Patient Selection Criteria for Laparoscopic Surgery
Introduction:
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, has revolutionized the field of surgery by offering patients a less invasive alternative to traditional open procedures. This technique involves making small incisions through which a camera and specialized instruments are inserted, allowing surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater precision. However, not all patients are suitable candidates for laparoscopic surgery, and careful consideration of various factors is crucial to ensure optimal outcomes. This article delves into the intricate details of patient selection criteria for laparoscopic surgery, highlighting the importance of personalized assessments and the evolution of these criteria over time.
Evolution of Laparoscopic Surgery:
Laparoscopic surgery emerged in the late 20th century as a groundbreaking technique that promised shorter recovery times, reduced pain, and minimized scarring compared to open surgeries. Initially limited to simple procedures, technological advancements and surgical expertise have expanded the scope of laparoscopic surgery to encompass a wide range of complex interventions, including colorectal, gynecological, and urological surgeries.
The success of laparoscopic surgery relies heavily on patient selection, as not every individual is an ideal candidate for this approach. The criteria for selecting patients have evolved with the accumulation of clinical experience, research findings, and technological advancements. Today, a multidimensional approach is employed to assess patients thoroughly before recommending laparoscopic surgery.
Patient Selection Criteria:
-
Overall Health Status:
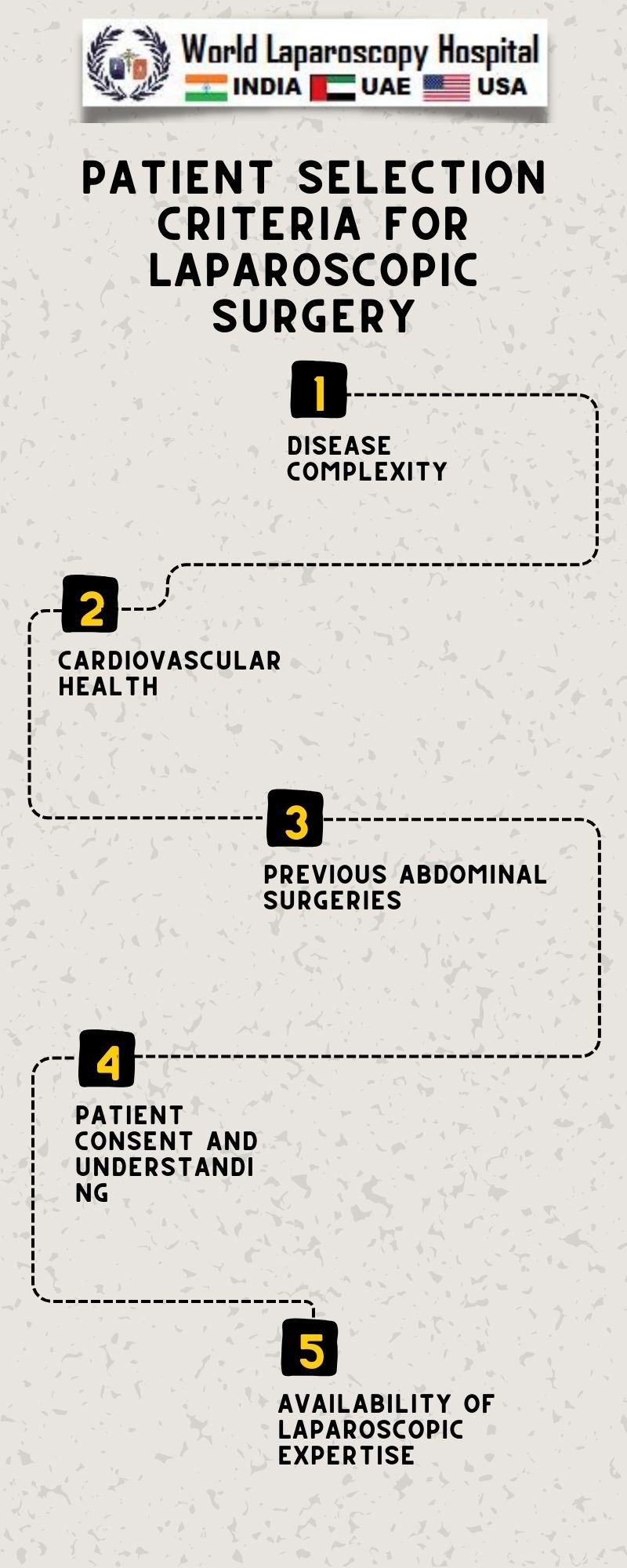
- One of the fundamental criteria for laparoscopic surgery is the patient's overall health. Candidates should generally be in good health with well-controlled medical conditions. Uncontrolled chronic diseases may increase the risk of complications during surgery.
- Assessment of cardiovascular health, respiratory function, and any existing medical conditions is essential. Patients with significant comorbidities may be better suited for traditional open surgery.
-
Body Mass Index (BMI):
- BMI plays a crucial role in determining the feasibility of laparoscopic surgery. Lower BMI is associated with easier access to the surgical site and reduced difficulty in manipulating instruments.
- Obese patients may face challenges due to increased abdominal fat, limiting visibility and access. However, advancements in equipment and techniques have expanded the applicability of laparoscopic surgery to certain obese individuals.
-
Type and Complexity of Surgery:
- The nature and complexity of the surgical procedure are key factors in patient selection. Laparoscopic surgery is well-suited for various procedures, but some may still require an open approach.
- Simple procedures like gallbladder removal and appendectomy are typically ideal for laparoscopic techniques. Complex surgeries, such as extensive cancer resections, may be better suited for open procedures.
-
Previous Abdominal Surgeries:
- Patients with a history of multiple abdominal surgeries may have adhesions or scar tissue, complicating laparoscopic access. However, this criterion is evolving as experienced surgeons can navigate such challenges using advanced techniques.
-
Patient Anatomy:
- Anatomical considerations are vital in laparoscopic surgery. The surgeon must evaluate the patient's abdominal anatomy to determine the feasibility of creating access ports and maneuvering instruments.
- Factors like the presence of previous surgical scars, variations in internal organ positioning, and abdominal wall thickness are carefully assessed to ensure a safe and effective laparoscopic procedure.
-
Patient Preferences:
- The patient's preferences and willingness to undergo laparoscopic surgery play a role in the decision-making process. Some patients may prefer the potential benefits of minimally invasive surgery, such as quicker recovery and reduced scarring.
- However, patient education is essential, as realistic expectations regarding potential risks, benefits, and recovery times must be communicated.
-
Surgeon Expertise:
- The skill and experience of the surgical team are critical in the success of laparoscopic procedures. Surgeons must be adept at handling laparoscopic instruments, interpreting images from the camera, and addressing any unexpected challenges during the surgery.
- Ongoing training and proficiency in laparoscopic techniques contribute to improved patient outcomes.
Challenges and Advances in Laparoscopic Surgery:
-
Obesity and Laparoscopic Surgery:
- Obesity poses challenges in laparoscopic surgery, primarily due to increased difficulty in accessing the surgical site and maneuvering instruments. However, advancements such as longer instruments and improved imaging systems have expanded the feasibility of laparoscopic procedures in obese patients.
- Bariatric laparoscopic surgery, specifically designed for obese individuals, has demonstrated success in achieving weight loss and improving metabolic health.
-
Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Surgery:
- The integration of robotic systems into laparoscopic surgery has further enhanced precision and maneuverability. Robot-assisted surgery allows for more intricate movements and precise suturing, making it suitable for complex procedures.
- However, the cost of robotic systems and the need for specialized training remain considerations in widespread adoption.
-
Patient-Tailored Approaches:
- Advances in imaging technology, such as three-dimensional laparoscopy, enable surgeons to visualize anatomical structures more accurately. This enhances the ability to plan and execute procedures tailored to the specific characteristics of each patient.
- Patient-specific considerations, such as the location of blood vessels and nerves, can be better addressed with these technologies.
-
Single-Incision Laparoscopic Surgery (SILS):
- SILS involves performing the entire surgery through a single small incision, further reducing scarring and potential complications. While not applicable to all procedures, SILS represents a minimally invasive alternative in selected cases.
- SILS is particularly beneficial in procedures like cholecystectomy and appendectomy, where a single incision can be strategically placed for optimal access.
Conclusion:
The evolution of laparoscopic surgery has transformed the landscape of modern surgical practice. Patient selection criteria for laparoscopic surgery are dynamic, adapting to advancements in technology, surgical techniques, and a deeper understanding of patient outcomes. As we move forward, the emphasis on personalized medicine continues to shape the criteria for laparoscopic surgery, ensuring that each patient receives the most suitable and effective treatment for their unique circumstances. Surgeons, equipped with refined skills and cutting-edge technologies, are ushering in an era where the benefits of minimally invasive surgery are maximized for a broader spectrum of patients, ultimately contributing to improved surgical outcomes and patient satisfaction.
