery. The da Vinci Surgical System, a pioneering robotic platform, allows surgeons to perform procedures with enhanced precision, control, and visualization. The system comprises robotic arms controlled by the surgeon from a console, translating their hand movements into precise actions performed by the robotic instruments. This level of sophistication surpasses the capabilities of traditional laparoscopy, providing a more advanced and versatile tool for surgeons.
Applications of Robotic Surgery in Colorectal Healthcare:
Colorectal Cancer:
Robotic surgery has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in the treatment of colorectal cancer. The system's high-definition 3D vision and articulating instruments enable surgeons to navigate complex anatomical structures with unparalleled precision. This translates to improved tumor removal, reduced blood loss, and faster recovery times for patients.
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD):
Patients with inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, often require surgical intervention when medications prove ineffective. Robotic surgery offers a minimally invasive option for procedures like colectomy and ileal pouch-anal anastomosis, minimizing the impact on patients' quality of life.
Diverticulitis:
Robotic surgery proves beneficial in the management of diverticulitis, a common condition characterized by inflammation of pouches in the colon. The precision of robotic instruments allows for meticulous dissection and suturing, reducing the risk of postoperative complications.
Polyp Removal:
The ability to manipulate robotic instruments with greater precision facilitates the removal of colorectal polyps. This is particularly significant in preventing the progression of benign polyps to cancer, as surgeons can ensure complete excision with minimal impact on surrounding healthy tissue.
Advantages of Robotic Surgery in Colorectal Procedures:
Enhanced Precision:
One of the primary advantages of robotic surgery is the enhanced precision it offers. The robotic arms' ability to mimic the surgeon's hand movements with exceptional accuracy allows for delicate maneuvers in tight spaces, reducing the risk of damage to surrounding structures.
Improved Visualization:
The da Vinci System provides surgeons with high-definition, three-dimensional visualization of the surgical site. This superior view allows for better identification of anatomical structures and enhanced decision-making during the procedure.
Minimally Invasive:
Robotic surgery is inherently minimally invasive, requiring only a few small incisions. This results in reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recoveries compared to traditional open surgery.
Reduced Blood Loss:
The precision of robotic instruments contributes to reduced blood loss during colorectal procedures. This is particularly crucial in surgeries where excessive bleeding can pose significant risks to the patient.
Quicker Recovery:
Patients undergoing robotic-assisted colorectal surgery often experience shorter recovery times. The minimally invasive nature of the procedures, coupled with the precision of robotic instruments, allows individuals to resume normal activities sooner than with traditional open surgery.
Challenges and Considerations:
While robotic surgery presents numerous advantages, it is essential to acknowledge potential challenges. The initial cost of acquiring and maintaining robotic systems can be substantial, and not all healthcare facilities may have access to this technology. Surgeons also require specialized training to operate the robotic system effectively. Additionally, concerns about the lack of tactile feedback and the learning curve associated with mastering robotic techniques should be addressed.
The Future of Colorectal Healthcare:
The integration of robotic surgery into colorectal healthcare marks a transformative era in surgical practices. As technology continues to advance, we can anticipate further refinements in robotic systems, addressing current limitations and expanding the scope of procedures that can be performed robotically. The ongoing development of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning may contribute to the automation of certain aspects of surgery, enhancing efficiency and outcomes.
Patient-Centered Care:
Ultimately, the introduction of robotic surgery in colorectal healthcare aligns with the broader goal of providing patient-centered care. By minimizing invasiveness, reducing recovery times, and improving surgical outcomes, robotic surgery contributes to a higher quality of life for individuals facing colorectal conditions. As the technology becomes more widely available, it has the potential to reach a broader patient population, ensuring that more individuals can benefit from these advanced surgical techniques.
Conclusion:
Robotic surgery represents a new hope in the realm of colorectal healthcare, offering unprecedented precision, enhanced visualization, and minimally invasive approaches to complex procedures. As this innovative technology continues to evolve, it holds the promise of improving patient outcomes, reducing complications, and shaping the future of colorectal surgery. The integration of robotic surgery into mainstream medical practices underscores the ongoing commitment to advancing healthcare and providing patients with cutting-edge treatment options.
