Introduction:
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, has revolutionized the field of urology, offering patients a less invasive alternative to traditional open surgery. This article delves into the innovations and outcomes of laparoscopic surgery for urological conditions, highlighting the transformative impact on patient care.
Evolution of Laparoscopic Urological Surgery:
A. Historical Perspective:
- Early developments and challenges.
- Initial skepticism and gradual acceptance in urology.
B. Technological Advancements:
- Introduction of robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery.
- Integration of augmented reality and artificial intelligence.
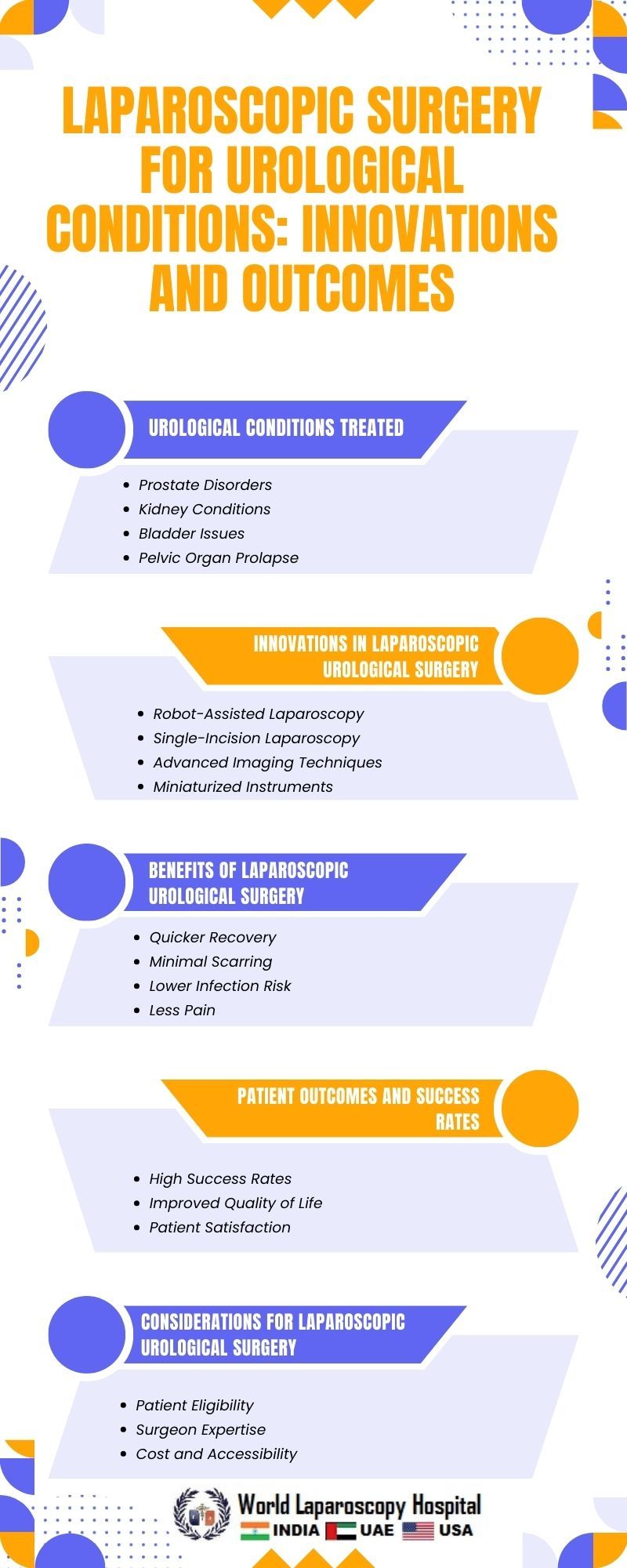
Common Urological Conditions Treated with Laparoscopy:
A. Prostate Conditions:
- Prostate cancer: A leading application of laparoscopic techniques.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and laparoscopic options.
B. Kidney Disorders:
- Renal cell carcinoma: Nephron-sparing laparoscopic surgery.
- Management of kidney stones through laparoscopy.
C. Bladder Issues:
- Laparoscopic cystectomy for bladder cancer.
- Addressing interstitial cystitis and overactive bladder.
D. Testicular and Penile Disorders:
- Orchidopexy for undescended testicles.
- Laparoscopic treatment of penile abnormalities.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Urological Surgery:
A. Reduced Invasiveness:
- Smaller incisions and decreased postoperative pain.
- Quicker recovery times compared to open surgery.
B. Improved Precision:
- High-definition imaging and magnification.
- Enhanced dexterity with robotic assistance.
C. Decreased Blood Loss and Infection Rates:
- Minimization of intraoperative bleeding.
- Lower risk of surgical site infections.
Challenges and Considerations:
A. Learning Curve:
- Training requirements for urologists.
- Mastery of advanced laparoscopic techniques.
B. Cost Considerations:
- Initial setup expenses for laparoscopic equipment.
- Long-term cost-effectiveness and reduced hospital stays.
C. Patient Selection:
- Criteria for suitable candidates.
- Tailoring the approach based on patient factors.
Future Directions in Laparoscopic Urological Surgery:
A. Continued Technological Integration:
- Advancements in robotic systems.
- Exploration of virtual reality for surgical training.
B. Personalized Medicine:
- Genetic considerations in urological conditions.
- Tailoring laparoscopic approaches based on individual patient characteristics.
C. Collaborative Research Initiatives:
- Multicenter studies on long-term outcomes.
- International cooperation for standardizing laparoscopic protocols.
Case Studies and Outcomes:
A. Success Stories:
- Notable cases of laparoscopic urological surgery.
- Patient testimonials on their experiences.
B. Complication Management:
- Addressing and mitigating potential complications.
- Strategies for improving overall safety.
Conclusion:
As laparoscopic surgery for urological conditions continues to evolve, it stands as a testament to the remarkable progress in medical technology and patient care. The ongoing innovations and positive outcomes underscore the significance of this minimally invasive approach in reshaping the landscape of urological interventions. With a promising future ahead, the integration of cutting-edge technologies and collaborative efforts will further refine and enhance the effectiveness of laparoscopic techniques, ultimately benefitting patients worldwide.