Innovation in the OR: The Promising Future of Laparoscopic Surgery
Introduction
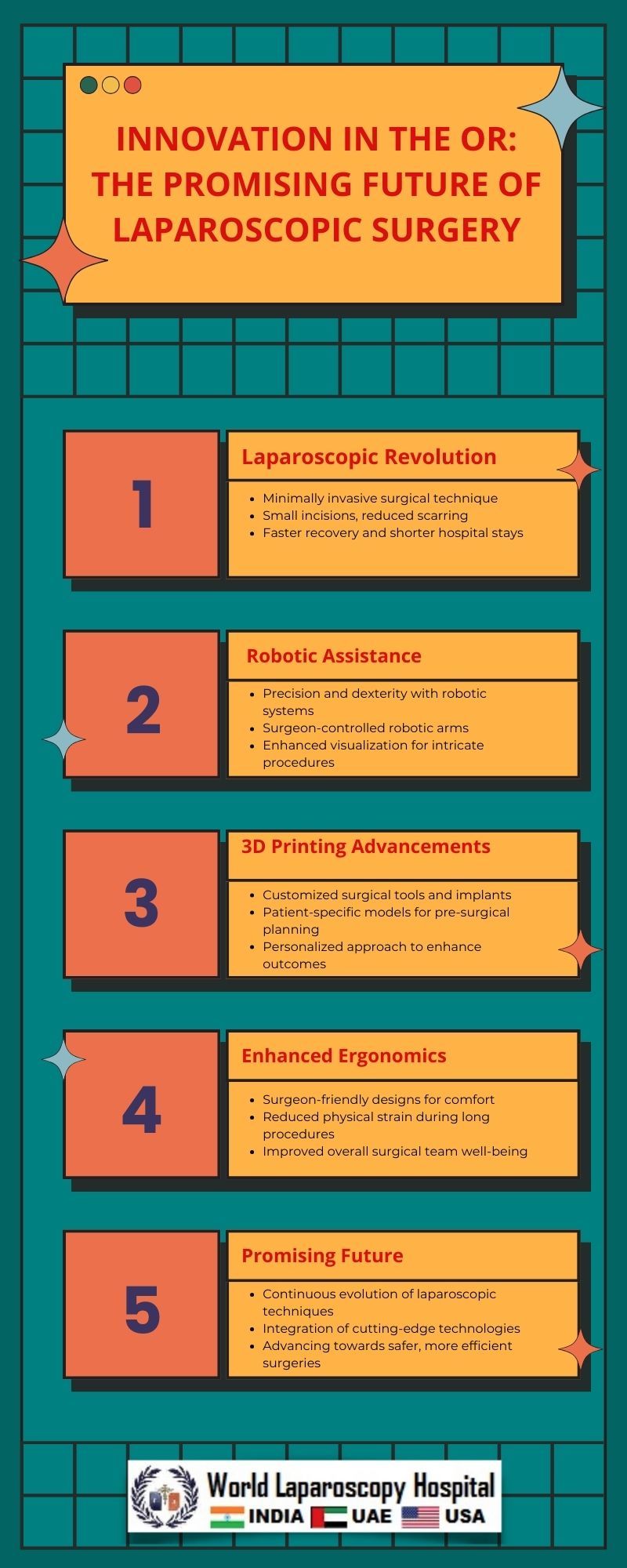
In the ever-evolving realm of medical science, laparoscopic surgery stands as a beacon of innovation, offering a promising future for the operating room (OR). This minimally invasive surgical technique has witnessed remarkable advancements in recent years, reshaping the landscape of traditional surgical practices. As we delve into the intricate world of laparoscopic surgery, this article explores the historical roots, technological breakthroughs, current applications, and the potential future developments that herald a new era in surgical precision and patient care.
The Genesis of Laparoscopic Surgery
The origins of laparoscopic surgery trace back to the mid-20th century, with its conceptualization credited to the pioneering work of George Kelling, a German surgeon, and Dimitri Ott, a Russian gynecologist. However, it was not until the 1980s that laparoscopy gained widespread recognition, primarily due to the groundbreaking efforts of Philippe Mouret, a French gynecologist, who performed the first laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
The advent of video technology in the 1990s further propelled laparoscopic surgery into mainstream medical practice, allowing surgeons to visualize and manipulate internal organs with unprecedented clarity. This marked a pivotal moment, laying the foundation for the transformative journey that laparoscopic surgery was about to embark upon.
Technological Breakthroughs
High-Definition Imaging:
One of the key catalysts for the evolution of laparoscopic surgery has been the integration of high-definition imaging systems. Traditional laparoscopy often faced challenges related to limited visibility and depth perception. With the advent of high-definition cameras and monitors, surgeons can now navigate with enhanced clarity, discerning intricate details and facilitating more precise maneuvers.
Robot-Assisted Laparoscopy:
The marriage of robotics and laparoscopic surgery has given rise to robot-assisted systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System. These platforms provide surgeons with advanced robotic arms, equipped with tiny instruments and cameras, offering unparalleled dexterity and control. The surgeon, operating from a console, can execute complex procedures with precision, further minimizing invasiveness and improving patient outcomes.
Miniaturization of Instruments:
As technology advances, so does the miniaturization of surgical instruments. Smaller, more refined tools enable surgeons to perform intricate procedures through tiny incisions, reducing trauma to surrounding tissues. This not only expedites patient recovery but also diminishes the risk of complications.
Current Applications and Advantages
Laparoscopic surgery has transcended its initial applications and is now employed across various medical disciplines, including gynecology, urology, gastroenterology, and general surgery. Some of the commonly performed laparoscopic procedures include cholecystectomy, appendectomy, colectomy, and hysterectomy.
Cholecystectomy:
Gallbladder removal through laparoscopic cholecystectomy has become the gold standard for treating gallstones. Compared to traditional open surgery, this approach results in shorter hospital stays, reduced postoperative pain, and quicker return to normal activities.
Appendectomy:
Laparoscopic appendectomy has revolutionized the treatment of appendicitis. The minimally invasive approach significantly decreases the risk of postoperative complications, accelerates recovery, and provides a cosmetically superior outcome compared to open surgery.
Colectomy:
Laparoscopic colectomy, involving the removal of a portion of the colon, has gained popularity for conditions such as colorectal cancer and inflammatory bowel disease. Patients undergoing laparoscopic colectomy often experience less pain, a shorter hospital stay, and faster recovery compared to open procedures.
Hysterectomy:
In gynecology, laparoscopic hysterectomy has emerged as a preferred option for the removal of the uterus. This approach reduces scarring, lowers the risk of infection, and allows for a quicker return to normal activities.
The advantages of laparoscopic surgery are multifaceted. Patients benefit from smaller incisions, reduced postoperative pain, decreased blood loss, and shorter hospital stays. Additionally, the cosmetic outcome is often superior, with minimal scarring. Surgeons appreciate the enhanced visualization and dexterity afforded by laparoscopic techniques, enabling them to perform complex procedures with greater precision.
The Future Landscape
The trajectory of laparoscopic surgery indicates a future filled with continued innovation and expanded applications. Several trends and developments are poised to shape the landscape of minimally invasive surgery in the coming years.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration:
The integration of artificial intelligence into laparoscopic surgery holds immense potential. AI algorithms can assist surgeons in real-time by analyzing imaging data, providing insights, and even recommending optimal pathways for procedures. This collaboration between human skill and artificial intelligence has the potential to elevate the precision and safety of laparoscopic surgery to unprecedented levels.
Augmented Reality (AR) in the Operating Room:
Augmented reality is on the horizon of OR innovation, offering surgeons an immersive experience during laparoscopic procedures. AR overlays digital information onto the surgeon's field of view, enhancing spatial awareness and procedural guidance. This technology has the potential to revolutionize training programs, as well as improve the efficiency and outcomes of laparoscopic surgeries.
Single-Incision Laparoscopy:
The quest for further reducing invasiveness has led to the exploration of single-incision laparoscopy, where multiple instruments are introduced through a single access point. This technique aims to minimize scarring and enhance cosmetic outcomes while maintaining the benefits of traditional laparoscopy.
Remote Surgery:
Advancements in communication technology may pave the way for remote or telesurgery. Surgeons could potentially perform laparoscopic procedures from a distant location, utilizing robotic systems and high-speed internet connections. This could revolutionize access to specialized surgical expertise, especially in remote or underserved areas.
Challenges and Considerations
While the future of laparoscopic surgery appears promising, it is essential to address challenges and considerations to ensure the responsible and ethical integration of these innovations.
Learning Curve:
The adoption of new technologies, such as robot-assisted systems, comes with a learning curve for surgeons. Comprehensive training programs are crucial to ensure that practitioners can harness the full potential of these innovations while maintaining patient safety.
Cost Implications:
The initial costs associated with acquiring and implementing advanced laparoscopic technologies, such as robotic systems, can be substantial. Health systems and institutions must carefully consider the cost-effectiveness and long-term benefits of these investments.
Ethical and Legal Considerations:
As technology advances, ethical and legal considerations surrounding issues like patient consent, data privacy, and the potential for remote surgery become increasingly important. Clear guidelines and regulations are essential to navigate these complex aspects of laparoscopic surgery.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgery, with its remarkable journey from conceptualization to widespread acceptance, stands at the forefront of surgical innovation. The continuous evolution of technologies, coupled with the exploration of artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and remote surgical capabilities, promises an exciting future for the field. As we navigate this transformative landscape, it is imperative to strike a balance between embracing innovation and addressing the ethical, training, and cost-related considerations. The promising horizon of laparoscopic surgery beckons us to a future where patient care is not only more effective but also more compassionate and individualized.