The Impact of 3D Imaging on Laparoscopic Surgical Procedures
The Impact of 3D Imaging on Laparoscopic Surgical Procedures
Introduction:
In the realm of medical advancements, the integration of cutting-edge technologies has continually redefined the landscape of surgical procedures. One such groundbreaking innovation making waves in the field of laparoscopic surgery is 3D imaging. This revolutionary technology has ushered in a new era of precision, transforming the way surgeons approach and execute minimally invasive procedures.
Understanding Laparoscopic Surgery:
Before delving into the impact of 3D imaging, it is crucial to grasp the essence of laparoscopic surgery itself. Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery, involves performing procedures through small incisions with the aid of a camera and specialized instruments. This technique offers numerous advantages, including reduced postoperative pain, faster recovery times, and diminished scarring compared to traditional open surgeries.
The Evolution of 3D Imaging:
The roots of 3D imaging in laparoscopic surgery trace back to the advent of traditional two-dimensional (2D) laparoscopic systems. While these systems marked a significant departure from open surgeries, they presented limitations in terms of depth perception and spatial orientation for surgeons. Recognizing the need for improvement, the medical community turned to three-dimensional imaging as a solution.
Early attempts at 3D imaging were met with challenges such as technological constraints and cost barriers. However, with persistent research and development, the technology has matured, and modern 3D laparoscopic systems now offer unparalleled clarity, precision, and depth perception.
Advantages of 3D Imaging in Laparoscopic Surgery:
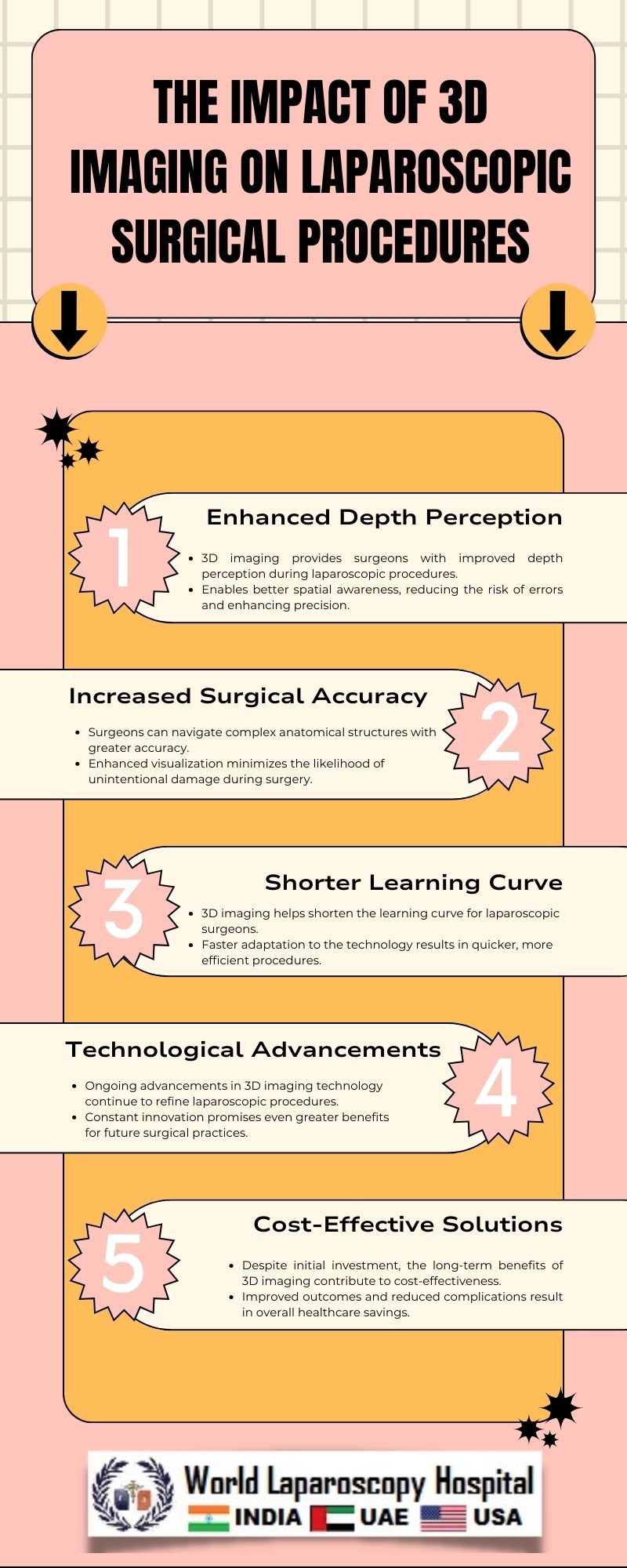
Enhanced Depth Perception:
One of the primary advantages of 3D imaging lies in its ability to provide surgeons with enhanced depth perception. Traditional 2D systems presented a flat representation of the surgical field, making it challenging to accurately gauge the distance between instruments and anatomical structures. With 3D imaging, surgeons can now perceive depth more naturally, facilitating precise manipulation of instruments within confined spaces.
Improved Spatial Orientation:
3D imaging addresses the limitations of spatial orientation inherent in 2D laparoscopic systems. Surgeons can now navigate through complex anatomical structures with greater ease and accuracy, leading to enhanced surgical outcomes. This improvement in spatial awareness is particularly crucial in intricate procedures where precision is paramount.
Optimal Visualization of Anatomy:
The high-definition, three-dimensional visualizations offered by this technology enable surgeons to observe anatomical structures with unprecedented clarity. This level of detail is invaluable, especially in surgeries involving intricate and delicate structures. Surgeons can identify and navigate around vessels, nerves, and other critical structures with enhanced precision, minimizing the risk of inadvertent damage.
Reduced Learning Curve:
3D imaging has been associated with a reduced learning curve for surgeons transitioning from open surgeries to laparoscopic procedures. The intuitive visualizations provided by 3D systems allow for a more seamless adaptation, enhancing the efficiency and confidence of surgeons in performing minimally invasive surgeries.
Enhanced Surgical Training:
The integration of 3D imaging has extended its benefits beyond the operating room, significantly impacting surgical training programs. Trainees can now immerse themselves in a more realistic and detailed surgical environment, honing their skills with a level of precision not previously possible. This translates to better-prepared surgeons entering the workforce.
Challenges and Considerations:
While the advantages of 3D imaging in laparoscopic surgery are substantial, it is essential to acknowledge and address the challenges associated with its implementation.
Cost Considerations:
The initial investment required for 3D laparoscopic systems can be a deterrent for some healthcare institutions. However, as technology advances and becomes more widespread, costs are expected to decrease, making this innovation more accessible.
Technological Integration:
Integrating 3D imaging into existing surgical workflows may pose logistical challenges. Hospitals and surgical teams need to invest in training and infrastructure to seamlessly incorporate this technology into their practices.
Standardization of Technology:
The medical community faces the challenge of standardizing 3D imaging technology to ensure compatibility across different platforms. This is crucial for collaboration and the exchange of expertise among healthcare professionals.
Clinical Applications:
The impact of 3D imaging on laparoscopic surgery extends across various medical specialties, with notable applications in:
Gastrointestinal Surgery:
In procedures such as laparoscopic colorectal surgery, where precise dissection and suturing are critical, 3D imaging significantly improves visualization. Surgeons can navigate through the complex anatomy of the gastrointestinal tract with enhanced precision, leading to better outcomes for patients.
Gynecological Surgery:
Gynecological procedures, including hysterectomies and ovarian surgeries, benefit from the improved depth perception provided by 3D imaging. Surgeons can navigate delicate structures with increased accuracy, reducing the risk of complications.
Urological Surgery:
3D imaging has proven invaluable in urological procedures, such as laparoscopic prostate surgery and nephrectomies. Enhanced visualization allows for meticulous dissection and reconstruction, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
Cardiothoracic Surgery:
Even in the realm of cardiothoracic surgery, where the complexity of the anatomy demands precision, 3D imaging has found applications. Surgeons can navigate the intricacies of the heart and lungs with improved spatial awareness, contributing to safer and more effective procedures.
Future Directions and Innovations:
The evolution of 3D imaging in laparoscopic surgery is far from stagnant, with ongoing research and development paving the way for further innovations. Some potential future directions include:
Augmented Reality Integration:
The integration of augmented reality (AR) into 3D laparoscopic systems holds promise for providing surgeons with real-time, interactive information during procedures. This could include overlaying patient-specific data, enhancing decision-making in the operating room.
Haptic Feedback Technology:
Incorporating haptic feedback technology into 3D systems could further improve the surgeon's sense of touch during minimally invasive procedures. This innovation has the potential to make laparoscopic surgery even more intuitive and responsive.
Artificial Intelligence Assistance:
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms into 3D imaging systems could assist surgeons by providing real-time feedback and predictive analytics. This could enhance precision, reduce errors, and contribute to improved patient outcomes.
Conclusion:
The impact of 3D imaging on laparoscopic surgical procedures is nothing short of transformative. As technology continues to advance, surgeons are equipped with powerful tools that enhance their ability to provide precise, minimally invasive interventions. The benefits extend beyond the operating room, influencing surgical training and setting new standards for patient care. While challenges persist, the ongoing evolution of 3D imaging holds the promise of further revolutionizing the field of laparoscopic surgery, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike.
Top
Introduction:
In the realm of medical advancements, the integration of cutting-edge technologies has continually redefined the landscape of surgical procedures. One such groundbreaking innovation making waves in the field of laparoscopic surgery is 3D imaging. This revolutionary technology has ushered in a new era of precision, transforming the way surgeons approach and execute minimally invasive procedures.

Understanding Laparoscopic Surgery:
Before delving into the impact of 3D imaging, it is crucial to grasp the essence of laparoscopic surgery itself. Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery, involves performing procedures through small incisions with the aid of a camera and specialized instruments. This technique offers numerous advantages, including reduced postoperative pain, faster recovery times, and diminished scarring compared to traditional open surgeries.
The Evolution of 3D Imaging:
The roots of 3D imaging in laparoscopic surgery trace back to the advent of traditional two-dimensional (2D) laparoscopic systems. While these systems marked a significant departure from open surgeries, they presented limitations in terms of depth perception and spatial orientation for surgeons. Recognizing the need for improvement, the medical community turned to three-dimensional imaging as a solution.
Early attempts at 3D imaging were met with challenges such as technological constraints and cost barriers. However, with persistent research and development, the technology has matured, and modern 3D laparoscopic systems now offer unparalleled clarity, precision, and depth perception.
Advantages of 3D Imaging in Laparoscopic Surgery:
Enhanced Depth Perception:
One of the primary advantages of 3D imaging lies in its ability to provide surgeons with enhanced depth perception. Traditional 2D systems presented a flat representation of the surgical field, making it challenging to accurately gauge the distance between instruments and anatomical structures. With 3D imaging, surgeons can now perceive depth more naturally, facilitating precise manipulation of instruments within confined spaces.
Improved Spatial Orientation:
3D imaging addresses the limitations of spatial orientation inherent in 2D laparoscopic systems. Surgeons can now navigate through complex anatomical structures with greater ease and accuracy, leading to enhanced surgical outcomes. This improvement in spatial awareness is particularly crucial in intricate procedures where precision is paramount.
Optimal Visualization of Anatomy:
The high-definition, three-dimensional visualizations offered by this technology enable surgeons to observe anatomical structures with unprecedented clarity. This level of detail is invaluable, especially in surgeries involving intricate and delicate structures. Surgeons can identify and navigate around vessels, nerves, and other critical structures with enhanced precision, minimizing the risk of inadvertent damage.
Reduced Learning Curve:
3D imaging has been associated with a reduced learning curve for surgeons transitioning from open surgeries to laparoscopic procedures. The intuitive visualizations provided by 3D systems allow for a more seamless adaptation, enhancing the efficiency and confidence of surgeons in performing minimally invasive surgeries.
Enhanced Surgical Training:
The integration of 3D imaging has extended its benefits beyond the operating room, significantly impacting surgical training programs. Trainees can now immerse themselves in a more realistic and detailed surgical environment, honing their skills with a level of precision not previously possible. This translates to better-prepared surgeons entering the workforce.
Challenges and Considerations:
While the advantages of 3D imaging in laparoscopic surgery are substantial, it is essential to acknowledge and address the challenges associated with its implementation.
Cost Considerations:
The initial investment required for 3D laparoscopic systems can be a deterrent for some healthcare institutions. However, as technology advances and becomes more widespread, costs are expected to decrease, making this innovation more accessible.
Technological Integration:
Integrating 3D imaging into existing surgical workflows may pose logistical challenges. Hospitals and surgical teams need to invest in training and infrastructure to seamlessly incorporate this technology into their practices.
Standardization of Technology:
The medical community faces the challenge of standardizing 3D imaging technology to ensure compatibility across different platforms. This is crucial for collaboration and the exchange of expertise among healthcare professionals.
Clinical Applications:
The impact of 3D imaging on laparoscopic surgery extends across various medical specialties, with notable applications in:
Gastrointestinal Surgery:
In procedures such as laparoscopic colorectal surgery, where precise dissection and suturing are critical, 3D imaging significantly improves visualization. Surgeons can navigate through the complex anatomy of the gastrointestinal tract with enhanced precision, leading to better outcomes for patients.
Gynecological Surgery:
Gynecological procedures, including hysterectomies and ovarian surgeries, benefit from the improved depth perception provided by 3D imaging. Surgeons can navigate delicate structures with increased accuracy, reducing the risk of complications.
Urological Surgery:
3D imaging has proven invaluable in urological procedures, such as laparoscopic prostate surgery and nephrectomies. Enhanced visualization allows for meticulous dissection and reconstruction, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
Cardiothoracic Surgery:
Even in the realm of cardiothoracic surgery, where the complexity of the anatomy demands precision, 3D imaging has found applications. Surgeons can navigate the intricacies of the heart and lungs with improved spatial awareness, contributing to safer and more effective procedures.
Future Directions and Innovations:
The evolution of 3D imaging in laparoscopic surgery is far from stagnant, with ongoing research and development paving the way for further innovations. Some potential future directions include:
Augmented Reality Integration:
The integration of augmented reality (AR) into 3D laparoscopic systems holds promise for providing surgeons with real-time, interactive information during procedures. This could include overlaying patient-specific data, enhancing decision-making in the operating room.
Haptic Feedback Technology:
Incorporating haptic feedback technology into 3D systems could further improve the surgeon's sense of touch during minimally invasive procedures. This innovation has the potential to make laparoscopic surgery even more intuitive and responsive.
Artificial Intelligence Assistance:
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms into 3D imaging systems could assist surgeons by providing real-time feedback and predictive analytics. This could enhance precision, reduce errors, and contribute to improved patient outcomes.
Conclusion:
The impact of 3D imaging on laparoscopic surgical procedures is nothing short of transformative. As technology continues to advance, surgeons are equipped with powerful tools that enhance their ability to provide precise, minimally invasive interventions. The benefits extend beyond the operating room, influencing surgical training and setting new standards for patient care. While challenges persist, the ongoing evolution of 3D imaging holds the promise of further revolutionizing the field of laparoscopic surgery, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike.