Inside Laparoscopic Surgery: The Technique That’s Changing Medicine
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of medical advancements, laparoscopic surgery stands out as a transformative technique that has redefined the way surgical procedures are conducted. This minimally invasive approach has gained widespread recognition and is changing the face of medicine. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of laparoscopic surgery, exploring its history, techniques, applications across medical specialties, advantages, challenges, and the potential future developments.
Historical Perspective
The roots of laparoscopic surgery can be traced back to the early 20th century, but it wasn't until the 1980s that the technique gained prominence. The first laparoscopic cholecystectomy, the removal of the gallbladder, was performed by Dr. Erich Mühe in Germany in 1985. This groundbreaking procedure marked the beginning of a new era in surgery.
Techniques and Instruments
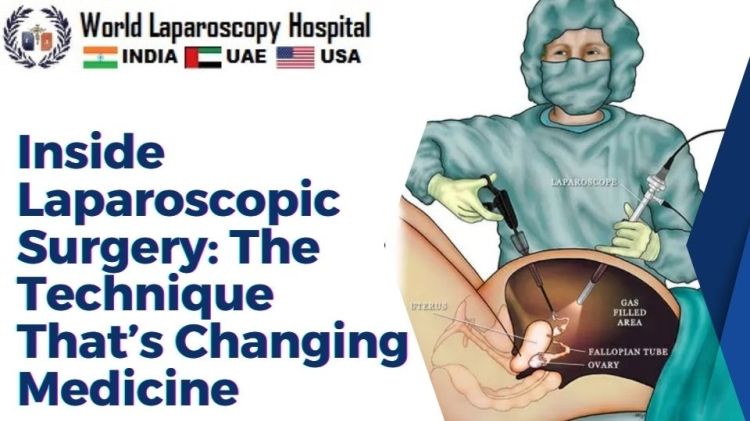
Laparoscopic surgery, often referred to as minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery, involves making small incisions through which a laparoscope – a thin tube with a light and camera – is inserted. This provides real-time visualization of the internal organs on a monitor. Additionally, specialized instruments are introduced through other small incisions to carry out the surgical procedure.
The key instruments used in laparoscopic surgery include trocars for creating access ports, graspers for holding and manipulating tissues, scissors and dissectors for cutting and separating tissues, and staplers for sealing blood vessels or tissues. The surgeon maneuvers these instruments with precision, guided by the visual feed from the laparoscope.
Applications Across Medical Specialties
Laparoscopic surgery has expanded its reach across various medical specialties, revolutionizing the way a wide range of procedures are performed. Some notable applications include:
Gastrointestinal Surgery:
Laparoscopic techniques are commonly employed in procedures such as cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal), appendectomy, and bariatric surgery. The reduced trauma to abdominal muscles results in quicker recovery times for patients.
Gynecological Surgery:
In gynecology, laparoscopy is used for procedures such as hysterectomy, ovarian cyst removal, and tubal ligation. The minimally invasive approach is particularly beneficial for reducing scarring and postoperative pain.
Urological Surgery:
Laparoscopic techniques are applied in urology for procedures like nephrectomy (kidney removal), prostatectomy, and pyeloplasty. This approach minimizes blood loss and accelerates patient recovery.
Orthopedic Surgery:
While traditionally associated with abdominal procedures, laparoscopic techniques are now making inroads into orthopedic surgery, offering minimally invasive options for joint surgeries and spinal procedures.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Surgery
The widespread adoption of laparoscopic surgery can be attributed to its numerous advantages over traditional open surgery. Some key benefits include:
Minimized Trauma:
The smaller incisions used in laparoscopic surgery result in reduced trauma to surrounding tissues and muscles. This contributes to less postoperative pain and a quicker recovery.
Faster Recovery Times:
Patients undergoing laparoscopic procedures typically experience shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times compared to open surgery. This is especially crucial in promoting early mobilization and reducing the risk of complications.
Reduced Blood Loss:
The precision of laparoscopic instruments and the ability to visualize blood vessels more clearly contribute to minimized blood loss during surgery.
Cosmetic Benefits:
The smaller incisions leave minimal scars, providing cosmetic advantages for patients concerned about the aesthetic impact of surgery.
Challenges and Considerations
While laparoscopic surgery has revolutionized the field of surgery, it is not without challenges. Some notable considerations include:
Steep Learning Curve:
Mastering laparoscopic techniques requires specialized training and a steep learning curve for surgeons. The hand-eye coordination needed to manipulate instruments in a three-dimensional space differs from that in open surgery.
Equipment Costs:
The initial costs associated with laparoscopic equipment and technology can be substantial. However, proponents argue that the long-term benefits in terms of patient outcomes and reduced hospital stays justify these investments.
Not Applicable to All Cases:
While laparoscopic surgery is suitable for a wide range of procedures, there are instances where open surgery remains the preferred option. Emergency cases, extensive adhesions, or certain complex procedures may necessitate an open approach.
Limited Haptic Feedback:
One of the challenges in laparoscopic surgery is the lack of haptic feedback, the sense of touch, which is available in open surgery. Surgeons rely on visual cues and must develop a heightened sense of awareness to compensate for this limitation.
Future Developments and Innovations
As technology continues to advance, the future of laparoscopic surgery holds exciting possibilities. Some areas of innovation and development include:
Robot-Assisted Laparoscopy:
Robotic systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, are increasingly being used to enhance the capabilities of laparoscopic surgery. These systems provide improved dexterity and precision, allowing for more complex procedures.
Augmented Reality:
The integration of augmented reality into laparoscopic surgery may provide surgeons with enhanced visualization and navigation capabilities. This could improve surgical accuracy and reduce the learning curve for less experienced surgeons.
Miniaturized Instruments:
Ongoing efforts to miniaturize laparoscopic instruments aim to further reduce the invasiveness of the procedure. Smaller instruments could enable surgeons to perform delicate procedures with even less tissue disruption.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI applications in laparoscopic surgery include image recognition, decision support, and predictive analytics. These technologies could assist surgeons in real-time decision-making and contribute to improved outcomes.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgery has emerged as a revolutionary technique that continues to reshape the landscape of modern medicine. Its applications span across various medical specialties, offering patients less invasive options and faster recovery times. While challenges exist, ongoing technological advancements and innovations are paving the way for an even more refined and efficient approach to surgery. As the field evolves, the future holds the promise of further enhancing the capabilities of laparoscopic surgery, ultimately benefiting patients and surgeons alike.