Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of medical advancements, laparoscopic surgery has emerged as a transformative approach, not only revolutionizing the technical aspects of procedures but also profoundly impacting the psychological well-being of patients. This article delves into the intricate tapestry of emotions and mental states experienced by individuals undergoing laparoscopic surgery, exploring how this minimally invasive technique shapes the psychological landscape of the surgical journey.
Understanding Laparoscopic Surgery:
Before delving into the psychological realm, it's essential to comprehend the fundamental aspects of laparoscopic surgery. Unlike traditional open surgeries, laparoscopic procedures involve small incisions through which a camera and specialized surgical instruments are inserted. This minimally invasive approach allows surgeons to visualize and operate within the body without the need for large, disruptive incisions.
The Anxious Prelude:
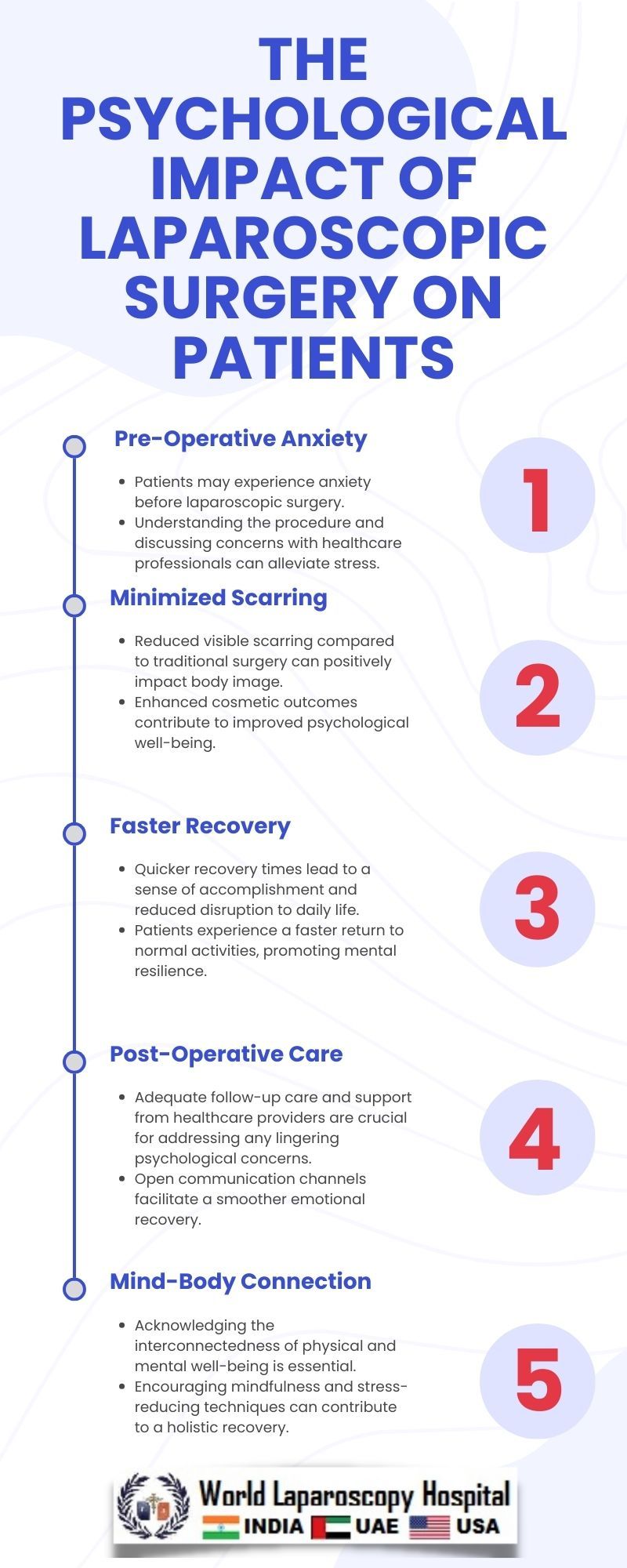
The journey of a patient begins well before the operating room, often characterized by anxiety and uncertainty. The fear of the unknown, concerns about pain, and the anticipation of a surgical outcome can significantly impact a patient's mental state. However, studies have shown that the prospect of undergoing laparoscopic surgery tends to alleviate some of these anxieties.
The Promise of Minimally Invasive Techniques:
One of the primary contributors to the psychological relief associated with laparoscopic surgery is the promise of reduced invasiveness. The smaller incisions translate to less tissue trauma, minimizing postoperative pain and discomfort. This tangible reduction in physical distress plays a pivotal role in shaping a positive psychological outlook.
Empowering Patients Through Information:
The availability of information, coupled with effective communication between healthcare professionals and patients, further empowers individuals undergoing laparoscopic surgery. Knowing what to expect, understanding the procedure, and being aware of the benefits contribute to a sense of control and preparedness. This, in turn, fosters a more positive mindset, as patients feel actively engaged in their healthcare journey.
The Role of Perceived Control:
Perceived control is a psychological concept that plays a crucial role in how individuals cope with stressors. Laparoscopic surgery, by its very nature, enhances the perception of control. Patients, armed with knowledge and a sense of participation in decision-making, feel more in control of their surgical experience. This empowerment has been linked to reduced stress and improved overall psychological well-being.
Reducing the Fear of Scarring:
The aesthetic concerns associated with surgical scars often contribute to preoperative anxiety. Laparoscopic surgery addresses this concern by minimizing visible scarring. The tiny incisions result in scars that are significantly less conspicuous than those resulting from open surgeries. This aspect of laparoscopic surgery contributes to a positive body image and self-esteem postoperatively.
The Impact on Recovery Time:
Postoperative recovery is a critical phase that significantly influences a patient's psychological state. Laparoscopic surgery's shorter recovery times, compared to traditional open procedures, translate to a quicker return to normalcy. Reduced hospital stays and faster resumption of daily activities contribute to a sense of achievement and a swifter escape from the confines of illness.
Mitigating Pain: A Key Contributor to Emotional Well-being
Pain is a formidable adversary in the realm of surgery, often influencing the emotional experience of patients. Laparoscopic surgery's ability to minimize tissue trauma inherently leads to reduced postoperative pain. This diminished pain experience is a cornerstone in shaping a positive psychological response, as patients associate the surgical journey with less suffering and a smoother recovery.
The Positive Feedback Loop:
Laparoscopic surgery creates a positive feedback loop where reduced pain and a faster recovery contribute to an overall improved psychological state. As patients experience a smoother rehabilitation process, their confidence in the efficacy of the procedure grows. This positive reinforcement not only affects the immediate postoperative period but also contributes to a long-term optimistic outlook on health and medical interventions.
The Role of Social Support:
The psychological impact of laparoscopic surgery extends beyond the individual to the broader support network. Family and friends play a pivotal role in providing emotional support. The minimally invasive nature of laparoscopic procedures, with its associated benefits, alleviates the concerns of caregivers and loved ones, fostering a supportive environment conducive to the patient's mental well-being.
Challenges and Coping Strategies:
While laparoscopic surgery offers a host of psychological benefits, it is essential to acknowledge that challenges and stressors may still arise. Potential complications, unexpected outcomes, and the inherent vulnerability associated with any surgery can trigger emotional responses. Coping strategies, such as preoperative counseling, support groups, and ongoing communication with healthcare providers, are crucial in addressing these challenges and promoting resilience.
Conclusion:
Laparoscopic surgery transcends its technical prowess to become a holistic experience that significantly shapes the psychological landscape of patients. From the preoperative anxieties to the postoperative triumphs, the minimally invasive approach touches upon various facets of the human psyche. As medical science continues to advance, understanding and addressing the psychological dimensions of surgery become integral in providing comprehensive healthcare that not only heals the body but also nurtures the mind. Laparoscopic surgery, with its promise of reduced invasiveness and enhanced recovery, stands as a beacon in this evolving paradigm, offering patients not just a surgical solution but a pathway to psychological well-being.