Bariatric surgery is a medical procedure that involves altering the digestive system to promote weight loss. In recent years, the indication of bariatric surgery to treat diabetes mellitus has been increasing. Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by the inability of the body to produce enough insulin or use it effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels. Obesity is one of the risk factors for diabetes mellitus. Bariatric surgery has been shown to be effective in promoting weight loss and improving the control of blood sugar levels in people with diabetes mellitus. In this essay, we will discuss the indication of bariatric surgery to treat diabetes mellitus and the reasons for its increasing use.
Indication of Bariatric Surgery:
The indication of bariatric surgery to treat diabetes mellitus is based on several factors, including the severity of the disease, the degree of obesity, and the failure of other treatment options. Bariatric surgery is generally recommended for people with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or more, or a BMI of 35 or more with other obesity-related medical conditions such as diabetes mellitus. However, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends bariatric surgery for people with a BMI of 30 or more who have inadequately controlled diabetes mellitus despite optimal medical therapy.
Bariatric surgery is indicated for people with type 2 diabetes mellitus, which is the most common form of diabetes. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is characterized by insulin resistance, which means that the body does not respond to insulin effectively. Bariatric surgery has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin resistance, leading to better control of blood sugar levels. Bariatric surgery can also improve the function of pancreatic beta cells, which produce insulin, leading to increased insulin secretion.
Bariatric Surgery Procedures:
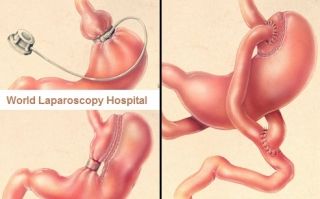
There are several types of bariatric surgery procedures, including gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding. Gastric bypass involves creating a small pouch in the stomach and connecting it directly to the small intestine, bypassing the rest of the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine. Sleeve gastrectomy involves removing a large portion of the stomach to create a smaller, tube-like stomach. Adjustable gastric banding involves placing a band around the upper part of the stomach to create a smaller stomach pouch.
The most commonly used bariatric surgery procedure for treating diabetes mellitus is gastric bypass. Gastric bypass has been shown to be effective in promoting weight loss and improving the control of blood sugar levels in people with diabetes mellitus. Sleeve gastrectomy has also been shown to be effective in promoting weight loss and improving the control of blood sugar levels, but it is less commonly used for treating diabetes mellitus. Adjustable gastric banding is less effective in promoting weight loss and improving the control of blood sugar levels, and it is not recommended for treating diabetes mellitus.
Reasons for Increasing Indication of Bariatric Surgery:
The indication of bariatric surgery to treat diabetes mellitus has been increasing in recent years for several reasons. First, the prevalence of obesity and diabetes mellitus is increasing worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the global prevalence of obesity has nearly tripled since 1975. In 2016, more than 1.9 billion adults were overweight, and of these, over 650 million were obese. The prevalence of diabetes mellitus has also been increasing, with an estimated 463 million adults living with diabetes mellitus worldwide in 2019.
Second, bariatric surgery has been shown to be effective in promoting weight loss and improving the control of blood sugar levels in people with diabetes mellitus. Several studies have shown that bariatric surgery cansignificantly reduce or even eliminate the need for diabetes medication in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. For example, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2012 found that gastric bypass was more effective in achieving glycemic control than intensive medical therapy in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus and a BMI of 27 to 43. Another study published in JAMA Surgery in 2017 found that sleeve gastrectomy was as effective as gastric bypass in improving glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus and a BMI of 30 to 40.
Third, bariatric surgery has been shown to improve other health outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus, such as cardiovascular risk factors, sleep apnea, and quality of life. For example, a study published in JAMA in 2014 found that gastric bypass was more effective than intensive medical therapy in improving cardiovascular risk factors, such as blood pressure, lipid levels, and inflammation, in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus and a BMI of 27 to 43. Another study published in Diabetes Care in 2016 found that bariatric surgery was effective in improving sleep apnea in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity.
Fourth, bariatric surgery has become safer and less invasive in recent years, leading to more widespread use. The use of laparoscopic techniques and robotic-assisted surgery has reduced the risk of complications and improved recovery times. Bariatric surgery is now considered a safe and effective option for treating obesity and its related health conditions, including diabetes mellitus.
Fifth, the cost-effectiveness of bariatric surgery has been demonstrated in several studies. Although bariatric surgery is initially expensive, it can lead to long-term cost savings by reducing the need for medication, hospitalization, and other medical interventions. A study published in Diabetes Care in 2013 found that bariatric surgery was cost-effective compared to conventional medical therapy in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus and a BMI of 30 to 39.
Conclusion:
The indication of bariatric surgery to treat diabetes mellitus is increasing due to the rising prevalence of obesity and diabetes mellitus, the effectiveness of bariatric surgery in promoting weight loss and improving the control of blood sugar levels, the improvement of other health outcomes, the safety and invasiveness of bariatric surgery, and the cost-effectiveness of the procedure. Bariatric surgery is a promising option for people with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity who have failed to achieve adequate glycemic control with conventional medical therapy. However, bariatric surgery is not a cure for diabetes mellitus and requires ongoing lifestyle changes and medical follow-up to maintain its benefits. Further research is needed to determine the long-term outcomes and safety of bariatric surgery in treating diabetes mellitus.