Advancements in Laparoscopic Appendectomy Techniques
Introduction:
Laparoscopic appendectomy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure for removing the appendix, has witnessed remarkable advancements in recent years. This article delves into the various innovations that have reshaped this surgical technique, exploring the benefits they bring to both surgeons and patients.
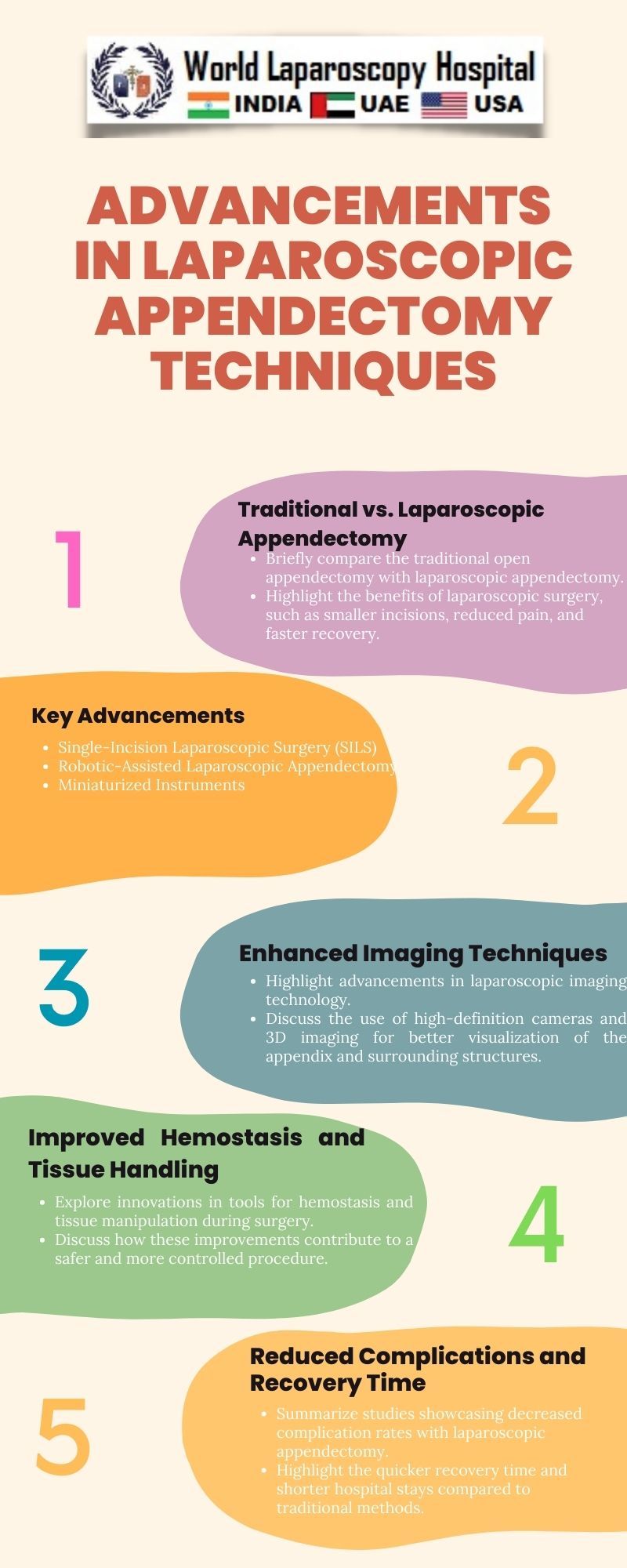
Evolution of Laparoscopic Appendectomy:
To comprehend the recent advancements, it is essential to trace the evolution of laparoscopic appendectomy. Initially introduced as an alternative to open appendectomy in the late 20th century, laparoscopic techniques aimed to reduce postoperative pain, hasten recovery, and improve cosmetic outcomes.
Enhanced Imaging Technologies:
One of the pivotal advancements is the integration of enhanced imaging technologies. High-definition laparoscopes and advanced imaging systems provide surgeons with clearer and more detailed visuals of the abdominal cavity. This precision allows for better identification of anatomical structures, reducing the risk of complications during surgery.
Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Appendectomy:
Robotic-assisted surgery has emerged as a game-changer in the field of laparoscopic procedures. The utilization of robotic systems enhances the surgeon's dexterity and provides greater maneuverability of instruments. This leads to improved accuracy, especially in complex cases, contributing to reduced surgical errors and enhanced patient safety.
Single-Incision Laparoscopic Appendectomy:
A notable stride in patient-centric care is the development of single-incision laparoscopic appendectomy. Unlike traditional laparoscopy, which involves multiple small incisions, this technique requires only one incision, often made in the patient's navel. This approach minimizes scarring, lowers the risk of infection, and accelerates the recovery process.
Mini-Laparoscopic Appendectomy:
Mini-laparoscopic instruments, with diameters smaller than traditional laparoscopic tools, have become increasingly prevalent. These instruments facilitate smaller incisions without compromising the surgeon's ability to perform the procedure effectively. Mini-laparoscopic appendectomy aims to further reduce postoperative pain and enhance the cosmetic aspects of surgery.
Improved Instrumentation and Ergonomics:
Advancements in laparoscopic instrumentation have resulted in more ergonomic and versatile tools. These instruments allow for greater precision and ease of use, enabling surgeons to perform laparoscopic appendectomy with enhanced efficiency. Improved ergonomics also contribute to reduced surgeon fatigue during prolonged procedures.
Hydrodissection and Hydrodissection-Assisted Appendectomy:
Hydrodissection involves the injection of fluid to create a space between tissues, facilitating dissection. In laparoscopic appendectomy, hydrodissection has proven beneficial in separating the appendix from surrounding structures with minimal trauma. Hydrodissection-assisted techniques aim to make the procedure even less invasive, promoting faster recovery and minimizing complications.
Hemostasis and Stapling Innovations:
Advancements in hemostasis techniques and stapling devices have contributed to safer and more efficient laparoscopic appendectomy. Improved control over bleeding during surgery reduces the risk of postoperative complications. Additionally, innovations in stapling devices enhance the closure of incisions, promoting better wound healing.
Patient Outcomes and Recovery:
The cumulative effect of these advancements is reflected in improved patient outcomes and enhanced recovery experiences. Reduced postoperative pain, smaller incisions, and shorter recovery times contribute to a higher overall satisfaction among patients undergoing laparoscopic appendectomy. Faster recovery also means a quicker return to normal daily activities.
Challenges and Considerations:
Despite the numerous benefits, challenges persist in the widespread adoption of advanced laparoscopic appendectomy techniques. These challenges include the cost of implementing robotic systems, the learning curve associated with new technologies, and the need for specialized training. Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensuring equitable access to these innovative approaches.
Future Directions and Emerging Technologies:
The landscape of laparoscopic appendectomy continues to evolve, with ongoing research and development focusing on further enhancing the procedure. Emerging technologies, such as augmented reality and artificial intelligence, hold the potential to revolutionize surgical planning and execution. The integration of these technologies may further refine the precision and safety of laparoscopic appendectomy in the future.
Conclusion:
The advancements in laparoscopic appendectomy techniques represent a paradigm shift in surgical practice, offering benefits ranging from improved visualization and precision to enhanced patient outcomes. As technology continues to advance, the field holds the promise of even more refined approaches, solidifying laparoscopic appendectomy as a cornerstone of modern surgical care. Surgeons, researchers, and healthcare providers must collaboratively embrace these innovations to ensure that the benefits of advanced laparoscopic techniques are accessible to a broader patient population.