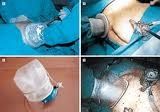
Laparoscopic intestinal surgery can be used to perform the following operations: Proctosigmoidectomy. Surgical removal of the diseased portion of the rectum and sigmoid colon. Accustomed to treat cancers and noncancerous growths or polyps, and complications of diverticulitis. Right colectomy or Ileocolectomy. During a right colectomy, the best side of the colon is taken away. During an ileocolectomy, the final segment from the small intestine - that is attached to the right side of the colon, known as the ileum, can also be removed. Accustomed to remove cancers, noncancerous growths or polyps, and inflammation from Crohn's disease. Total abdominal colectomy. Surgical removal of the large intestine. Used to treat ulcerative colitis,Crohn's disease, familial polyposis and possibly constipation. Fecal diversion. Surgical advance of whether temporary or permanent ileostomy (opening between the surface of the skin and the small intestine) or (colostomy (opening between the top of the skin and also the colon). Used to treat complex rectal and anal problems, including poor bowel control. Abdominoperineal resection. Surgical removal from the anus, rectum and sigmoid colon. Accustomed to remove cancer in the lower rectum or perhaps in the anus, near to the sphincter (control) muscles.
Rectopexy. A procedure in which stitches are used to secure the rectum in the proper position. Used to correct rectal prolapse. Total proctocolectomy. This is the most extensive bowel operation performed and involves the elimination of both the rectum and also the colon. When the surgeon has the capacity to leave the anus and it works properly, then sometimes an ileal pouch can be produced to be able to go to the bathroom. An ileal pouch is really a surgically created chamber comprised of the lowest part of the small intestine (the ileum). However, sometimes, a lasting ileostomy (opening between your surface of the skin and also the small intestine) is required especially if the anus must be removed, is weak, or continues to be damaged.
Hand-assisted laparoscopic surgery (HALS) is a type of minimally invasive surgical procedure that combines the advantages of laparoscopic surgery with the tactile feedback of traditional open surgery. In HALS, a small incision is made in the abdomen, and a surgeon's hand is inserted into the incision to help guide the surgical instruments. In recent years, HALS has become increasingly popular as a surgical approach, particularly in the fields of urology, colorectal surgery, and general surgery. In this essay, we will discuss the rise of HALS, its advantages and disadvantages, and its potential applications in various surgical specialties.
Background
HALS was first introduced in the 1990s as a modification of traditional laparoscopic surgery. Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical approach that uses a laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera on the end, to guide surgical instruments through small incisions in the abdomen. While laparoscopic surgery offers many advantages over traditional open surgery, such as less pain and scarring, it also has some disadvantages, including a lack of tactile feedback.
HALS was developed to address this issue. By allowing the surgeon to insert their hand into the surgical field, HALS provides tactile feedback that can help guide the surgical instruments and ensure a more precise and accurate surgery.
Advantages of HALS
One of the main advantages of HALS is the tactile feedback it provides. This can be particularly important in procedures such as cancer surgery or organ removal, where precise tissue dissection is critical. Additionally, HALS allows for the use of larger surgical instruments than traditional laparoscopic surgery, which can be helpful in certain procedures.
Another advantage of HALS is its versatility. HALS can be used in a variety of surgical specialties, including urology, colorectal surgery, and general surgery. Additionally, HALS can be used in both elective and emergency surgeries.
Finally, HALS can be useful in cases where a laparoscopic or traditional open approach may not be feasible. For example, in cases where the patient has extensive scarring or adhesions, HALS may be the best approach to ensure a successful surgery.
Disadvantages of HALS
One of the main disadvantages of HALS is the larger incision required compared to traditional laparoscopic surgery. This can result in more pain and scarring than laparoscopic surgery. Additionally, the larger incision may result in a longer recovery time and a longer hospital stay.
Another disadvantage of HALS is the increased risk of infection compared to traditional laparoscopic surgery. The hand that is inserted into the surgical field may introduce bacteria into the surgical site, increasing the risk of infection. Additionally, the larger incision required for HALS may result in a greater risk of wound infections.
Finally, HALS requires specialized training and experience. Surgeons must be able to use their hand to guide the surgical instruments while also monitoring the laparoscope. This can be a challenging technique to master, and it may take time for surgeons to become proficient in its use.
Potential Applications of HALS
HALS has potential applications in a variety of surgical specialties. In urology, HALS can be used for procedures such as prostatectomy and nephrectomy. In colorectal surgery, HALS can be used for procedures such as colectomy and rectal resection. In general surgery, HALS can be used for procedures such as cholecystectomy and hernia repair.
Additionally, HALS may be useful in cases where a laparoscopic or traditional open approach may not be feasible. For example, in cases where the patient has extensive scarring or adhesions, HALS may be the best approach to ensure a successful surgery.
Hand-assisted laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical approach that combines the advantages of laparoscopic surgery with the tactile feedback of traditional open surgery. HALS has several advantages over traditional laparoscopic surgery, including the ability to provide tactile feedback and use larger surgical instruments. Additionally, HALS has potential applications in a variety of surgical specialties, including urology, colorectal surgery, and general surgery.
However, HALS also has several disadvantages, including the larger incision required and the increased risk of infection compared to traditional laparoscopic surgery. Additionally, HALS requires specialized training and experience, which can make it challenging for some surgeons to master.
Despite its disadvantages, HALS has become increasingly popular as a surgical approach. This may be due in part to its versatility and potential applications in a variety of surgical specialties. Additionally, HALS may be a useful approach in cases where a laparoscopic or traditional open approach may not be feasible.
In conclusion, HALS is a minimally invasive surgical approach that provides the tactile feedback of traditional open surgery. While HALS has several advantages over traditional laparoscopic surgery, it also has several disadvantages that must be carefully considered. Ultimately, the decision to use HALS should be made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the patient's medical history, the complexity of the procedure, and the risks and benefits of each surgical approach.