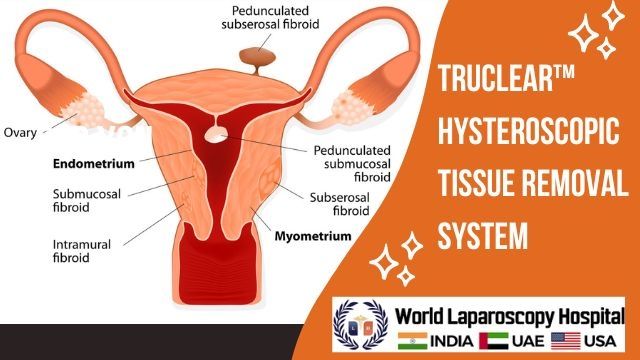
TruClear™ Hysteroscopic Tissue Removal System
The TruClear™ system is a comprehensive technology platform specifically developed for the removal of various intrauterine abnormalities. This advanced hysteroscopic tissue retrieval system is designed to deliver optimal performance.
Unlike alternative treatment options for intrauterine abnormalities that utilize high-frequency electric currents, the TruClear™ system employs a straightforward mechanical approach to remove intrauterine tissue. This mechanical method eliminates the risk of scarring caused by thermal energy or energy discharge. Additionally, the absence of bubbles or electrical energy within the uterus significantly reduces the chances of air or gas emboli, minimizing potential harm to the patient.
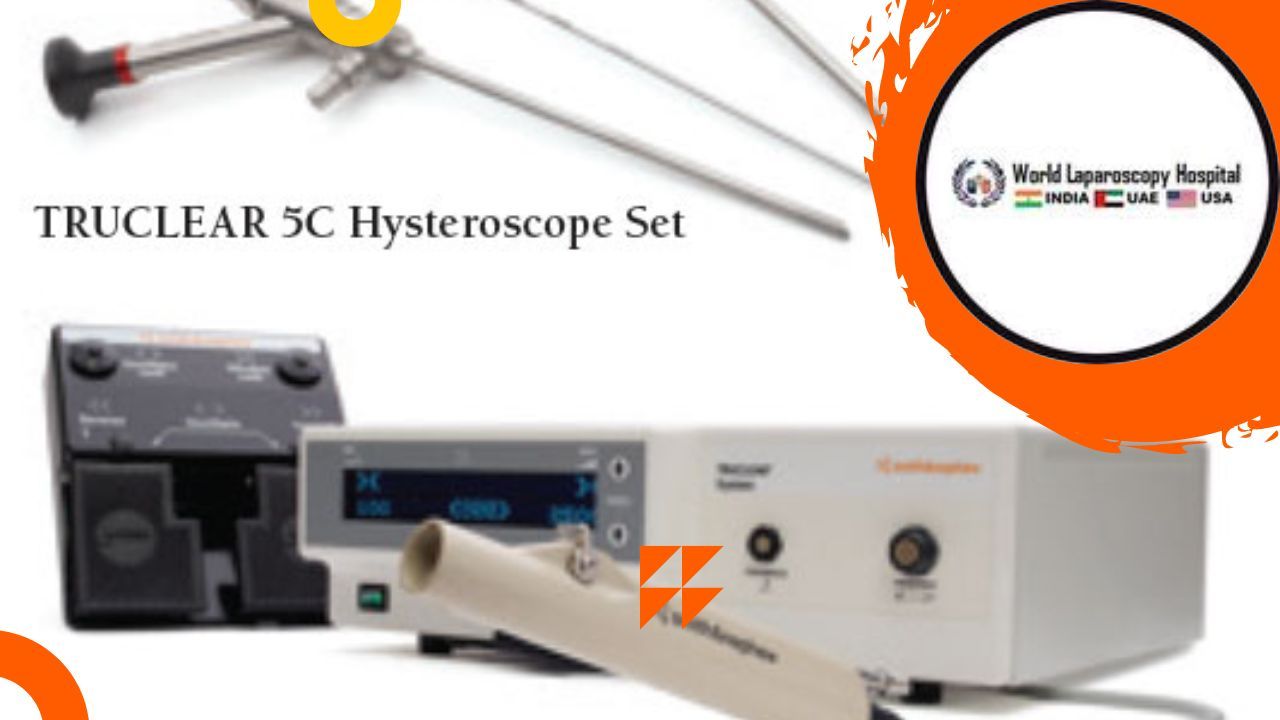
The TruClear™ system consists of a control unit, handpiece, and footswitch, providing healthcare professionals with a complete and user-friendly solution for performing hysteroscopic tissue removal procedures.
Introduction:
Operative hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that has revolutionized the field of gynecology. It involves the use of a hysteroscope, a thin telescope-like instrument, to visualize and treat various intrauterine pathologies. Operative hysteroscopy offers numerous benefits, such as reduced invasiveness, improved patient outcomes, and enhanced diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities. This essay will delve into the advancements and applications of operative hysteroscopy, highlighting its significance in modern gynecological practice.
Advancements in Operative Hysteroscopy:
Over the years, operative hysteroscopy has seen significant advancements in both equipment and techniques. The introduction of smaller hysteroscopes with improved optics and better maneuverability has enhanced visualization within the uterine cavity. High-definition imaging and the incorporation of digital systems have further improved the quality and accuracy of visual feedback during procedures. Additionally, the development of advanced surgical instruments, such as bipolar electrodes and mechanical tissue removal systems, has expanded the scope of operative hysteroscopy.
Applications of Operative Hysteroscopy:
Diagnosis and Evaluation:
Operative hysteroscopy allows for the precise diagnosis and evaluation of intrauterine abnormalities. It enables the direct visualization of uterine structures, such as polyps, fibroids, adhesions, and congenital malformations, providing valuable information for appropriate management decisions.
Tissue Resection and Removal:
Operative hysteroscopy enables the removal of intrauterine pathology through various techniques. Excision or resection of polyps, fibroids, or uterine septa can be performed, thereby alleviating symptoms and improving fertility outcomes. The use of mechanical tissue removal systems, such as the TruClear™ system, has minimized the risk of thermal injury and improved patient safety during tissue retrieval.
Endometrial Ablation:
Operative hysteroscopy plays a crucial role in endometrial ablation procedures. It allows for the precise destruction or removal of the endometrial lining, providing a minimally invasive treatment option for women suffering from heavy menstrual bleeding. Techniques like rollerball, laser, or bipolar ablation can be performed using the hysteroscope, reducing the need for invasive hysterectomy.
Intrauterine Adhesiolysis:
The presence of intrauterine adhesions or Asherman's syndrome can result in infertility and menstrual abnormalities. Operative hysteroscopy allows for the meticulous lysis of adhesions, restoring the normal anatomical and functional integrity of the uterine cavity.
Hysteroscopic Sterilization:
Operative hysteroscopy can be utilized for permanent contraception through hysteroscopic sterilization procedures. This technique involves the placement of small inserts into the fallopian tubes, leading to their occlusion over time. It offers a non-surgical alternative to traditional tubal ligation, with minimal discomfort and a quicker recovery period.
Conclusion:
Operative hysteroscopy has revolutionized the field of gynecology by providing a minimally invasive approach to diagnose and treat a range of intrauterine abnormalities. The advancements in equipment and techniques have significantly improved visualization, precision, and patient outcomes. The applications of operative hysteroscopy encompass diagnosis, tissue resection, endometrial ablation, adhesiolysis, and sterilization. Its growing role in modern gynecological practice underscores its importance in improving patient care, fertility outcomes, and quality of life for women worldwide. As technology continues to advance, operative hysteroscopy will likely continue to evolve, offering even greater potential for innovation and improving gynecological healthcare.
Top
Unlike alternative treatment options for intrauterine abnormalities that utilize high-frequency electric currents, the TruClear™ system employs a straightforward mechanical approach to remove intrauterine tissue. This mechanical method eliminates the risk of scarring caused by thermal energy or energy discharge. Additionally, the absence of bubbles or electrical energy within the uterus significantly reduces the chances of air or gas emboli, minimizing potential harm to the patient.
The TruClear™ system consists of a control unit, handpiece, and footswitch, providing healthcare professionals with a complete and user-friendly solution for performing hysteroscopic tissue removal procedures.

Introduction:
Operative hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that has revolutionized the field of gynecology. It involves the use of a hysteroscope, a thin telescope-like instrument, to visualize and treat various intrauterine pathologies. Operative hysteroscopy offers numerous benefits, such as reduced invasiveness, improved patient outcomes, and enhanced diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities. This essay will delve into the advancements and applications of operative hysteroscopy, highlighting its significance in modern gynecological practice.
Advancements in Operative Hysteroscopy:
Over the years, operative hysteroscopy has seen significant advancements in both equipment and techniques. The introduction of smaller hysteroscopes with improved optics and better maneuverability has enhanced visualization within the uterine cavity. High-definition imaging and the incorporation of digital systems have further improved the quality and accuracy of visual feedback during procedures. Additionally, the development of advanced surgical instruments, such as bipolar electrodes and mechanical tissue removal systems, has expanded the scope of operative hysteroscopy.
Applications of Operative Hysteroscopy:
Diagnosis and Evaluation:
Operative hysteroscopy allows for the precise diagnosis and evaluation of intrauterine abnormalities. It enables the direct visualization of uterine structures, such as polyps, fibroids, adhesions, and congenital malformations, providing valuable information for appropriate management decisions.
Tissue Resection and Removal:
Operative hysteroscopy enables the removal of intrauterine pathology through various techniques. Excision or resection of polyps, fibroids, or uterine septa can be performed, thereby alleviating symptoms and improving fertility outcomes. The use of mechanical tissue removal systems, such as the TruClear™ system, has minimized the risk of thermal injury and improved patient safety during tissue retrieval.
Endometrial Ablation:
Operative hysteroscopy plays a crucial role in endometrial ablation procedures. It allows for the precise destruction or removal of the endometrial lining, providing a minimally invasive treatment option for women suffering from heavy menstrual bleeding. Techniques like rollerball, laser, or bipolar ablation can be performed using the hysteroscope, reducing the need for invasive hysterectomy.
Intrauterine Adhesiolysis:
The presence of intrauterine adhesions or Asherman's syndrome can result in infertility and menstrual abnormalities. Operative hysteroscopy allows for the meticulous lysis of adhesions, restoring the normal anatomical and functional integrity of the uterine cavity.
Hysteroscopic Sterilization:
Operative hysteroscopy can be utilized for permanent contraception through hysteroscopic sterilization procedures. This technique involves the placement of small inserts into the fallopian tubes, leading to their occlusion over time. It offers a non-surgical alternative to traditional tubal ligation, with minimal discomfort and a quicker recovery period.
Conclusion:
Operative hysteroscopy has revolutionized the field of gynecology by providing a minimally invasive approach to diagnose and treat a range of intrauterine abnormalities. The advancements in equipment and techniques have significantly improved visualization, precision, and patient outcomes. The applications of operative hysteroscopy encompass diagnosis, tissue resection, endometrial ablation, adhesiolysis, and sterilization. Its growing role in modern gynecological practice underscores its importance in improving patient care, fertility outcomes, and quality of life for women worldwide. As technology continues to advance, operative hysteroscopy will likely continue to evolve, offering even greater potential for innovation and improving gynecological healthcare.