Introduction
In the rapidly evolving field of surgery, the demand for skilled laparoscopic surgeons is higher than ever. Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, has revolutionized the way many surgical procedures are performed. Its advantages, including smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, and faster recovery times, make it a preferred choice for both patients and surgeons. As the landscape of surgical techniques continues to expand, training the next generation of laparoscopic surgeons becomes paramount. This article explores the multifaceted approach required to cultivate precision and expertise in aspiring laparoscopic surgeons.
The Significance of Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery involves performing procedures through small incisions using specialized instruments and a camera. The surgeon navigates through the body with the help of a video monitor, allowing for a magnified and detailed view of the internal organs. This approach minimizes trauma to the patient's body, leading to shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery times, and decreased postoperative pain.
The significance of laparoscopic surgery extends beyond its immediate benefits. It has become a cornerstone of various medical specialties, including general surgery, gynecology, urology, and gastroenterology. Procedures such as cholecystectomy, appendectomy, and hysterectomy are now commonly performed laparoscopically. As technology advances, so does the potential for expanding the scope of laparoscopic interventions.
Challenges in Laparoscopic Surgical Training
While laparoscopic surgery offers numerous advantages, mastering the technique presents unique challenges for aspiring surgeons. Unlike traditional open surgery, where the surgeon has direct tactile feedback, laparoscopic surgery relies heavily on hand-eye coordination and spatial awareness. The transition from three-dimensional vision to the two-dimensional view on the monitor demands a new set of skills that must be honed through rigorous training.
Furthermore, laparoscopic instruments have limited degrees of freedom compared to the human hand, requiring surgeons to adapt to this constraint. The learning curve for laparoscopic surgery is steep, and proficiency is achieved through a combination of theoretical knowledge, simulated practice, and hands-on experience.
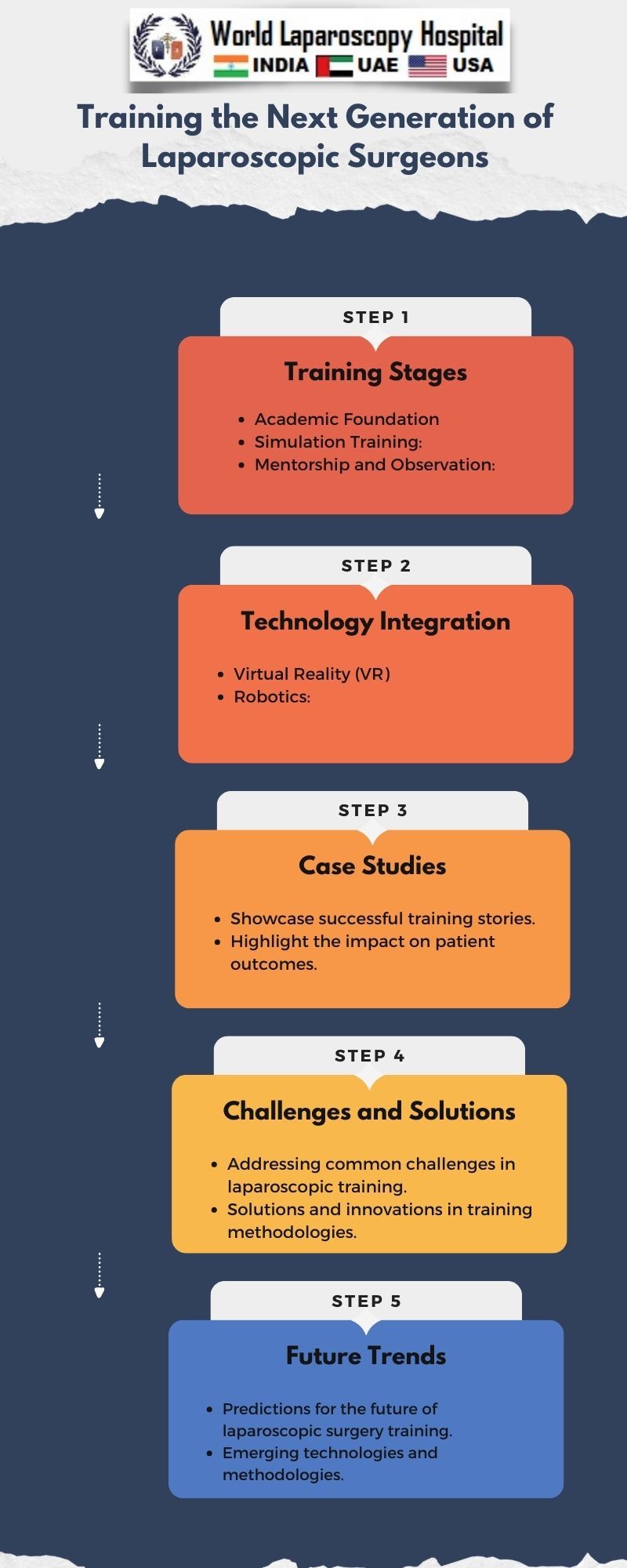
Comprehensive Training Approaches
Theoretical Foundation:
Developing a strong theoretical foundation is the first step in training laparoscopic surgeons. Understanding anatomy, physiology, and the principles of laparoscopic surgery is crucial. This knowledge forms the basis for decision-making during procedures and enhances the surgeon's ability to navigate complex anatomical structures.
Theoretical training is often delivered through lectures, interactive seminars, and online courses. Additionally, the integration of virtual reality (VR) technology allows students to explore three-dimensional anatomical models, gaining a deeper understanding of spatial relationships.
Virtual Simulations:
Virtual simulations play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between theory and practical application. Simulators provide a risk-free environment where trainees can practice and refine their skills before entering the operating room. These simulations mimic real surgical scenarios, allowing surgeons to navigate through various challenges and complications.
Advanced laparoscopic simulators incorporate haptic feedback, enhancing the realism of the training experience. Haptic feedback simulates the sensation of tissue resistance and instrument interaction, further improving the trainee's ability to manipulate instruments with precision.
Hands-on Training:
The importance of hands-on training cannot be overstated. Transitioning from virtual simulations to hands-on experience in a controlled environment is a critical phase in the training process. This is typically achieved through laboratory-based training using animal models or synthetic training platforms.
Surgical skills laboratories equipped with state-of-the-art instrumentation provide a realistic setting for trainees to practice under the guidance of experienced mentors. These mentors, often seasoned laparoscopic surgeons, offer valuable insights and corrective feedback, accelerating the learning process.
Mentorship and Apprenticeship: Mentorship is a cornerstone of surgical training. Aspiring laparoscopic surgeons benefit immensely from working alongside experienced mentors in the operating room. Observing and assisting in real surgical procedures allows trainees to apply their knowledge and skills in a clinical setting.
Apprenticeship models, where trainees gradually assume more responsibility under supervision, facilitate a smooth transition to independent practice. The mentor-mentee relationship fosters not only technical proficiency but also the development of professional judgment and decision-making skills.
Procedural Variation and Specialization:
Laparoscopic surgery encompasses a wide range of procedures across different medical specialties. Exposure to procedural variation is essential for a well-rounded training experience. Trainees should have the opportunity to participate in diverse laparoscopic interventions, from simple appendectomies to complex oncological resections.
Specialization within laparoscopic surgery is also gaining prominence. Surgeons may choose to focus on a specific subspecialty, such as laparoscopic colorectal surgery or laparoscopic bariatric surgery. Specialized training programs cater to these preferences, ensuring that surgeons are equipped with the expertise required in their chosen field.
Technological Advancements in Laparoscopic Training
Robotic-assisted Surgery:
The integration of robotic technology has further refined laparoscopic surgical training. Robotic-assisted surgery allows for enhanced dexterity and precision, with the surgeon controlling robotic arms equipped with instruments. The three-dimensional visualization and wristed instruments mimic the movements of the human hand, providing a more intuitive experience.
Training in robotic-assisted surgery involves specialized simulators and hands-on practice with robotic systems. As the use of robotics in surgery becomes more widespread, proficiency in this technology is increasingly considered a valuable skill for laparoscopic surgeons.
Augmented Reality (AR):
Augmented reality has found applications in laparoscopic surgery training, offering an immersive and interactive experience. AR overlays computer-generated images onto the surgeon's view of the real-world environment. This technology enhances spatial awareness and can provide real-time guidance during surgery.
In training, AR allows for dynamic visualizations, where trainees can interact with virtual elements superimposed on the surgical field. This innovation is particularly valuable in complex procedures, enabling surgeons to navigate intricate anatomical structures with greater precision.
Telesurgery and Remote Mentoring:
The concept of telesurgery involves performing surgery at a distance, with the assistance of robotic or remote-controlled systems. While telesurgery is not yet commonplace, it holds promise for the future of laparoscopic training. Remote mentoring, facilitated by advanced communication technologies, allows experienced surgeons to guide and instruct trainees from a remote location.
These technological advancements address the challenges of geographical barriers and enable access to mentorship and expertise regardless of the trainee's location. Telesurgery also has the potential to expand the reach of surgical training to underserved areas.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the progress made in laparoscopic surgical training, challenges persist. The cost of acquiring and maintaining advanced simulators and robotic systems can be a barrier for some training programs. Additionally, ensuring standardization in training curricula and assessment methods remains an ongoing concern.
The evolving landscape of surgical techniques, including the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, poses both opportunities and challenges for training programs. Incorporating these technologies into training modules may enhance the assessment of surgical skills and provide personalized feedback to trainees.
The ethical considerations of training on live animals are also a topic of debate. While animal models have been instrumental in surgical education, there is an increasing emphasis on developing alternative methods, such as synthetic models and virtual simulations, to reduce reliance on animal testing.
Conclusion
Training the next generation of laparoscopic surgeons requires a multifaceted approach that integrates theoretical knowledge, virtual simulations, hands-on training, mentorship, and exposure to technological advancements. As the field continues to advance, training programs must adapt to incorporate the latest technologies and methodologies to ensure that surgeons are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of laparoscopic surgery.
The commitment to lifelong learning is inherent in the surgical profession, and laparoscopic surgeons must stay abreast of emerging technologies and evolving best practices. By investing in comprehensive and innovative training programs, we can ensure that the next generation of laparoscopic surgeons not only meets but exceeds the demands of modern surgical practice. Ultimately, the pursuit of excellence in laparoscopic surgery training is a commitment to improving patient outcomes and advancing the frontiers of surgical innovation.
