Navigating Complications in Laparoscopic Surgery
Navigating Complications in Laparoscopic Surgery
Introduction
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, has revolutionized the field of surgical interventions. With its smaller incisions, reduced scarring, and faster recovery times, laparoscopy has become a preferred choice for many patients and surgeons alike. However, like any medical procedure, laparoscopic surgery is not without its challenges. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of navigating complications in laparoscopic surgery, exploring the common hurdles faced by surgeons and the strategies employed to overcome them.
Understanding the Basics of Laparoscopic Surgery
Before we explore complications, it's essential to understand the fundamentals of laparoscopic surgery. This technique involves making small incisions through which a camera and specialized instruments are inserted. The surgeon views the internal organs on a monitor, guiding the instruments to perform the necessary procedures. While laparoscopy offers numerous benefits, such as decreased postoperative pain and shorter hospital stays, it requires a high level of skill and precision.
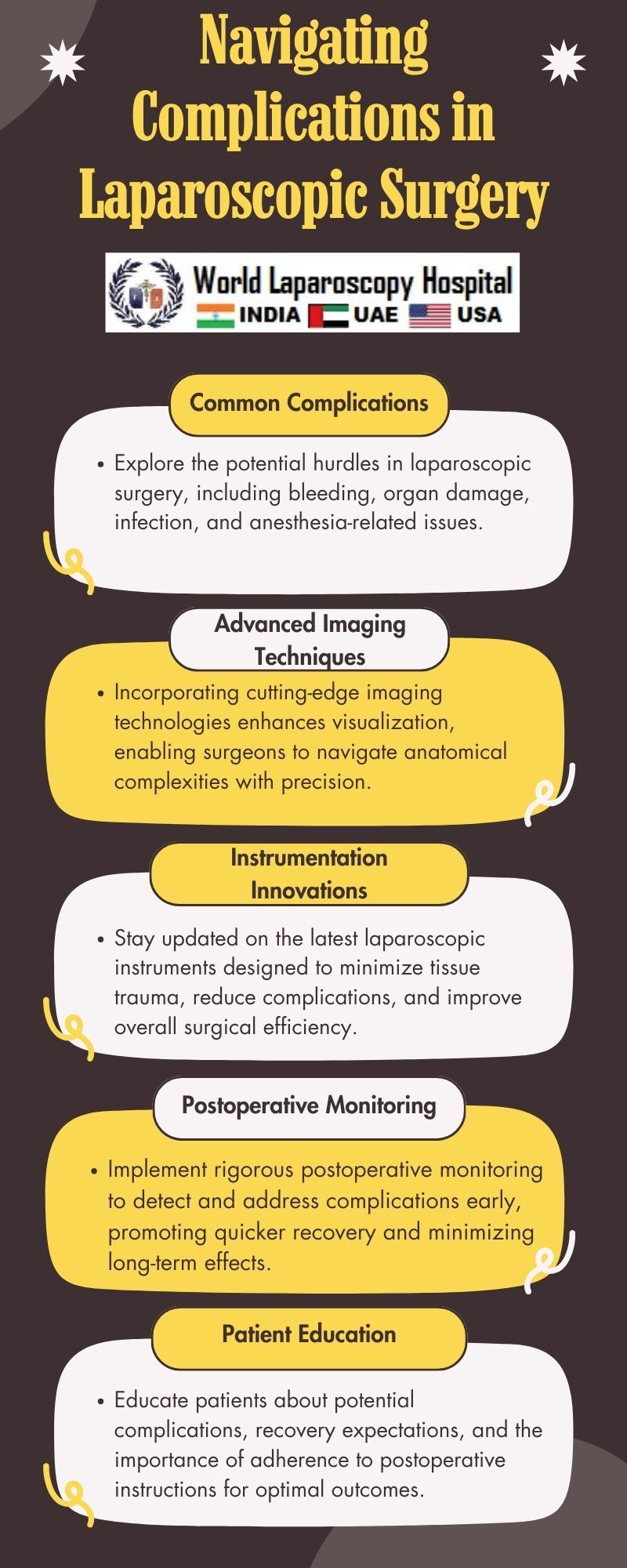
Common Complications in Laparoscopic Surgery
Instrument Limitations:
Laparoscopic instruments are designed to replicate the movements of the surgeon's hand within the confined space of the body. However, these instruments have limitations in terms of range of motion and tactile feedback. Surgeons must adapt to these constraints, often requiring advanced training and experience.
Anatomical Variations:
Human anatomy can vary significantly from person to person. Surgeons may encounter unexpected anatomical structures or variations that were not apparent in preoperative imaging. Adapting to these variations during surgery is crucial to avoid complications.
Bleeding:
Unforeseen bleeding can occur during laparoscopic procedures, necessitating quick and precise responses. The limited field of vision in laparoscopy makes it challenging to identify and control bleeding compared to traditional open surgery. Surgeons must be adept at using hemostatic techniques and have a thorough understanding of vascular anatomy.
Pneumoperitoneum-related Complications:
Creating a pneumoperitoneum, which involves inflating the abdominal cavity with carbon dioxide, is a necessary step in laparoscopic surgery. However, this can lead to complications such as subcutaneous emphysema, pneumothorax, and changes in cardiovascular dynamics. Monitoring and managing these complications are crucial for patient safety.
Infection Risk:
Despite the minimally invasive nature of laparoscopy, the risk of infection remains. Proper sterile techniques, careful handling of instruments, and meticulous closure of incisions are essential to minimize this risk.
Strategies for Navigating Complications
Comprehensive Training:
Surgeons must undergo rigorous training in laparoscopic techniques. Simulated training environments, virtual reality simulations, and hands-on practice with laparoscopic trainers can help improve skills and familiarity with instrument handling.
Preoperative Planning:
Thorough preoperative planning, including a careful review of imaging studies, helps surgeons anticipate potential challenges. Understanding the patient's anatomy and identifying potential variations allows for better preparedness during surgery.
Effective Communication:
Laparoscopic surgery is often performed by a team of surgeons, nurses, and other healthcare professionals. Clear and effective communication among team members is essential for coordinated efforts in managing complications as they arise.
Continuous Monitoring:
Vigilant monitoring of the patient's vital signs and physiological parameters during surgery is crucial. Early detection of complications allows for prompt intervention and mitigates potential adverse outcomes.
Adaptability and Problem-solving Skills:
Laparoscopic surgeons must be adaptable and possess strong problem-solving skills. The ability to quickly assess a situation, identify the root cause of a complication, and implement corrective measures is vital for success.
Postoperative Care and Follow-up:
A comprehensive postoperative care plan is essential for ensuring a smooth recovery. Regular follow-up visits allow surgeons to monitor for any delayed complications and address patient concerns.
Case Studies: Learning from Experience
To further illustrate the complexities of navigating complications in laparoscopic surgery, let's explore a few case studies:
Unexpected Anatomical Variation
During a laparoscopic cholecystectomy, the surgeon encountered an unexpected variation in the patient's biliary anatomy. With a thorough understanding of biliary anatomy and the ability to adapt the surgical plan, the surgeon successfully completed the procedure without complications.
Managing Bleeding in Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
In a laparoscopic hysterectomy, the surgeon encountered unexpected bleeding from a uterine artery. The use of advanced hemostatic techniques, quick decision-making, and collaboration with the surgical team allowed the surgeon to control the bleeding and complete the procedure successfully.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgery offers numerous advantages, but mastering it requires a combination of skill, training, and adaptability. Navigating complications in laparoscopic surgery is an ongoing challenge that demands continuous learning and improvement. Surgeons who embrace these challenges, invest in comprehensive training, and employ effective strategies for managing complications contribute to the continued success and evolution of laparoscopic surgery. As technology advances and surgical techniques evolve, the field of laparoscopy will undoubtedly continue to thrive, offering patients safer and more efficient surgical options.
Top
Introduction
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, has revolutionized the field of surgical interventions. With its smaller incisions, reduced scarring, and faster recovery times, laparoscopy has become a preferred choice for many patients and surgeons alike. However, like any medical procedure, laparoscopic surgery is not without its challenges. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of navigating complications in laparoscopic surgery, exploring the common hurdles faced by surgeons and the strategies employed to overcome them.

Understanding the Basics of Laparoscopic Surgery
Before we explore complications, it's essential to understand the fundamentals of laparoscopic surgery. This technique involves making small incisions through which a camera and specialized instruments are inserted. The surgeon views the internal organs on a monitor, guiding the instruments to perform the necessary procedures. While laparoscopy offers numerous benefits, such as decreased postoperative pain and shorter hospital stays, it requires a high level of skill and precision.
Common Complications in Laparoscopic Surgery
Instrument Limitations:
Laparoscopic instruments are designed to replicate the movements of the surgeon's hand within the confined space of the body. However, these instruments have limitations in terms of range of motion and tactile feedback. Surgeons must adapt to these constraints, often requiring advanced training and experience.
Anatomical Variations:
Human anatomy can vary significantly from person to person. Surgeons may encounter unexpected anatomical structures or variations that were not apparent in preoperative imaging. Adapting to these variations during surgery is crucial to avoid complications.
Bleeding:
Unforeseen bleeding can occur during laparoscopic procedures, necessitating quick and precise responses. The limited field of vision in laparoscopy makes it challenging to identify and control bleeding compared to traditional open surgery. Surgeons must be adept at using hemostatic techniques and have a thorough understanding of vascular anatomy.
Pneumoperitoneum-related Complications:
Creating a pneumoperitoneum, which involves inflating the abdominal cavity with carbon dioxide, is a necessary step in laparoscopic surgery. However, this can lead to complications such as subcutaneous emphysema, pneumothorax, and changes in cardiovascular dynamics. Monitoring and managing these complications are crucial for patient safety.
Infection Risk:
Despite the minimally invasive nature of laparoscopy, the risk of infection remains. Proper sterile techniques, careful handling of instruments, and meticulous closure of incisions are essential to minimize this risk.
Strategies for Navigating Complications
Comprehensive Training:
Surgeons must undergo rigorous training in laparoscopic techniques. Simulated training environments, virtual reality simulations, and hands-on practice with laparoscopic trainers can help improve skills and familiarity with instrument handling.
Preoperative Planning:
Thorough preoperative planning, including a careful review of imaging studies, helps surgeons anticipate potential challenges. Understanding the patient's anatomy and identifying potential variations allows for better preparedness during surgery.
Effective Communication:
Laparoscopic surgery is often performed by a team of surgeons, nurses, and other healthcare professionals. Clear and effective communication among team members is essential for coordinated efforts in managing complications as they arise.
Continuous Monitoring:
Vigilant monitoring of the patient's vital signs and physiological parameters during surgery is crucial. Early detection of complications allows for prompt intervention and mitigates potential adverse outcomes.
Adaptability and Problem-solving Skills:
Laparoscopic surgeons must be adaptable and possess strong problem-solving skills. The ability to quickly assess a situation, identify the root cause of a complication, and implement corrective measures is vital for success.
Postoperative Care and Follow-up:
A comprehensive postoperative care plan is essential for ensuring a smooth recovery. Regular follow-up visits allow surgeons to monitor for any delayed complications and address patient concerns.
Case Studies: Learning from Experience
To further illustrate the complexities of navigating complications in laparoscopic surgery, let's explore a few case studies:
Unexpected Anatomical Variation
During a laparoscopic cholecystectomy, the surgeon encountered an unexpected variation in the patient's biliary anatomy. With a thorough understanding of biliary anatomy and the ability to adapt the surgical plan, the surgeon successfully completed the procedure without complications.
Managing Bleeding in Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
In a laparoscopic hysterectomy, the surgeon encountered unexpected bleeding from a uterine artery. The use of advanced hemostatic techniques, quick decision-making, and collaboration with the surgical team allowed the surgeon to control the bleeding and complete the procedure successfully.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgery offers numerous advantages, but mastering it requires a combination of skill, training, and adaptability. Navigating complications in laparoscopic surgery is an ongoing challenge that demands continuous learning and improvement. Surgeons who embrace these challenges, invest in comprehensive training, and employ effective strategies for managing complications contribute to the continued success and evolution of laparoscopic surgery. As technology advances and surgical techniques evolve, the field of laparoscopy will undoubtedly continue to thrive, offering patients safer and more efficient surgical options.