The 3rd World Congress on the Recent Advances of Minimal Access Surgery (RAMAS) was held in 2019 in Mumbai, India. The conference brought together leading experts in the field of minimal access surgery to share their knowledge and experiences. The theme of the conference was "Innovations and Challenges in Minimal Access Surgery," with a focus on the latest advances and techniques in the field. This essay will provide an overview of the key themes and topics discussed at the 3rd RAMAS Congress.
Advancements in Minimal Access Surgery
Minimal access surgery (MAS) is a surgical technique that uses small incisions to perform surgical procedures, resulting in less pain, scarring, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery. MAS is widely used in various surgical specialties, including urology, gynecology, and general surgery. The 3rd RAMAS Congress highlighted several advancements in MAS, including:
-
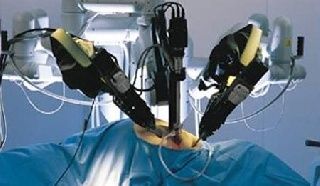
Robotic surgery: Robotic surgery is a type of MAS that uses robotic systems to perform surgical procedures. The robotic systems are controlled by a surgeon who sits at a console and manipulates the robotic arms and instruments. Robotic surgery offers numerous advantages over traditional open surgery and laparoscopic surgery, including improved surgical outcomes, reduced complications, and faster recovery times.
-
Single-incision laparoscopic surgery: Single-incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS) is a type of MAS that uses a single incision instead of multiple incisions to perform surgical procedures. SILS offers several advantages over traditional laparoscopic surgery, including reduced scarring, faster recovery times, and improved cosmesis.
-
Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery: Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) is a type of MAS that uses natural orifices, such as the mouth, vagina, or rectum, to access the surgical site. NOTES offers several advantages over traditional laparoscopic surgery, including reduced scarring, faster recovery times, and improved cosmesis.
Challenges in Minimal Access Surgery
Despite the numerous advantages of MAS, there are also challenges that must be addressed. The 3rd RAMAS Congress highlighted several challenges in MAS, including:
-
Training and education: Surgeons require specialized training and education to perform MAS, which can be time-consuming and expensive. The lack of trained surgeons can limit access to MAS in some regions.
-
Cost: The cost of acquiring and maintaining the equipment required for MAS can be high, which can limit access to MAS for some patients and healthcare facilities.
-
Safety: MAS can pose safety risks to patients, including risks associated with the use of anesthesia, the potential for instrument malfunction, and the risk of surgical errors.
-
Technical limitations: MAS has technical limitations, including limited dexterity and range of motion of instruments, which can make some surgical procedures challenging.
-
Patient selection: Not all patients are suitable candidates for MAS, and patient selection is critical to ensure optimal outcomes. Patient factors such as obesity, previous surgeries, and anatomical variations can make MAS challenging or impossible.
Future of Minimal Access Surgery
The 3rd RAMAS Congress also discussed the future of MAS, with a focus on the latest developments and trends in the field. Some of the key areas of development include:
-
Artificial intelligence: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into MAS is expected to improve surgical outcomes and reduce complications. AI algorithms can analyze patient data, predict surgical outcomes, and assist surgeons in decision-making during surgery.
-
Telepresence: Telepresence technology allows surgeons to perform surgeries remotely, using robotic systems to manipulate surgical instruments. This technology can help overcome geographical barriers and provide access to surgical care in remote areas.
-
Augmented reality: Augmented reality technology can provide surgeons with real-time, interactive visualization of the surgical site, which can improve surgical precision and accuracy. This technology can also provide surgeons with access to patient-specific data, such as MRI and CT scans, to optimize surgical planning.
Nanorobotics: Nanorobotics is the use of microscopic robots to perform surgical procedures at the cellular and molecular level. This technology has the potential to revolutionize surgical care by providing targeted drug delivery and tissue repair.
Personalized medicine: MAS is expected to become more personalized, with the use of patient-specific data to optimize surgical outcomes. This data can include genetic information, imaging data, and other health metrics.
Conclusion
The 3rd World Congress on the Recent Advances of Minimal Access Surgery provided valuable insights into the latest developments and challenges in the field of MAS. The conference highlighted the numerous advantages of MAS, including improved surgical outcomes, reduced complications, and faster recovery times. The conference also discussed the challenges in MAS, including training and education, cost, safety, technical limitations, and patient selection. The future of MAS looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and research. MAS is expected to become more intelligent, accessible, and personalized, with the potential to revolutionize surgical care. However, there are also challenges that must be addressed to ensure that patients receive the highest quality care possible. Healthcare facilities must invest in MAS and ensure that surgeons are adequately trained to perform these procedures.