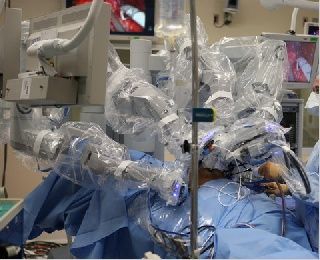
Researchers note that over all, the number of operations increased slightly during the study period, possibly reflecting a plateau in cancer cases or a shift to other treatments. But when the data were examined at the hospital and regional levels, the researchers found that the purchase of a robot was associated with a pronounced change in treatment trends. The findings are concerning because surgical removal of the prostate, called radical prostatectomy, can reduce a number of complications, including incontinence and impotence. Some research suggests the robotic procedure reduces hospital stays and blood loss, compared with regular surgery, The advantages of these systems are many because they overcome many of the obstacles of laparoscopic surgery. They increase dexterity, restore proper hand-eye coordination and an ergonomic position, and improve visualization. In addition, these systems make surgeries that were technically difficult or unfeasible previously, now possible. Another important advantage is the restoration of proper hand-eye coordination and an ergonomic position.
Surgical robots have become increasingly popular in recent years as a tool for performing minimally invasive surgery. These robots use advanced technology to assist surgeons in performing procedures with greater precision and control, leading to improved outcomes for patients. However, the high cost of acquiring and maintaining surgical robots has raised questions about their essentiality in hospital settings. This essay will explore the role of surgical robots in performing minimal access surgery and whether they are essential in hospitals.
Definition of Minimal Access Surgery:
Minimal access surgery (MAS) is a surgical technique that involves making small incisions in the body and using specialized instruments to perform procedures. MAS is also known as laparoscopic surgery, keyhole surgery, or minimally invasive surgery. The goal of MAS is to minimize the trauma to the patient's body, reduce postoperative pain, and speed up recovery times. Common procedures that are performed using MAS include appendectomies, cholecystectomies, hernia repairs, and gastric bypass surgery.
Role of Surgical Robots in Minimal Access Surgery:
Surgical robots are advanced machines that are used to assist surgeons in performing MAS procedures. The robots consist of a console that is operated by the surgeon and a set of robotic arms that are inserted into the patient's body through small incisions. The robotic arms are equipped with specialized instruments that can perform a range of tasks, such as cutting, suturing, and manipulating tissue. The console provides the surgeon with a 3D view of the surgical site and allows them to control the robotic arms with greater precision and accuracy than is possible with traditional laparoscopic instruments.
Surgical robots have several advantages over traditional laparoscopic instruments. These advantages include:
-
Greater Precision: Surgical robots are designed to perform precise movements with greater accuracy than is possible with traditional laparoscopic instruments. This can lead to better outcomes for patients, such as reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times.
-
Improved Visualization: The 3D view provided by the robotic console allows the surgeon to see the surgical site in greater detail than is possible with traditional laparoscopic instruments. This can help the surgeon to identify and avoid important structures, such as blood vessels and nerves, and reduce the risk of complications.
-
Reduced Fatigue: Performing laparoscopic surgery can be physically demanding for surgeons, as they must maintain a fixed position for extended periods of time. Surgical robots can reduce the physical demands on the surgeon by allowing them to sit comfortably at the console while controlling the robotic arms.
-
Better Ergonomics: The design of surgical robots allows for better ergonomics than traditional laparoscopic instruments. The console can be adjusted to the surgeon's height and posture, reducing the risk of musculoskeletal injuries.
Essentiality of Surgical Robots in Hospital Settings:
The high cost of acquiring and maintaining surgical robots has raised questions about their essentiality in hospital settings. Critics argue that the benefits of surgical robots do not justify their high cost and that traditional laparoscopic instruments can achieve similar outcomes at a lower cost. However, proponents of surgical robots argue that they are essential in hospital settings, particularly for performing complex and delicate procedures.
There is evidence to support both arguments. Studies have shown that surgical robots can lead to better outcomes for patients in certain procedures, such as prostatectomies and hysterectomies. However, there is also evidence to suggest that the benefits of surgical robots may be overstated and that traditional laparoscopic instruments can achieve similar outcomes in many cases.
The essentiality of surgical robots in hospital settings may depend on several factors, including the availability of trained surgeons and the types of procedures performed at the hospital. Hospitals that perform a high volume of complex and delicate procedures may find that surgical robots are essential for achieving the best outcomes for patients. However, hospitals thatperform fewer complex procedures may find that traditional laparoscopic instruments are sufficient for achieving good outcomes.
Another factor that may influence the essentiality of surgical robots is the cost-effectiveness of the technology. While surgical robots can lead to better outcomes for patients in certain procedures, they are also expensive to acquire and maintain. Hospitals must weigh the benefits of surgical robots against their costs and determine whether the technology is a cost-effective investment.
In addition to the cost-effectiveness of surgical robots, hospitals must also consider the availability of trained surgeons who can operate the technology. Surgical robots require specialized training, and not all surgeons may be comfortable using the technology. Hospitals must ensure that they have a sufficient number of trained surgeons to operate the robots before investing in the technology.
Conclusion:
Surgical robots have become increasingly popular in recent years as a tool for performing minimally invasive surgery. While the technology offers several advantages over traditional laparoscopic instruments, including greater precision, improved visualization, reduced fatigue, and better ergonomics, the high cost of acquiring and maintaining the robots has raised questions about their essentiality in hospital settings.
The essentiality of surgical robots in hospital settings may depend on several factors, including the availability of trained surgeons, the types of procedures performed at the hospital, and the cost-effectiveness of the technology. While surgical robots can lead to better outcomes for patients in certain procedures, hospitals must carefully consider the costs and benefits of the technology before investing in it.
Overall, surgical robots are a valuable tool for performing minimally invasive surgery and can improve outcomes for patients in certain procedures. However, hospitals must carefully consider the factors that influence their essentiality before investing in the technology. By doing so, hospitals can ensure that they are providing the best possible care for their patients while also being mindful of costs and resources.