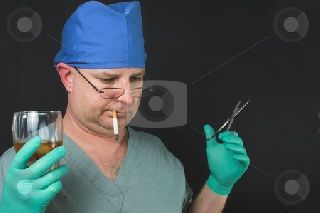
Introduction:
Surgeons are responsible for performing complex procedures that require a high level of skill and precision. The success of surgery depends heavily on the surgeon's ability to perform the procedure accurately and safely. However, like any other profession, surgeons are not immune to the effects of alcohol consumption. Drinking alcohol before performing surgery can impair a surgeon's judgment and motor skills, increasing the risk of errors and complications. In this essay, we will explore the effects of alcohol consumption on surgical performance and the potential consequences of surgeons operating while under the influence.
The Effects of Alcohol on Surgical Performance:
Alcohol consumption can have several negative effects on surgical performance, including impaired judgment, decreased motor skills, and decreased attention and concentration.
Impaired Judgment:
Alcohol consumption can impair a surgeon's judgment, leading to poor decision-making during surgery. Impaired judgment can lead to errors, such as misidentification of organs or vessels or accidental damage to healthy tissue. Additionally, impaired judgment can make it difficult for a surgeon to assess the potential risks and benefits of a procedure accurately.
Decreased Motor Skills:
Alcohol consumption can also decrease a surgeon's motor skills, making it more difficult to perform delicate surgical procedures accurately. Decreased motor skills can lead to errors, such as difficulty controlling instruments or accidentally damaging healthy tissue. Additionally, decreased motor skills can make it more difficult for a surgeon to perform complex procedures accurately, increasing the risk of complications.
Decreased Attention and Concentration:
Alcohol consumption can also decrease a surgeon's attention and concentration, making it more difficult to focus on the task at hand. Decreased attention and concentration can lead to errors, such as missing important details or failing to notice changes in the patient's condition. Additionally, decreased attention and concentration can make it more difficult for a surgeon to perform complex procedures accurately, increasing the risk of complications.
The Consequences of Surgeons Operating While Under the Influence:
The consequences of surgeons operating while under the influence can be severe, both for the patient and the surgeon. Potential consequences include:
Complications: Surgeons operating while under the influence are at a higher risk of making errors that can lead to complications, such as bleeding, infections, or organ damage.
Increased Hospital Stays: Complications resulting from surgeon error can lead to longer hospital stays, increasing the patient's risk of infection and other complications.
Long-Term Health Consequences: Complications resulting from surgeon error can also have long-term health consequences for the patient, including chronic pain, disability, and reduced quality of life.
Legal Consequences: Surgeons operating while under the influence can face legal consequences, including lawsuits and loss of medical license.
Professional Consequences: Surgeons operating while under the influence can also face professional consequences, including damage to their reputation and loss of trust from colleagues and patients.To prevent surgeons from operating while under the influence, hospitals and medical institutions must have policies in place to ensure that surgeons are not impaired by alcohol or drugs when performing surgery. Some potential strategies include:
Drug and Alcohol Testing: Hospitals and medical institutions can require surgeons to undergo drug and alcohol testing before performing surgery to ensure that they are not impaired. This can be done through random testing or testing after an incident.
Education and Training: Hospitals and medical institutions can provide education and training to surgeons on the dangers of alcohol and drug consumption on surgical performance. This can include information on the effects of alcohol and drugs on the body, as well as strategies for avoiding alcohol and drugs before surgery.
Policies and Procedures: Hospitals and medical institutions can develop policies and procedures that prohibit surgeons from consuming alcohol or drugs before performing surgery. These policies can include disciplinary action for surgeons who violate the policy.
Peer Monitoring: Hospitals and medical institutions can encourage peer monitoring, where surgeons observe and provide feedback to each other to ensure that they are not impaired by alcohol or drugs when performing surgery.
Mental Health Support: Hospitals and medical institutions can provide mental health support to surgeons who are struggling with alcohol or drug addiction. This can include access to counseling, support groups, and rehabilitation programs.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, preventing surgeons from operating while under the influence is essential to ensure the safety of patients and the integrity of the medical profession. Alcohol and drug consumption can impair a surgeon's judgment, motor skills, and attention and concentration, increasing the risk of errors and complications during surgery. Hospitals and medical institutions must have policies in place to prevent surgeons from consuming alcohol or drugs before performing surgery, including drug and alcohol testing, education and training, policies and procedures, peer monitoring, and mental health support. By taking steps to prevent surgeons from operating while under the influence, hospitals and medical institutions can ensure the highest level of care for their patients and uphold the professionalism and integrity of the medical profession.