Title: Virtual Reality Simulation in Laparoscopic Training: A New Frontier
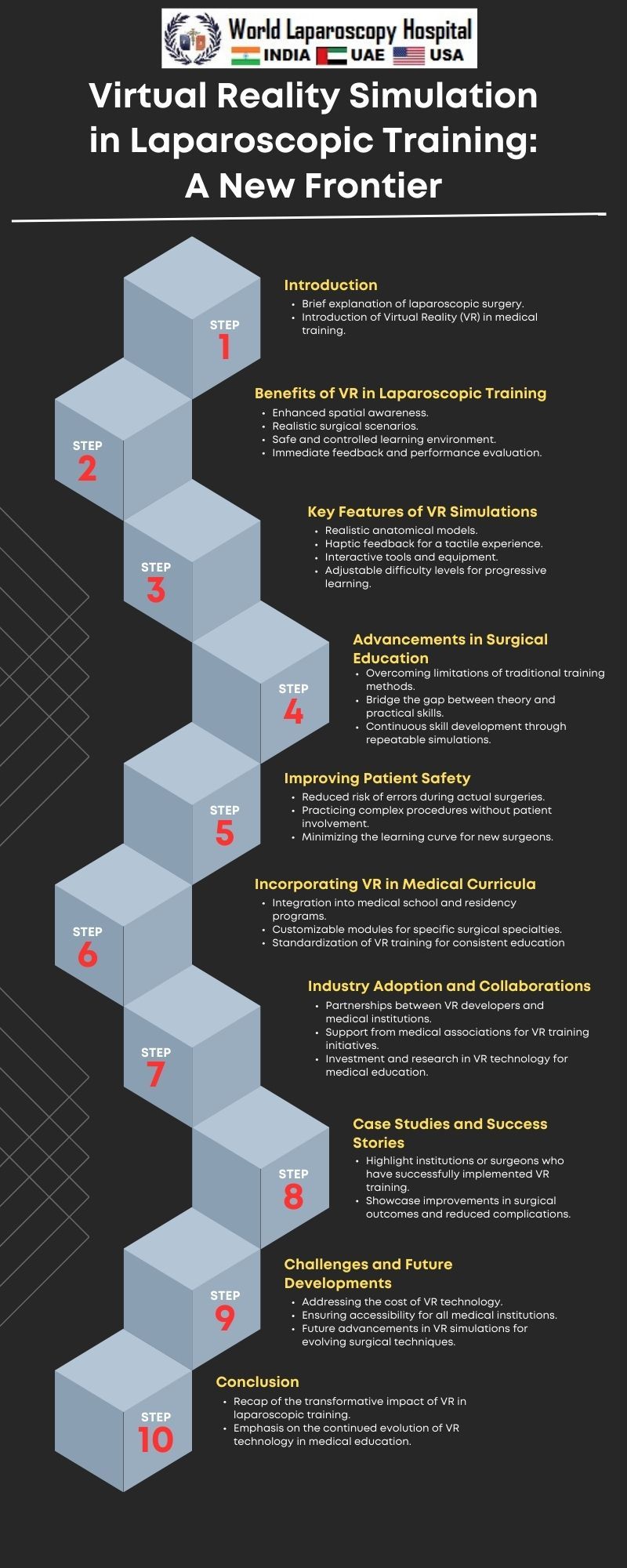
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of medical education and surgical training, virtual reality (VR) simulation has emerged as a groundbreaking tool, particularly in the field of laparoscopic surgery. Laparoscopic procedures, also known as minimally invasive surgeries, involve making small incisions and using a camera and specialized instruments to perform surgeries. The precision required in laparoscopic surgery demands extensive training, and virtual reality offers a dynamic and immersive platform for honing these skills. This article explores the integration of virtual reality simulation in laparoscopic training, examining its benefits, challenges, and the potential it holds for the future of surgical education.
The Evolution of Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery has come a long way since its inception. Traditionally, surgeons were trained through a combination of didactic lectures, observation of experienced surgeons, and hands-on experience in the operating room. While this approach has proven effective, it has limitations, particularly in providing a standardized and structured training experience.
The advent of laparoscopic surgery in the late 20th century revolutionized the field by minimizing trauma, reducing recovery times, and improving patient outcomes. However, the transition from open surgery to laparoscopy introduced new challenges for surgeons. The shift from a direct, three-dimensional view to a two-dimensional video monitor required a reevaluation of surgical techniques and spatial orientation. Surgeons needed a new set of skills, including hand-eye coordination, depth perception, and precise instrument control.
Enter Virtual Reality Simulation
Virtual reality simulation in laparoscopic training addresses the shortcomings of traditional methods by providing an immersive, interactive, and controlled learning environment. VR simulations replicate the surgical experience in a realistic virtual setting, allowing trainees to practice and refine their skills in a risk-free environment before entering the operating room.
Benefits of Virtual Reality in Laparoscopic Training
Realistic Replication of Surgical Environments:
VR simulations recreate the surgical environment with remarkable fidelity. From the operating room setup to patient positioning, trainees can experience a highly realistic simulation that closely mirrors the conditions they will encounter during an actual surgery.
Skill Acquisition and Refinement:
Virtual reality allows for repetitive practice, enabling surgeons to acquire and refine specific skills crucial for laparoscopic procedures. Trainees can focus on tasks such as hand-eye coordination, instrument manipulation, and tissue dissection until they achieve mastery.
Objective Performance Assessment:
VR platforms come equipped with performance metrics and assessment tools that objectively evaluate a trainee's performance. These metrics include factors like time taken, precision, and accuracy, providing valuable feedback for improvement.
Customizable Learning Modules:
Virtual reality simulations offer a customizable learning experience. Training modules can be tailored to address the specific needs and skill levels of individual learners, allowing for a personalized and adaptive training curriculum.
Reduced Risk and Cost:
One of the most significant advantages of VR simulation is the elimination of risks associated with traditional training methods. Mistakes made in a virtual environment have no real-world consequences, reducing the potential for patient harm. Additionally, the cost of materials and resources for training is substantially lower in a virtual setting.
Challenges in Implementing VR in Laparoscopic Training
While the benefits of virtual reality in laparoscopic training are substantial, several challenges must be addressed for widespread adoption.
Initial Cost and Infrastructure:
Implementing VR training programs requires a significant upfront investment in technology and infrastructure. Surgical institutions must invest in high-quality VR hardware, software, and associated equipment, as well as provide adequate training for instructors.
Integration with Existing Curricula:
Incorporating VR into existing laparoscopic training curricula may present logistical challenges. Institutions must develop seamless integration strategies to ensure that virtual reality complements rather than disrupts the overall training program.
Maintenance and Updates:
VR technology is continually evolving, necessitating regular updates and maintenance. Institutions must allocate resources for ongoing support and updates to ensure that the virtual simulations remain current and effective.
Acceptance and Resistance:
The introduction of VR in laparoscopic training may face resistance from traditionalists who are accustomed to conventional training methods. Convincing surgeons and educators of the benefits and efficacy of virtual reality is crucial for successful integration.
The Future of Laparoscopic Training: Opportunities and Innovations
As virtual reality continues to advance, the future of laparoscopic training holds exciting possibilities.
Haptic Feedback Integration:
Current VR systems primarily focus on visual and auditory feedback. The integration of haptic feedback—providing a sense of touch and resistance—will further enhance the realism of simulations, allowing trainees to experience the tactile aspects of surgery.
Artificial Intelligence and Adaptive Learning:
The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) in VR simulations can enable adaptive learning experiences. AI algorithms can analyze a trainee's performance in real-time and adjust the difficulty of tasks based on individual progress, optimizing the learning curve.
Global Collaboration and Remote Training:
Virtual reality has the potential to facilitate global collaboration in surgical education. Surgeons from different parts of the world can participate in collaborative virtual training sessions, sharing expertise and knowledge. Additionally, VR platforms can support remote training, allowing trainees to access high-quality education regardless of their geographical location.
Patient-Specific Simulations:
Advancements in medical imaging and VR technology may lead to the development of patient-specific simulations. Surgeons could practice procedures on virtual models generated from a patient's unique anatomy, allowing for personalized and targeted training.
Conclusion
Virtual reality simulation in laparoscopic training represents a transformative shift in the way surgeons are educated and prepared for the challenges of modern medicine. The benefits of realistic replication, skill acquisition, objective assessment, and reduced risk make VR an invaluable tool in the surgical training arsenal.
While challenges such as initial costs, integration, and resistance must be overcome, the ongoing evolution of VR technology holds great promise for the future. As haptic feedback, artificial intelligence, and global collaboration become integral components of virtual reality simulations, the training experience for laparoscopic surgeons is likely to become more immersive, effective, and accessible.
As institutions and educators embrace this new frontier in surgical training, the continued refinement and integration of virtual reality will undoubtedly contribute to the advancement of laparoscopic surgery and, ultimately, improve patient outcomes worldwide.