Leading the Charge: How Laparoscopy is Transforming Surgical Practices
Title: Leading the Charge: Laparoscopy's Revolutionary Impact on Surgical Practices
Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of medical science, laparoscopy has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping traditional surgical practices. This minimally invasive technique, also known as keyhole surgery, involves making small incisions through which a camera-equipped instrument is inserted, allowing surgeons to visualize and perform procedures internally. Over the years, laparoscopy has become the gold standard in various surgical specialties, revolutionizing patient care and outcomes.
Historical Perspective:
The roots of laparoscopy can be traced back to the early 20th century when the first attempts at exploring the abdominal cavity were made. However, it wasn't until the mid-20th century that technological advancements allowed for significant progress. The introduction of fiber optics and camera systems in the 1970s paved the way for the modern era of laparoscopy.
Key Components of Laparoscopy:
Laparoscopic procedures typically involve three key components: a laparoscope (camera), specialized instruments, and insufflation. The laparoscope, a thin tube with a light and camera on the end, provides high-quality visualization of the surgical site. Specialized instruments designed for precise movements are inserted through additional small incisions. Insufflation involves inflating the abdominal cavity with gas (usually carbon dioxide) to create a workspace for the surgeon.
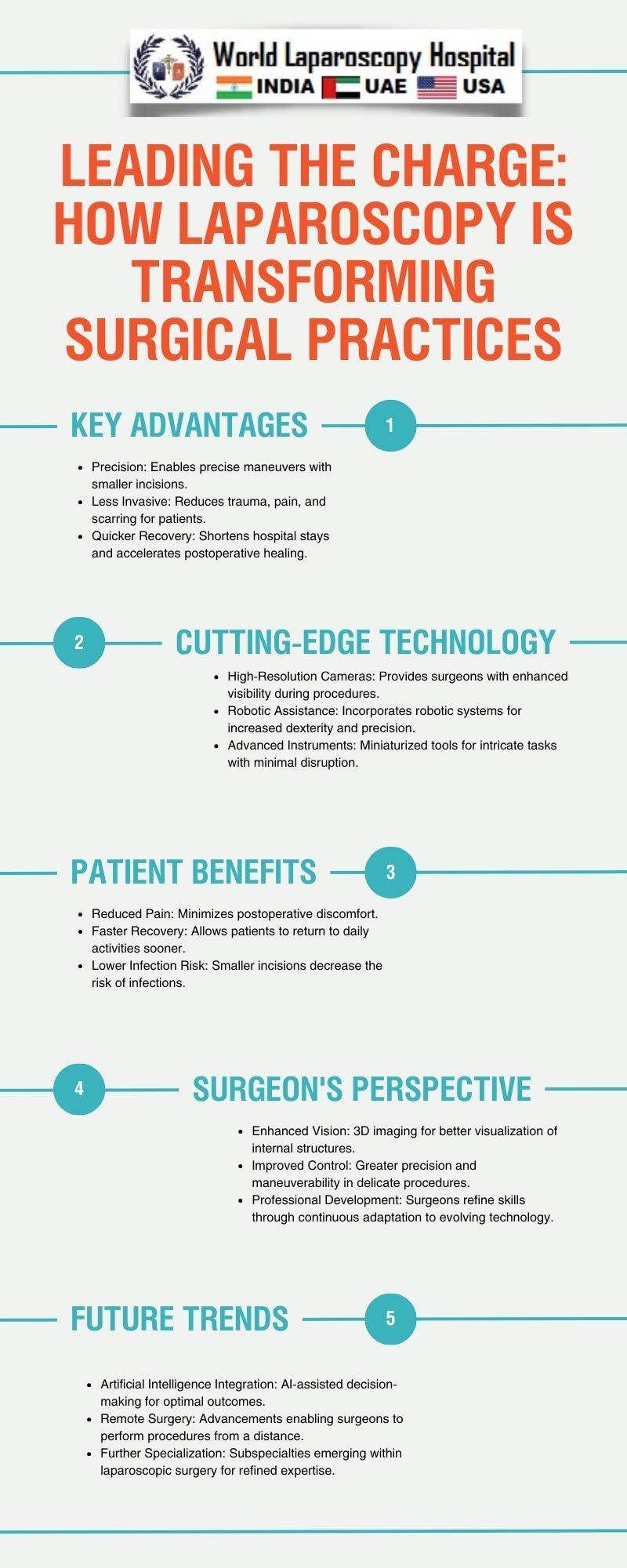
Advantages of Laparoscopy:
Minimally Invasive:
Unlike traditional open surgery, laparoscopy requires only small incisions, reducing trauma to surrounding tissues. This results in less pain and a quicker recovery for patients.
Reduced Blood Loss:
The minimally invasive nature of laparoscopy contributes to decreased blood loss during surgery, lowering the risk of complications and the need for blood transfusions.
Shorter Hospital Stays:
Patients undergoing laparoscopic procedures often experience shorter hospital stays compared to those undergoing traditional surgery, leading to cost savings and improved resource utilization.
Faster Recovery:
The smaller incisions and reduced trauma allow for faster recovery times, enabling patients to return to their normal activities sooner.
Cosmetic Benefits:
The smaller incisions result in minimal scarring, providing both physical and psychological benefits for patients concerned about the aesthetic aspects of surgery.
Applications Across Surgical Specialties:
Laparoscopy's impact extends across various surgical disciplines, including:
Gastrointestinal Surgery:
Laparoscopy is widely employed for procedures such as cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal), appendectomy, and colorectal surgeries. The technique has proven particularly effective in managing conditions like diverticulitis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Gynecology:
In gynecological surgery, laparoscopy has become instrumental in procedures like hysterectomy, ovarian cyst removal, and tubal ligation. Its use in the field has significantly reduced postoperative pain and shortened recovery times for patients.
Urology: Laparoscopic techniques are applied in urological surgeries, including nephrectomy (kidney removal), prostatectomy, and cystectomy. The precision offered by laparoscopic instruments enhances outcomes while minimizing the impact on surrounding organs.
Orthopedics:
Though traditionally associated with soft tissue surgeries, laparoscopy is making inroads into orthopedic procedures. Joint surgeries and arthroscopic interventions benefit from the minimally invasive approach, leading to quicker rehabilitation and less joint trauma.
Cardiothoracic Surgery:
Laparoscopy is also making strides in cardiothoracic surgery, with minimally invasive procedures for conditions such as mitral valve repair, coronary artery bypass, and thoracic sympathectomy. These approaches offer reduced postoperative pain and faster recovery for patients.
Challenges and Considerations:
While laparoscopy has transformed surgical practices, it is not without challenges. The learning curve for surgeons transitioning from open to laparoscopic techniques can be steep. Additionally, equipment costs and the need for specialized training contribute to initial barriers. Patient selection is crucial, and not all cases are suitable for laparoscopy. However, ongoing advancements in technology and increased training opportunities are gradually addressing these challenges.
Future Directions:
As technology continues to advance, the future of laparoscopy holds even more promise. Robotics, augmented reality, and artificial intelligence are being integrated into laparoscopic systems, enhancing precision and expanding the range of feasible procedures. The development of miniaturized instruments and improved imaging systems will further refine the capabilities of laparoscopy.
Conclusion:
Laparoscopy's transformative impact on surgical practices is undeniable. From its humble beginnings to its current status as a standard in various surgical specialties, this minimally invasive technique has redefined patient care. The benefits of reduced invasiveness, quicker recovery times, and improved outcomes position laparoscopy as a cornerstone of modern surgery. As technology continues to propel the field forward, the ongoing evolution of laparoscopy promises a future where surgical interventions are not only effective but increasingly patient-centric.
